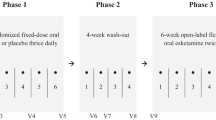
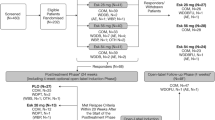
Abstract
Intranasal esketamine (Spravato™), the S-enantiomer of ketamine, targets the glutamatergic system via non-competitive antagonism of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, thereby providing a novel approach to traditional antidepressants that target modulation of the monoaminergic system. In conjunction with an oral antidepressant (OAD), intranasal esketamine is approved in the USA for use in adult patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Given its novel mechanism and rapid onset of action, convenient weekly or once every 2 weeks maintenance regimen, and the current paucity of approved pharmacotherapy options for TRD, esketamine nasal spray in conjunction with an OAD provides an important treatment option for this difficult-to-treat high-risk patient population. In pivotal clinical trials in adult patients with TRD, flexible-dose intranasal esketamine in conjunction with a newly initiated OAD provided rapid and sustained improvements in depression symptoms, and had a manageable tolerability and safety profile. Further long-term clinical experience is required to fully define the potential benefits and risks of esketamine therapy in combination with an OAD in TRD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper MD, Rosenblat JD, Cha DS, et al. Strategies to mitigate dissociative and psychotomimetic effects of ketamine in the treatment of major depressive episodes: a narrative review. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2017;18(6):410–23.
Johnston KM, Powell LC, Anderson IA, et al. The burden of treatment-resistant depression: a systematic review of the economic and quality of life literature. J Affect Dis. 2019;24:195–210.
Demyttenaere K, van Duppen Z. The impact of (the concept of) treatment-resistant depression: an opinion review. Int J Neuropsychopharm. 2019;22(2):85–92.
Caraci F, Calabrese F, Molteni R, et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharamcology CIV: the neurobiology of treatment-resistant depression—from antidepressant classifications to novel pharmacological targets. Pharmacol Rev. 2018;70:475–504.
Amos TB, Tandon N, Lefebvre P, et al. Direct and indirect cost burden and change of employment status in treatment-resistant depression: a matched-cohort study using a US commercial claims database. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(2):17m11725.
Garay RP, Zarate CA Jr, Charpeaud T, et al. Investigational drugs in recent clinical trials for treatment-resistant depression. Expert Rev Neurother. 2017;17(6):593–609.
Andrade C. Ketamine for depression, 3: does chirality matter? J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78(6):e674–7.
Spravato™ (esketamine) nasal spray, CIII: US prescribing information. Titusville (NJ): Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2019.
Bahr R, Lopez A, Rey JA. Intranasal esketamine (Spravato™) for use in treatment-resistant depression in conjunction with an oral antidepressant. PT. 2019;44(6):340–75.
Molero P, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Martin-Santos R, et al. Antidepressant efficacy and tolerability of ketamine and esketamine: a critical review. CNS Drugs. 2018;32(5):411–20.
Fedgchin M, Trivedi M, Daly E, et al. Efficacy and safety of fixed-dose esketamine nasal spray combined with a new oral antidepressant in treatment-resistant depression: results of a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study (TRANSFORM-1). Int J Neuropsychpharmacol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyz039.
Popova V, Daly EJ, Trivedi M, et al. Efficacy and safety of flexibly dosed esketamine nasal spray combined with a newly initiated oral antidepressant in treatment-resistant depression: a randomized double-blind active-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176(6):428–38.
Ochs-Ross R, Daly E, Zhang Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of esketamine nasal spray plus an oral antidepressant in elderly patients with treatment-resistant depression [abstract no. P.533 + poster]. Eur Neuropyschopharmacol. 2019;29(Suppl 1):355–6.
Shawi M, Alphs LD, Cooper K, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of flexibly dosed intranasal esketamine in a U.S. population of patients with treatment-resistant depression [abstract no. 49]. In: 171st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. 2018.
Shawi M, Alphs LD, Popova V, et al. Clinical response, remission, and safety of flexibly dosed intranasal esketamine in a U.S. population of patients with treatment-resistant depression [abstract no. 50]. In: 171st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. 2018.
Ochs-Ross R, Daly EJ, Zhang Y, et al. Post hoc analyses of esketamine nasal spray plus an oral antidepressant in elderly patients with treatment-resistant depression [abstract no. NR-6 + poster]. Am J Geriatric Psychiatry. 2019;27(3 Suppl):S140–1.
Starr HL, Alphs LD, Ochs-Ross R, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of intranasal esketamine in a U.S. population of geriatric patients with treatment-resistant depression [abstract no. 52]. In: 171st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. 2018.
Starr HL, Alphs LD, Ochs-Ross R, et al. Clinical response, remission, and safety of intranasal esketamine in a U.S. population of geriatric patients with treatment-resistant depression [abstract no. 51]. In: 171st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. 2018.
Daly EJ, Trivedi MH, Janik A, et al. Efficacy of esketamine nasal spray plus oral antidepressant treatment for relapse prevention in patients with treatment-resistant depression: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.1189.
Wajs E, Leah A, Morrision R, et al. Long-term safety of esketamine nasal spray plus oral antidepressant in patients with treatment-resistant depression: SUSTAIN-2 phase 3 study [abstract no. P.012 + poster]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;29(Suppl 1):s44–5.
Nijs M, Wajs E, Aluisio L, et al. Managing esketamine treatment frequency toward successful outcomes: analysis of phase 3 data [poster no. P8-030]. In: Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2019.
Aluisio L, Wajs E, DiBernardo A, et al. Withdrawal symptom assessment - intranasal esketamine: open-label safety study in treatment-resistant depression [poster no. 132]. In: American Society of Clinical Pathology Meeting: 2019.
Morrison RL, Fedgchin M, Singh J, et al. Effect of intranasal esketamine on cognitive functioning in healthy participants: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Psychopharmacology. 2018;235(4):1107–19.
Fua S, Gogate J, Starr L, et al. The relationship between adverse event reporting and events identified by scales/vital sign measurement with esketamine nasal spray plus an oral antidepressant in treatment-resistant depression (SUSTAIN-2 Study) [abstract + poster]. In: International Society for CNS Clinical Trials and Methodology (ISCTM) 15th Annual Scientific Meeting; 2019.
Daly EJ, Singh JB, Fedgchin M, et al. Efficacy and safety of intranasal esketamine adjunctive to oral antidepressant therapy in treatment-resistant depression: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75(2):139–48.
Doherty T, Wajs E, Melkote R, et al. Cardiac safety of esketamine nasal spray in treatment-resistant depression: results from the clinical development program [poster no. P8-031]. In: 172nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association: 2019.
van de Loo A, Bervoets AC, Mooren L, et al. Effect of intranasal esketamine on cognitive functioning in healthy participants: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Psychopharmacology. 2017;234(21):3175–83.
Hernandez LG, Li S, Toro-Diaz H, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of esketamine in treatment-resistant depression in the United States [abstract no. PMH19 + poster]. Value Health. 2019;22(Suppl 1).
Le HH, Zhang Q, Sheehan J. Budget impact analysis of esketamine in treatment-resistant depression in the United States [abstract no. PMH23 + poster]. Value Health. 2019;22(Suppl 1).
Acknowledgements
The manuscript was reviewed by: S. Kasper, Department of General Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria; A. Winkour. Department of Psychiatry, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT, USA. During the peer review process, Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc., the marketing-authorization holder of esketamine, was offered an opportunity to provide a scientific accuracy review of their data. Changes resulting from comments received were made on the basis of scientific and editorial merit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Conflicts of interest
Lesley Scott is an employee of Adis International Ltd./Springer Nature, is responsible for the article content and declares no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Enhanced material for this Adis Drug Q&A can be found at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.9866693.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, L.J. Intranasal esketamine in treatment-resistant depression: a profile of its use. Drugs Ther Perspect 35, 536–545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-019-00675-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-019-00675-z