Abstract
Objectives
Elderly psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients may show greater inflammatory activity and worse prognoses than patients of other ages. However, these patients may be at risk of receiving fewer systemic treatments. In this report, we have analysed disease outcomes in PsA by age groups.
Methods
This cross-sectional, multicentre study included 227 PsA patients under biological and non-biological systemic therapies. The study population was divided into four categories by age: < 40, 40‒49, 50‒65 and > 65 years. Physical functioning, disease activity, remission rates and disease impact were compared.
Results
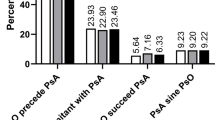
Thirty-one patients (13.7%) were under 40 years, 26.9% (n = 61) were 40–49 years, 26.4% (n = 60) were 50–65 years and 33.0% (n = 75) were patients > 65 years. Compared with the other age groups, disease duration was significantly higher in subjects older than 65 years (p < 0.001). Only 8% of patients older than 65 years received corticosteroids compared with 29% of patients aged < 40 years, 13.1% of patients aged 40–49 years and 26.7% of patients aged 50–65 years (p = 0.007). Similarly, only 36% of patients over 65 years of age received a biological therapy compared with between 51.6 and 59% for the other age groups (p = 0.036). However, remission rates were not statistically different between groups. Disease-associated physical disability was similar among groups. Compared with patients aged < 40 years, more patients > 65 years achieved low disease impact (10.7% vs 37.7%, respectively; p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Fewer older patients received corticosteroids and biological therapy. However, disease outcomes were similar or even better compared with those observed in younger patients. Therefore, treatment strategies for older patients with PsA should be similar to those offered to younger individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ritchlin CT, Colbert RA, Gladman DD. Psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:957–70.
Wilson FC, Icen M, Crowson CS, McEvoy MT, Gabriel SE, Kremers HM. Time trends in epidemiology and characteristics of psoriatic arthritis over 3 decades: a population-based study. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:361–7.
Liew JW, Ramiro S, Gensler LS. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32:369–89.
Henseler T, Christophers E. Psoriasis of early and late onset: characterization of two types of psoriasis vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;13:450–6.
Olivieri I, Pipitone N, D’ Angelo S, Padula A, Salvarani C. Late-onset rheumatoid arthritis and late-onset spondyloarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27(4 Suppl 55):S139–45.
Queiro R, Tejon P, Alonso S, Coto P. Age at disease onset: a key factor for understanding psoriatic disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53:1178–85.
Caso F, Tasso M, Chimenti MS, Navarini L, Perricone C, Girolimetto N, et al. Late-onset and elderly psoriatic arthritis: clinical aspects and management. Drugs Aging. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-019-00688-3.
Queiro R, Cañete JD, Montilla C, Abad M, Montoro M, Gómez S, et al. MAAPS study group. Minimal disease activity and impact of disease in psoriatic arthritis: a Spanish cross-sectional multicenter study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):72.
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H, CASPAR Study Group. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2665–73.
Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum. 1983;26:1346–53.
Schoels MM, Aletaha D, Alasti F, Smolen JS. Disease activity in psoriatic arthritis (PsA): defining remission and treatment success using the DAPSA score. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:811–8.
Gossec L, de Wit M, Kiltz U, Braun J, Kalyoncu U, Scrivo R, et al. A patient-derived and patient-reported outcome measure for assessing psoriatic arthritis: elaboration and preliminary validation of the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID) questionnaire, a 13-country EULAR initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1012–9.
Punzi L, Pianon M, Rossini P, Schiavon F, Gambari PF. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of elderly onset psoriatic arthritis: a comparison with younger onset disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999;58:226–9.
Kobak S, Yildiz F, Karaarslan A, Semiz H, Orman M. Characteristics of Turkish patients with elderly onset psoriatic arthritis: a retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(33):e7833.
Polachek A, Al-Johani R, Li S, Ye JY, Chandran V, Gladman D. Late onset psoriatic arthritis in a longitudinal cohort: disease presentation, activity over time and prognosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;48:834–9.
Rea IM, Gibson DS, McGilligan V, McNerlan SE, Alexander HD, Ross OA. Age and age-related diseases: role of inflammation triggers and cytokines. Front Immunol. 2018;9:586.
Patel P, Rosen CF, Chandran V, Ye YJ, Gladman DD. Addressing comorbidities in psoriatic disease. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38:219–27.
Queiro R, Cañete JD. Impact of cardiovascular risk factors on the achievement of therapeutic goals in psoriatic arthritis: is there any association? Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37:661–6.
Costa L, Lubrano E, Ramonda R, Chimenti MS, Vezzù M, Perrotta FM, et al. Elderly psoriatic arthritis patients on TNF-α blockers: results of an Italian multicenter study on minimal disease activity and drug discontinuation rate. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36:1797–802.
Acknowledgements
MAAPs (Minimal Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis) Study Group: J.D. Cañete (H. Clinic, Barcelona, Spain); C. Montilla (HU. Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain); M.A. Abad (H. Virgen del Puerto, Plasencia, Spain); S. Gómez (Pfizer Medical Department, Madrid, Spain); M. Montoro (Pfizer Medical Department, Madrid, Spain); A. Cabez (Pfizer Medical Department, Madrid, Spain); J.C. Torre Alonso (H. Monte Naranco, Oviedo, Spain); J.A. Román-Ivorra [Hospital Universitario (HU) La Fe, Valencia, Spain]; J. Sanz (HU Puerta de Hierro, Madrid, Spain); J. Salvatierra (HU San Cecilio, Granada, Spain); J. Calvo-Alén (HU Sierrallana, Torrelavega, Spain); A. Sellas (Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, Spain); F.J. Rodriguez (Santa Lucia, Cartagena, Spain); A. Bermúdez (Virgen de la Arrixaca, Murcia, Spain); M. Romero (Complejo hospitalario Jaén, Spain); M. Riesco (Rheumatology H. Juan Ramón Jiménez, Huelva, Spain); J.C. Cobeta (H. Royo Villanova, Zaragoza, Spain); F. Medina (H. Puerta del Mar, Cádiz, Spain); A. Aragón (H. Getafe, Madrid, Spain); M.L. García (HU Basurto, Bilbao, Spain); A. Urruticoechea (H. Can Misses, Ibiza, Spain); C.M. González (HU Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, Spain); E. Judez (HU, Albacete, Spain); B. González (HU Nta. Sra de la Candelaria, Tenerife, Spain); P. Fernández (HU 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain); L. Pantoja (H. del Bierzo, Leon, Spain); R. Morlá (H. Sant Pau y Sta. Tecla, Tarragona, Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The MAAPS study was funded by Pfizer.
Conflict of interest
RQ, EP, LC, SA, LA and MA declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Queiro, R., Pardo, E., Charca, L. et al. Analysis by Age Group of Disease Outcomes in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Multicentre Study. Drugs Aging 37, 99–104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-019-00724-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-019-00724-2