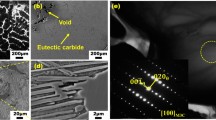
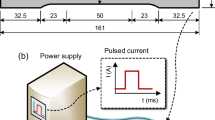
Abstract
Residual stress in high-carbon steel affects the dimensional accuracy, structural stability, and integrity of components. Although the evolution of residual stress under an electric field has received extensive attention, its elimination mechanism has not been fully clarified. In this study, it was found that the residual stress of high-carbon steel could be effectively relieved within a few minutes through the application of a low density pulse current. The difference between the current pulse treatment and traditional heat treatment in reducing residual stress is that the electric pulse provides additional Gibbs free energy for the system, which promotes dislocation annihilation and carbon atom diffusion to form carbides, thus reducing the free energy of the system. The electroplastic and thermal effects of the pulse current promoted the movement of dislocations under the electric field, thus eliminating the internal stress caused by dislocation entanglement. The precipitation of carbides reduced the carbon content of the steel matrix and lattice shrinkage, thereby reducing the residual tensile stress. Considering that a pulsed current has the advantages of small size, small power requirement, continuous output, and continuously controllable parameters, it has broad application prospects for eliminating residual stress.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Gumao, Generation and Countermeasures of Residual Stress (Machinery Industry Press, Beijing, 1983)
J.Q. Hao, H.X. Zhang, X.F. Zhang, C.B. Liu, Steel Res. Int. 91, 2000041 (2020)
L. Huang, R. Zhang, X. Zhou, Y. Tu, J. Jiang, J. Appl. Phys. 126, 245102 (2019)
R.A. Savrai, A.V. Makarov, I.Y. Malygina, E.G. Volkova, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 734, 506 (2018)
H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 268 (2012)
Y.J. Cao, J.Q. Sun, F. Ma, Y.Y. Chen, X.Z. Cheng, X. Gao, K. Xie, Tribol. Int. 115, 108 (2017)
S. Sackl, H. Leitner, H. Clemens, S. Primig, Mater. Charact. 120, 323 (2016)
Y. Wei, X. Yu, Y. Su, X. Shen, Y. Xia, W. Yang, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 10, 651 (2021)
X.B. Liu, W.J. Lu, X.F. Zhang, Acta Mater. 183, 51 (2020)
W.J. Lu, X.F. Zhang, R.S. Qin, Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 1530 (2015)
S.Q. Xiang, X.F. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 761, 138026 (2019)
R.S. Qin, Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 203 (2014)
Y. Jiang, G. Tang, C. Shek, Y. Zhu, Z. Xu, Acta Mater. 57, 4797 (2009)
Z. Xu, G. Tang, S. Tian, F. Ding, H. Tian, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 182, 128 (2007)
Y.H. Zhu, S. To, W.B. Lee, X.M. Liu, Y.B. Jiang, G.Y. Tang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 501, 125 (2009)
J. Zhang, Z. Liu, J. Sun, H. Zhao, Q. Shi, D. Ma, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 782, 139213 (2020)
Y. Wang, G. Chen, Z. Chen, H. Wan, H. Xiao, X. Chang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 841, 143066 (2022)
L. Lobanov, V. Pivtorak, N. Paschin, V. Savitsky, G. Tkachuk, Adv. Mater. Res. 996, 386 (2014)
L. Pan, W. He, B. Gu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 662, 404 (2016)
L. Pan, B. Wang, Z. Xu, J. Alloys Compd. 792, 994 (2019)
G. Stepanov, A. Babutskii, I. Mameev, Strength Mater. 41, 623 (2009)
L. Pan, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1187, 032054 (2019)
X. Song, F. Wang, D. Qian, L. Hua, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 780, 139171 (2020)
V.Y. Kravchenko, Sov. Phys. JETP 24, 1135 (1967)
A. Roshchupkin, V. Miloshenko, V. Kalinin, Fiz. Tverd. Tela 21, 909 (1979)
X. Huang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 6287 (2011)
K. Okazaki, M. Kagawa, H. Conrad, Mater. Sci. Eng. 45, 109 (1980)
G. S. Schajer, Practical Residual Stress Measurement methods (John Wiley & Sons, 2013)
G. Williamson, W. Hall, Acta Metall. 1, 22 (1953)
J.E. Bailey, P.B. Hirsch, Philos. Mag. 5, 485 (1960)
H. Mecking, U. Kocks, Acta Metall. 29, 1865 (1981)
A.T.W. Barrow, J.H. Kang, P.E.J. Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, Acta Mater. 60, 2805 (2012)
J. Zhang, Z. Dai, L. Zeng, X. Zuo, J. Wan, Y. Rong, N. Chen, J. Lu, H. Chen, Acta Mater. 217, 117176 (2021)
S.Q. Xiang, X.F. Zhang, Acta Metall. Sin. -Engl. Lett. 33, 281 (2019)
H. Krishnaswamy, M.J. Kim, S.T. Hong, D. Kim, J.H. Song, M.G. Lee, H.N. Han, Mater. Des. 124, 131 (2017)
M.J. Kim, K. Lee, K.H. Oh, I.S. Choi, H.H. Yu, S.T. Hong, H.N. Han, Scr. Mater. 75, 58 (2014)
H.J. Jeong, J.W. Park, K.J. Jeong, N.M. Hwang, S.T. Hong, H.N. Han, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 6, 315 (2019)
M.J. Kim, S. Yoon, S. Park, H.J. Jeong, J.W. Park, K. Kim, J. Jo, T. Heo, S.T. Hong, S.H. Cho, Appl. Mater. Today 21, 100874 (2020)
X. Li, Q. Zhu, Y. Hong, H. Zheng, J. Wang, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 13, 6503 (2022)
S. Morito, X. Huang, T. Furuhara, T. Maki, N. Hansen, Acta Mater. 54, 5323 (2006)
S. Morito, H. Tanaka, R. Konishi, T. Furuhara, T. Maki, Acta Mater. 51, 1789 (2003)
C. Bellot, P. Lamesle, D. Delagnes, Acta. Metall. Sin. 26, 553 (2013)
Y. Dolinsky, T. Elperin, Phys. Rev. B 50, 52 (1994)
T. Masumura, T. Taniguchi, S. Uranaka, I. Hirashima, T. Tsuchiyama, N. Maruyama, H. Shirahata, R. Uemori, ISIJ Int. 61, 1708 (2021)
Y. Ohmori, S. Sugisawa, Trans. JPN. Inst. Met. 12, 170 (1971)
J.Y. Gao, X.B. Liu, H.F. Zhou, X.F. Zhang, Acta Metall Sin. -Engl. Lett. 31, 1233 (2018)
Y. Jiang, G. Tang, L. Guan, S. Wang, Z. Xu, C. Shek, Y. Zhu, J. Mater. Res. 23, 2685 (2008)
N.B. Dhokey, A. Hake, S. Kadu, I. Bhoskar, G.K. Dey, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45, 1508 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality (2222065), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21B2082), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-22-02C2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, K., Xiang, S., Zhou, M. et al. Altering the Residual Stress in High-Carbon Steel through Promoted Dislocation Movement and Accelerated Carbon Diffusion by Pulsed Electric Current. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 36, 1511–1522 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-023-01556-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-023-01556-1