Abstract
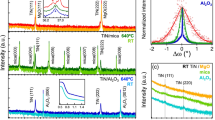
Indium tin oxide (ITO) thin films were prepared on alumina ceramic substrates by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. The samples were subsequently annealed in air at temperatures ranging from 500 to 1,100 °C for 1 h. The influences of the annealing temperature on the microstructure and electrical properties of the ITO thin films were investigated, and the results indicate that the as-deposited ITO thin films are amorphous in nature. All samples were crystallized by annealing at 500 °C. As the annealing temperature increases, the predominant orientation shifts from (222) to (400). The carrier concentration decreases initially and then increases when the annealing temperature rises beyond 1,000 °C. The resistivity of the ITO thin films increases smoothly as the annealing temperature increases to just below 900 °C. Beyond 900 °C, however, the resistivity of the films increases sharply. The annealing temperature has a significant effect on the stability of the ITO/Pt thin film thermocouples (TFTCs). TFTCs annealed at 1,000 °C show improved high-temperature stability and Seebeck coefficients of up to 77.73 μV/°C.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.C. Martin, G.C. Fralick, K.F. Taylor, NASA TM-208812 (1999)
L.C. Martin, J.D. Wrbanek, G.C. Fralick, NASA TM-211149 (2001)
J.D. Wrbanek, G.C. Fralick, S.C. Farmer, A. Sayir, C.A. Blaha, J.M. Gonzalez, NASA TM-213211 (2004)
D. Burgess, M. Yust, K.G. Kreider, Sens. Actuators A 34, 95 (1990)
K.G. Kreider, G. Gillen, Thin Solid Films 376, 32 (2000)
H.D. Bhatt, R. Vedula, S.B. Desu, G.C. Fralick, Thin Solid Films 342, 214 (1999)
H.D. Bhatt, R. Vedula, S.B. Desu, G.C. Fralick, Thin Solid Films 350, 249 (1999)
B.H. Lee, L.G. Kim, S.W. Cho, S.H. Lee, Thin Solid Films 302, 25 (1997)
S.K. Park, J.I. Han, W.K. Kim, M.G. Kwak, Thin Solid Films 397, 49 (2001)
Y.H. Tak, K.B. Kim, H.G. Park, K.H. Lee, J.R. Lee, Thin Solid Films 411, 12 (2002)
O.J. Gregory, E. Busch, G.C. Fralick, X.M. Chen, Thin Solid Films 518, 6093 (2010)
O.J. Gregory, M. Amani, G.C. Fralick, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 013107 (2011)
X.M. Chen, O.J. Gregory, M. Amani, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94(3), 854 (2011)
O.J. Gregory, M. Amani, I.M. Tougas, A.J. Drehman, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(2), 705 (2012)
C.H. Yang, S.C. Lee, S.C. Chen, T.C. Lin, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 129, 154 (2006)
G. Goncalves, E. Elangovan, P. Barquinha, L. Pereira, R. Martins, E. Fortunato, Thin Solid Films 515, 8562 (2007)
T.S. Sathiaraj, Microelectron. J. 39, 1444 (2008)
I. Hamberg, C.G. Granqvist, J. Appl. Phys. 60, R123 (1986)
S. Bhagwat, R.P. Howson, Surf. Coat. Technol. 111, 163 (1999)
K. Ellmer, R. Mientus, Thin Solid Films 516, 5829 (2008)
C.M. Bhandari, CRC Handbook of Thermoelectricity (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1995), pp. 12–14
S.S. Kubakaddi, B.G. Mulimani, J. Appl. Phys. 58, 3643 (1985)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61223002), the State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices Foundation of China (No. KFJJ201206) and Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of Sichuan (No. 2012ZZ020). We are grateful to the China Gas Turbine Establishment for their assistance with the calibration experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://link.springer.com/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Jiang, H., Jiang, S. et al. Influence of Annealing Temperature on the Microstructure and Electrical Properties of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 27, 368–372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-014-0059-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-014-0059-x