Abstract
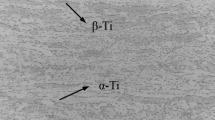
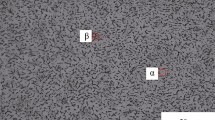
TC4 titanium alloy was brazed with Ti–18Zr–15Cu–10Ni (wt%) filler in a vacuum brazing furnace. The effects of the brazing time on the microstructure and tensile properties of the brazed joints were investigated, and the microstructure evolution during the brazing process and the high-cycle fatigue properties were further analyzed. The interfacial microstructure of the brazed joint at 940 °C for 60 min consists of coarse acicular α Ti, (Ti/Zr)2(Cu/Ni) intermetallics, eutectoid α Ti, and residual β Ti. The nucleation and growth of α Ti cause the component segregation, resulting in the rich of Cu, Ni, and V in β Ti to form βrich Ti, which in turn leads to the eutectoid decomposition reaction of βrich Ti, and the formation of granular intermetallic compounds at the edge of residual β Ti. The tensile strength increases first and then decreases with the brazing time, the maximum tensile strength (984.90 MPa) is obtained at 940 °C for 60 min, and the elongation at break increases with the prolongation of the brazing time; the maximum elongation at break (12.39%) is obtained at the brazing time of 90 min due to the large size of the αp phase. The fatigue limit of the brazed joints at 940 °C for 60 min is 492 MPa. The location of fracture is highly dependent on the fatigue load stress amplitude, and the growth rate of the fatigue crack is greatly affected by the microstructure of the fracture area.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes RA, De Oliveiraa MCL, Salvador CAF (2018) Materials selection of optimized titanium alloys for aircraft applications. Mater Res 21(2):e20170979. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2017-0979
Zhu ZS, Shang GQ, Wang XN et al (2020) Microstructure controlling technology and mechanical properties relationship of titanium alloys for aviation applications. JAM 40(3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000086
Boyer RR, Briggs RD (2013) The use of β titanium alloys in the aerospace industry. J Mater Eng Perform 22(10):2916–2920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0728-3
Liu XY, Chu PK, Ding CX (2004) Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 47(3–4):49–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2004.11.001
Guan J, Jiang XT, Xiang Q, Yang F, Liu J (2021) Corrosion and tribocorrosion behavior of titanium surfaces designed by electromagnetic induction nitriding for biomedical applications. Surf Coat Tech 409:126844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.126844
Dai JJ, Zhu JY, Chen CZ, Weng F (2016) High temperature oxidation behavior and research status of modifications on improving high temperature oxidation resistance of titanium alloys and titanium aluminides: a review. J Alloy Compd 685:784–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.06.212
Olson DL, Siewert TA, Liu S, Edwards GR (1993) ASM handbook volume 6: welding, brazing and soldering, ASM Int. Materials Park, OH. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v06.9781627081733
Schwartz M (1995) Brazing: for the engineering technologist, ASM Int. Materials Park, OH. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.32-6252
Lee MK, Lee JG (2013) Mechanical and corrosion properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints brazed with a low-melting-point 62.7Zr–11.0Ti–13.2Cu–9.8Ni–3.8Be amorphous filler metal. Mater Charact 81:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.04.002
Chang E, Chen CH (1997) Low-melting-point titanium-base brazing alloys–pare 1: characteristics of two-, three-, and four-component filler metals. J Mater Eng Perform 6:792–796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-997-0083-3
Wu ZY, Shiue RK, Chang CS (2009) Transmission electron microscopy study of infrared brazed titanium alloy using Clad Ti–25Cu–15Ni filler. ISIJ Int 49(6):931–933. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.49.931
Ganjeh E, Sarkhosh H (2013) Microstructural, mechanical and fractographical study of titanium-CP and Ti–6Al–4V similar brazing with Ti-based filler. Mater Sci Eng A 559:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.08.043
Liu SL, Miao JK, Zhang WW et al (2020) Interfacial microstructure and shear strength of TC4 alloy joints vacuum brazed with Ti–Zr–Ni–Cu filler metal. Mater Sci Eng A 775:138990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.138990
Jing YJ, Yue XS, Gao XQ, Su DY, Hou JB (2016) The influence of Zr content on the performance of TiZrCuNi brazing filler. Mater Sci Eng A 678:190–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.115
Liu D, Song YY, Zhou YH et al (2018) Brazing of C/C composite and Ti-6Al-4V with graphene strengthened AgCuTi filler: effects of graphene on wettability, microstructure and mechanical properties. Chinese J Aeronaut 31(7):1602–1608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2017.08.017
Guo W, Xue JL, Zhang HQ, Cui H et al (2020) The role of foam on microstructure and strength of the brazed C/C composites/Ti6Al4V alloy joint. Vacuum 179:109543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109543
Guo W, Li K, Zhang HQ, Zhu Y et al (2022) Low residual stress C/C composite-titanium alloy joints brazed by foam interlayer. Ceram 48:5260–5266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.067
Ba J, Zheng XH, Ning R, Lin JH et al (2019) C/SiC composite-Ti6Al4V joints brazed with negative thermal expansion ZrP2WO12 nanoparticle reinforced AgCu alloy. J Eur Ceram Soc 39:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.12.028
Jing YJ, Xiong HP, Shang YL et al (2020) Design TiZrCuNi filler materials for vacuum brazing TA15 alloy. J Manuf Process 53:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.02.021
Liu Y, Hu J, Zhang Y, Guo Z (2013) Interface microstructure of the brazed zirconia and Ti-6Al-4V using Ti-based amorphous filler metal. Sci Sinter 45(3):313–321. https://doi.org/10.2298/SOS1303313L
Pang SJ, Sun LL, Xiong HP et al (2016) A multicomponent TiZr-based amorphous brazing filler metal for high-strength joining of titanium alloy. Scr Mater 117:55–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.02.006
Massalski TB (1990) Binary alloy phase diagrams. ASM Int. Materials Park, OH
Wu BS, Dong HG, Li P et al (2022) Vacuum diffusion bonding of TC4 titanium alloy and T2 copper by a slow cooling heat treatment. J Mater Process Technol 305:117595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117595
Jing YJ, Yang HB, Shang YL, Xiong HP (2021) The design of a new Ti–Zr–Cu–Ni–Ag brazing fller metal for brazing of titanium alloys. Weld World 65:2231–2237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-021-01181-5
Popov AA, Lugovaya KI, Popova EN, Makarov VV, Zhilyakova MA (2020) Features of the two-phase (α + α2) structure formation in the Ti–17 at % Al alloy. Phys Met Metallogr 121(8):791–796. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X20080062
Bikash K, Swagat D, Swarup B (2021) On the interaction of cooling rate with thermal-microstructural-mechanical characteristics of laser-welded α + β titanium alloy. Adv Mater Process Te 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2021.1946337
Dobromyslov AV (2021) Bainitic transformation in titanium alloys. Phys Met Metallogr 122(3):237–265. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X21030042
Rosenberg HW, Snow KS (1973) Microsegregation in titanium alloys. Light Metals 1:439–448
Yue GL, Chen TC, Shiue RK, Tsay LW (2021) Dissimilar brazing of Ti–15Mo–5Zr–3Al and commercially pure titanium using Ti–Cu–Ni foil. Materials 14(20):5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14205949
Lee JG, Kim GH, Lee MK, Rhee CK (2021) Intermetallic formation in a Ti–Cu dissimilar joint brazed using a Zr-based amorphous alloy filler. Intermetallics 18(4):529–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2009.10.005
Peng Y, Li JL, Du YJ (2021) Microstructure and mechanical properties of joints prepared by vacuum brazing on TC4 titanium alloy with Ag as filler metal. Vacuum 187:110134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110134
Zou ZH, Zeng FH et al (2017) The joint strength and fracture mechanisms of TC4/TC4 and TA0/TA0 brazed with Ti-25Cu-15Ni braze alloy. ASM Sci J 26:2079–2085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2554-5
Jing YJ, Su DY, Yue XS et al (2017) The development of high strength brazing technique for Ti-6Al-4V using TiZrCuNi amorphous filler. Mater Charact 131:526–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2017.07.039
Zhang H, Li JL, Ma PY, Xiong JT et al (2017) Study on microstructure and impact toughness of TC4 titanium alloy diffusion bonding joint. Vacuum 152:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.03.019
Fall A, Jahazia M et al (2017) Effect of process parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir-welded Ti-6Al-4V joints. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 91:2919–2931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9527-y
Sun WJ, Wang SL, Wu M et al (2021) Revealing tensile behaviors and fracture mechanism of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy electron-beam-welded joints using microstructure evolution and in situ tension observation. Mater Sci Eng A 824:141811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141811
Moletsane MG, Krakhmalev P et al (2016) Tensile properties and microstructure of direct metal laser-sintered TI6AL4V (ELI) alloy. S Afr J Ind Eng 27(3):110–121. https://doi.org/10.7166/27-3-1667
Zhao YX, Yang B (2008) Probabilistic measurement of the fatigue limit data from a small sampling up-and-down test method. Int J Fatigue 30(12):2094–2103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2008.06.004
Long J, Zhang LJ, Zhang LX et al (2022) Comparison of fatigue performance of TC4 titanium alloy welded by electron beam welding and laser welding with filler wire. Fatigue Fract Eng M 45(4):991–1004. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13644
Li TL, Wu HP, Wang B et al (2022) Fatigue crack growth behavior of TA15/TC4 dissimilar laminates fabricated by diffusion bonding. Int J Fatigue 156:0142–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106646
Wang SQ, Ma TJ, Li WY et al (2017) Microstructure and fatigue properties of linear friction welded TC4 titanium alloy joints. Sci Technol Weld Joi 22(3):177–181. https://doi.org/10.1080/13621718.2016.1212971
Oh J, Kim NJ, Lee S, Lee EW (2003) Correlation of fatigue properties and microstructure in investment cast Ti-6Al-4V welds. Mater Sci Eng A 340(1–2):232–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00176-4
Han W, Fu L, Chen HY (2018) Effect of welding speed on fatigue properties of TC18 thick plate by electron beam welding. Rare Metal Mat Eng 47(8):2335–2340. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(18)30188-7
Meng XK, Wang H, Tan WS (2020) Gradient microstructure and vibration fatigue properties of 2024–T351 aluminium alloy treated by laser shock peening. Surf Coat Tech 391:125698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125698
Huang ZY, Wagner D, Bathias C et al (2010) Subsurface crack initiation and propagation mechanisms in gigacycle fatigue. Acta Mater 58(18):6046–6054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.07.022
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the significant support from the Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC) and Shandong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission XVII - Brazing, Soldering and Diffusion Bonding
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, L., Teng, J. & Chen, M. Microstructure evolution, diffusion behavior and fatigue properties of TC4 titanium alloy joints brazed with Ti–Zr-based filler. Weld World 66, 2625–2638 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01387-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-022-01387-1