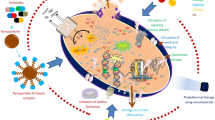
Abstract
Background
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an emerging treatment option for various therapeutic areas owing to its outstanding advantages compared with conventional therapies. PDT consists of three main components; a photosensitizer, a proper wavelength of light and oxygen. This alternative treatment is based on the selective accumulation of photosensitizers which generate reactive oxygen species to induce cell apoptosis and necrosis under the light irradiation. PDT provides less invasive way with high therapeutic efficacy and reduced side effects. When PDT is combined with nanoplatform, drug loading efficacy, tissue targeting efficiency and accumulation rate were enhanced leading to increase the therapeutic effect of PDT.
Area covered
In this review, we described progress and recent trends in nanoplatform-based PDT in various cancers and infectious diseases. We have selected lung cancer, liver cancer, and breast cancer for representative cancer types furthermore, bacteria-infected wound and acne vulgaris for typical infectious diseases. The above therapeutic areas were chosen since the researches on PDT with nanoparticles are actively ongoing with these indications. PDT as well as PDT with chemotherapy, and PDT with immunotherapy strategies were covered in this review.
Expert opinion
Nanotechnology combined with PDT greatly improved the therapeutic efficacy compared with PDT alone. In addition, novel combination strategies effectively enhanced the therapeutic outcomes with reduced side effects. However, more safety data will be needed to lead these innovative strategies to the clinical trials.

[Reprinted with permission from ACS publications (Song et al. 2018).]


[Reprinted with permission from John Wiley and Sons publications (Hu et al. 2021).]

[Reprinted with permission from John Wiley and Sons publications (Gao et al. 2018).]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghahosseini F, Arbabi-Kalati F, Fashtami LA et al (2006) Methylene blue-mediated photodynamic therapy: a possible alternative treatment for oral lichen planus. Lasers Surg Med 38:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20278
Ashkenazi H, Malik Z, Harth Y, Nitzan Y (2003) Eradication of Propionibacterium acnes by its endogenic porphyrins after illumination with high intensity blue light. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 35:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695x.2003.tb00644.x
Bade BC, Dela Cruz CS (2020) Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med 41:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccm.2019.10.001
Behranvand N, Nasri F, Emmameh Z et al (2021) Chemotherapy: a double-edged sword in cancer treatment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-03013-3
Bharathiraja S, Moorthy MS, Manivasagan P et al (2017) Chlorin e6 conjugated silica nanoparticles for targeted and effective photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 19:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.06.001
Boccalini G, Conti L, Montis C et al (2017) Methylene blue-containing liposomes as new photodynamic anti-bacterial agents. J Mater Chem B 5:2788–2797. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tb03367a
Brockmann L, Giannou AD, Gagliani N, Huber S (2017) Regulation of TH17 cells and associated cytokines in wound healing, tissue regeneration, and carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 18:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051033
Bu Y, Zhang L, Liu J et al (2016) Synthesis and properties of hemostatic and bacteria-responsive in situ hydrogels for emergency treatment in critical situations. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:12674–12683. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b03235
Candido NM, De Melo MT, Franchi LP et al (2018) Combining photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy: Improving breast cancer treatment with nanotechnology. J Biomed Nanotechnol 14:994–1008. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2018.2558
Castano AP, Mroz P, Hamblin MR (2006) Photodynamic therapy and anti-tumour immunity. Nat Rev Cancer 6:535–545. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1894
Chang JE, Yoon IS, Sun PL et al (2014) Anticancer efficacy of photodynamic therapy with hematoporphyrin-modified, doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles in liver cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 140:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.07.005
Chang JE, Cho HJ, Yi E et al (2016) Hypocrellin B and paclitaxel-encapsulated hyaluronic acid-ceramide nanoparticles for targeted photodynamic therapy in lung cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 158:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.02.035
Divaris DXG, Kennedy JC, Pottier RH (1990) Phototoxic damage to sebaceous glands and hair follicles of mice after systemic administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid correlates with localized protoporphyrin IX fluorescence. Am J Pathol 136:891–897
Dolmans DEJGJ, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2003) Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 3:380–387. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1071
El-Hussein A, Manoto SL, Ombinda-Lemboumba S et al (2021) A review of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy for lung cancer treatment. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 21:149–161. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520620666200403144945
Farrar MD, Ingham E (2004) Acne: inflammation. Clin Dermatol 22:380–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.03.006
Galle PR, Tovoli F, Foerster F et al (2017) The treatment of intermediate stage tumours beyond TACE: from surgery to systemic therapy. J Hepatol 67:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.007
Gao Q, Zhang X, Yin W et al (2018) Functionalized MoS2 nanovehicle with near-infrared laser-mediated nitric oxide release and photothermal activities for advanced bacteria-infected wound therapy. Small 14:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201802290
Garcia VG, De Lima MA, Okamoto T et al (2010) Effect of photodynamic therapy on the healing of cutaneous third-degree-burn: histological study in rats. Lasers Med Sci 25:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0694-z
Garrier J, Bezdetnaya L, Barlier C et al (2011) Foslip ®-based photodynamic therapy as a means to improve wound healing. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 8:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2011.06.003
Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, Longaker MT (2008) Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 453:314–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07039
Habiba K, Encarnacion-Rosado J, Garcia-Pabon K et al (2015) Improving cytotoxicity against cancer cells by chemo-photodynamic combined modalities using silver-graphene quantum dots nanocomposites. Int J Nanomedicine 11:107–119. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S95440
Hædersdal M, Togsverd-bo K, Wulf HC (2008) Evidence-based review of lasers, light sources and photodynamic therapy in the treatment of acne vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 22:267–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02503.x
Hamblin MR (2020) Photodynamic therapy for cancer: what’s past is prologue. Photochem Photobiol 96:506–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.13190
He H, Zhu R, Sun W et al (2018) Selective cancer treatment via photodynamic sensitization of hypoxia-responsive drug delivery. Nanoscale 10:2856–2865. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr07677k
Hijazi H, Campeau M-P, Roberge D et al (2016) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for inoperable liver tumors: results of a single institutional experience. Cureus 8:e935–e935. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.935
Hongcharu W, Taylor CR, Chang Y et al (2000) Topical ALA-photodynamic therapy for the treatment of acne vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 115:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00046.x
Hu D, Sheng Z, Gao G et al (2016) Activatable albumin-photosensitizer nanoassemblies for triple-modal imaging and thermal-modulated photodynamic therapy of cancer. Biomaterials 93:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.03.037
Hu C, He X, Chen Y et al (2021) Metformin mediated PD-L1 downregulation in combination with photodynamic-immunotherapy for treatment of breast cancer. Adv Funct Mater 31:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202007149
Hwang HS, Shin H, Han J, Na K (2018) Combination of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and anti-tumor immunity in cancer therapy. J Pharm Investig 48:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0377-x
Ji Y, Zhu J, Zhu L et al (2020) High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for unresectable primary and metastatic liver cancer: real-world research in a Chinese tertiary center with 275 cases. Front Oncol 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.519164
Kang SH, Nafiujjaman M, Nurunnabi M et al (2015) Hybrid photoactive nanomaterial composed of gold nanoparticles, pheophorbide-A and hyaluronic acid as a targeted bimodal phototherapy. Macromol Res 23:474–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-015-3061-x
Kawada A, Aragane Y, Kameyama H, Sangen Y (2002) Acne phototherapy with a high-intensity, enhanced, narrow-band, blue light source. J Dermatol 30:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0923-1811(02)00068-3
Lee MH, Thomas JL, Li JA et al (2021) Synthesis of multifunctional nanoparticles for the combination of photodynamic therapy and immunotherapy. Pharmaceuticals 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060508
Lee SY, You CE, Park MY (2007) Blue and red light combination LED phototherapy for acne vulgaris in patients with skin phototype IV. Lasers Surg Med 39:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20412
Ling LL, Schneider T, Peoples AJ et al (2015) A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 517:455–459. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14098
Liu ZT, Xiong L, Liu ZP et al (2014) In vivo and in vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of photosan-loaded hollow silica nanoparticles on liver cancer. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-9-319
Maughan KL, Lutterbie MA, Ham PS (2010) Treatment of breast cancer. Am Fam Physician 81:1339–1346. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199810013391407
Morrow DIJ, McCarron PA, Woolfson AD et al (2010) Hexyl aminolaevulinate is a more effective topical photosensitiser precursor than methyl aminolaevulinate and 5-aminolaevulinic acids when applied in equimolar doses. J Pharm Sci 99:3486–3498. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.22116
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M et al (2021) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2018, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2018/. Apr 2021
Natesan S, Krishnaswami V, Ponnusamy C et al (2017) Hypocrellin B and nano silver loaded polymeric nanoparticles: enhanced generation of singlet oxygen for improved photodynamic therapy. Mater Sci Eng C 77:935–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.179
Ong KS, Mawang CI, Daniel-Jambun D et al (2018) Current anti-biofilm strategies and potential of antioxidants in biofilm control. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 16:855–864. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2018.1535898
Oun R, Moussa YE, Wheate NJ (2018) The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: a review for chemists. Dalt Trans 47:6645–6653. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8dt00838h
Pelegrino MT, Weller RB, Chen X et al (2017) Chitosan nanoparticles for nitric oxide delivery in human skin. Medchemcomm 8:713–719. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6md00502k
Ratkay LG, Waterfield JD, Hunt DW (2000) Photodynamic therapy in immune (non-oncological) disorders: focus on benzoporphyrin derivatives. BioDrugs 14:127–135. https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200014020-00006
Reinhard A, Sandborn WJ, Melhem H et al (2015) Photodynamic therapy as a new treatment modality for inflammatory and infectious conditions. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 11:637–657. https://doi.org/10.1586/1744666X.2015.1032256
Saito M, Kato H, Konaka C et al (1996) Synchronous quadruple lung cancer treated curatively by photodynamic therapy. Diagn Ther Endosc 3:115–119. https://doi.org/10.1155/DTE.3.115
Sakamoto FH, Lopes JD, Anderson RR (2010) Photodynamic therapy for acne vulgaris: a critical review from basics to clinical practice—part I. Acne vulgaris: when and why consider photodynamic therapy? J Am Acad Dermatol 63:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2009.09.056
Samy NA, Salah MM, Ali MF, Sadek AM (2015) Effect of methylene blue-mediated photodynamic therapy for treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Lasers Med Sci 30:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-014-1609-1
Scott LJ, Goa KL (2000) Verteporfin. Drugs Aging 16:139–146. https://doi.org/10.2165/00002512-200016020-00005
Shanmugapriya K, Kang HW (2019) Engineering pharmaceutical nanocarriers for photodynamic therapy on wound healing: review. Mater Sci Eng C 105:110110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110110
Shi X, Zhang CY, Gao J, Wang Z (2019) Recent advances in photodynamic therapy for cancer and infectious diseases. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomedicine Nanobiotechnol 11:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1560
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Silva JCE, Lacava ZGM, Kuckelhaus S et al (2004) Evaluation of the use of low level laser and photosensitizer drugs in healing. Lasers Surg Med 34:451–457. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20062
Soares MV, Lanzarini CM, Oliveira DS et al (2010) Improving the phototoxicity of the zinc phthalocyanine by encapsulation in nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and phototherapy studies. Lat Am J Pharm 29:5–12
Soares MV, Oliveira MR, Dos EP et al (2011) Nanostructured delivery system for zinc phthalocyanine: preparation, characterization, and phototoxicity study against human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Int J Nanomed 6:227–238. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S15860
Soliman M, Salah M, Fadel M et al (2021) Contrasting the efficacy of pulsed dye laser and photodynamic methylene blue nanoemulgel therapy in treating acne vulgaris. Arch Dermatol Res 313:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-020-02093-y
Song W, Kuang J, Li CX et al (2018) Enhanced immunotherapy based on photodynamic therapy for both primary and lung metastasis tumor eradication. ACS Nano 12:1978–1989. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b09112
Spellberg B, Bartlett JG, Gilbert DN (2013) The future of antibiotics and resistance. N Engl J Med 368:299–302
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Thapa RK, Diep DB, Tønnesen HH (2021) Nanomedicine-based antimicrobial peptide delivery for bacterial infections: recent advances and future prospects. J Pharm Investig 51:377–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-021-00525-z
Tran P, Lee SE, Kim DH et al (2020) Recent advances of nanotechnology for the delivery of anticancer drugs for breast cancer treatment. J Pharm Investig 50:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-019-00459-7
Triesscheijn M, Baas P, Schellens JHM, Stewart FA (2006) Photodynamic therapy in oncology. Oncologist 11:1034–1044. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.11-9-1034
Wainwright M, Crossley KB (2004) Photosensitising agents—circumventing resistance and breaking down biofilms: a review. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 53:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2003.11.006
Wainwright M, Maisch T, Nonell S et al (2017) Photoantimicrobials—are we afraid of the light? Lancet Infect Dis 17:e49–e55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30268-7
Wang D, Wang T, Liu J et al (2016) Acid-activatable versatile micelleplexes for PD-L1 blockade-enhanced cancer photodynamic immunotherapy. Nano Lett 16:5503–5513. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01994
Wang N, Xu H, Sun S et al (2020a) Wound therapy via a photo-responsively antibacterial nano-graphene quantum dots conjugate. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 210:111978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.111978
Wang Y, Song J, Zhang F et al (2020b) Antifungal photodynamic activity of hexyl-aminolevulinate ethosomes against Candida albicans biofilm. Front Microbiol 11:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.02052
Wang T, Wu L, Wang Y et al (2021) Hexyl-aminolevulinate ethosome–mediated photodynamic therapy against acne: in vitro and in vivo analyses. Drug Deliv Transl Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-021-00942-5
Xu W, Qian J, Hou G et al (2018) PEGylated hydrazided gold nanorods for pH-triggered chemo/photodynamic/photothermal triple therapy of breast cancer. Acta Biomater 82:171–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2018.10.019
Yin M, Li Z, Ju E et al (2014) Multifunctional upconverting nanoparticles for near-infrared triggered and synergistic antibacterial resistance therapy. Chem Commun 50:10488–10490. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc04584j
Yung A, Stables GI, Fernandez C et al (2007) Microbiological effect of photodynamic therapy (PDT) in healthy volunteers: a comparative study using methyl aminolaevulinate and hexyl aminolaevulinate cream. Clin Exp Dermatol 32:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2007.02472.x
Zhu X, Li F, Peng X, Zeng K (2013) Formulation and evaluation of lidocaine base ethosomes for transdermal delivery. Anesth Analg 117:352–357
Zong J, Peng H, Qing X et al (2021) PH-Responsive pluronic F127-lenvatinib-encapsulated halogenated boron-dipyrromethene nanoparticles for combined photodynamic therapy and chemotherapy of liver cancer. ACS Omega 6:12331–12342. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01346
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2022R1F1A1065569).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors (K. Rhew, Y.J. Chae, and J.E. Chang) declare that they have no confict of interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors of this publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rhew, K., Chae, YJ. & Chang, JE. Progress and recent trends in photodynamic therapy with nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 52, 587–599 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-022-00594-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-022-00594-8