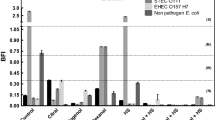
Abstract
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is a natural chemical ester composed of caffeic acid and (-)-quinic acid, and is further metabolized into active compounds in the living body. Here, we aimed to provide fundamental information on the antimicrobial action of CGA and related compounds against the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli IFO 3301. Bacteriostatic effects were assessed by spectrophotometry, and bactericidal effects were determined by enumerating viable cells on MacConkey agar plates. CGA and related compounds exhibited specific antimicrobial activity and corresponding reduction in log survival ratio, in which ferulic, isoferulic, benzoic, and hydroxybenzoic acids exhibited obvious antimicrobial activity against E. coli. In a time-kill assay, it was observed that bactericidal effects were associated with treatment time, temperature, and dose. A reduction in log survival ratio was observed at low pH as well as under thermal stress condition. Thus, we demonstrated that CGA and related compounds have not only bacteriostatic effects but also bactericidal effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albayrak S, Aksoy A, Sagdic O, and Hamzaoglu E (2010) Compositions, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Helichrysum (Asteraceae) species collected from Turkey. Food Chem 119, 114–22.
Alberto MR, Canavosio MAR, and Manca de Nadra MC (2006) Antimicrobial effect of polyphenols from apple skins on human bacterial pathogens. Electron J Biotechnol 9, 205–9.
Almajano MP, Carbó R, Delgado ME, and Gordon MH (2007) Effect of pH on the antimicrobial activity and oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions containing caffeic acid. J Food Sci 72, 258–63.
Almeida AAP, Farah A, Silva DAM, Nunan EA, and Gloória MBA (2006) Antibacterial activity of coffee extracts and selected coffee chemical compounds against enterobacteria. J Agric Food Chem 54, 8738–43.
Ayaz FA, Hayirlioglu-Ayaz S, Alpay-Karaoglu S, Gruz J, Valentova K, Ulrichova J et al. (2008) Phenolic acid contents of kale (Brassica oleraceae L. var. acephala DC.) extracts and their antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Food Chem 107, 19–25.
Biradar YS, Jagatap S, Khandelwal KR, and Singhania SS (2008) Exploring of antimicrobial activity of Triphala Mashi-an ayurvedic formulation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 5, 107–13.
Bouayed J, Rammal H, Dicko A, Younos C, and Soulimani R (2007) Chlorogenic acid, a polyphenol from Prunus domestica (Mirabelle), with coupled anxiolytic and antioxidant effects. J Neurol Sci 262, 77–84.
Campos FM, Couto JA, and Hogg TA (2003) Influence of phenolic acids on growth and inactivation of Oenococcus oeni and Lactobacillus hilgardii. J Appl Microbiol 94, 167–74.
Canillac N and Mourey A (2004) Effects of several environmental factors on the anti- Listeria monocytogenes activity of an essential oil of Picea excelsa. Int J Food Microbiol 92, 95–103.
Chiang YM, Chuang DY, Wang SY, Kuo YH, Tsai PW, and Shyur LF (2004) Metabolite profling and chemopreventive bioactivity of plant extracts from Bidens pilosa. J Ethnopharmacol 95, 409–19.
Cushnie TPT and Lamb AJ (2005) Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int J Antimicrob Agents 26, 343–56.
Erdemoglu N, Ozkan S, and Tosun F (2007) Alkaloid profile and antimicrobial activity of Lupinus angustifolius L. alkaloid extract. Phytochem Rev 6, 197–201.
Fattouch S, Caboni P, Coroneo V, Tuberoso CIG, Angioni A, Dessi S et al. (2007) Antimicrobial activity of Tunisian quince (Cydonia oblonga Miller) pulp and peel polyphenolic extracts. J Agric Food Chem 55, 963–9.
Friedman M and Jürgens HS (2000) Effect of pH on the stability of plant phenolic compounds. J Agric Food Chem 48, 2101–10.
Gonthier MP, Verny MA, Besson C, Rémésy C, and Scalbert A (2003) Chlorogenic acid bioavailability largely depends on its metabolism by the gut microflora in rats. J Nutr 133, 1853–9.
Hemaiswarya S and Doble M (2010) Synergistic interaction of phenylpropanoids with antibiotics against bacteria. J Med Microbiol 59, 1469–76.
Kim DO, Jeong SW, and Lee CY (2003) Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem 81, 321–6.
Leptihn S, Har JY, Wohland T, and Ding JL (2010) Correlation of charge, hydrophobicity, and structure with antimicrobial activity of S1 and MIRIAM peptides. Biochem 49, 9161–70.
Liu RH (2003) Health benefits of fruit and vegetables are from additive and synergistic combinations of phytochemicals. Am J Clin Nutr 78, 517S–20S.
Lou Z, Wang H, Lv W, Ma C, Wang Z, and Chen S (2010) Assessment of antibacterial activity of fractions from burdock leaf against food-related bacteria. Food Control 21, 1272–8.
Lou Z, Wang H, Zhu S, Ma C, and Wang Z (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of chlorogenic acid. J Food Sci 76, 398–403.
Moreno S, Scheyer T, Romano CS, and Vojnov AA (2006) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of rosemary extracts linked to their polyphenol composition. Free Radic Res 40, 223–31.
Nazzaro F, Caliendo G, Arnesi G, Veronesi A, Sarzi P, and Fratianni F (2009) Comparative content of some bioactive compounds in two varieties of capsicum annuum L. sweet pepper and evaluation of their antimicrobial and mutagenic activities. J Food Biochem 33, 852–68.
Olthof MR, Hollman PCH, Buijsman MNCP, Amelsvoort JMMV, and Katan MB (2003) Chlorogenic acid, quercetin-3-rutinoside and black tea phenols are extensively metabolized in humans. J Nutr 133, 1806–14.
Owusu-Ware SK, Chowdhry BZ, Leharne SA, and Antonijevic MD (2013) Quantitative analysis of overlapping processes in the non-isothermal decomposition of chlorogenic acid by peak fitting. Thermochim Acta 565, 27–33.
Plumb GW, Garcia-Conesa MT, Kroon PA, Rhodes M, Ridley S, and Williamson G (1999) Metabolism of chlorogenic acid by human plasma, liver, intestine and gut microflora. J Sci Food Agric 79, 390–2.
Sato Y, Itagaki S, Kurokawa T, Ogura J, Kobayashi M, Hirano T et al. (2011) In vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid. Int J Pharm 403, 136–8.
Senevirathne M, Kim SH, Siriwardhana N, Ha JH, Lee KW, and Jeon YJ (2006) Antioxidant potential of Ecklonia cava on reactive oxygen species scavenging, metal chelating, reducing power and lipid peroxidation inhibition. Food Sci Technol Intl 12, 27–38.
Szabo MR, Radu D, Gavrilas S, Chambre D, and Iditoiu C (2010) Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of selected spice extracts. Int J Food Prop 13, 535–45.
Xia D, Wu X, Shi J, Yang Q, and Zhang Y (2011) Phenolic compounds from the edible seeds extract of Chinese Mei (Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc) and their antimicrobial activity. LWT-Food Sci Technol 44, 347–9.
Zhao M, Wang H, Yang B, and Tao H (2010) Identification of cyclodextrin inclusion complex of chlorogenic acid and its antimicrobial activity. Food Chem 120, 1138–42.
Zhu X, Zhang H, and Lo R (2004) Phenolic compounds from the leaf extract of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and their antimicrobial activities. J Agric Food Chem 52, 7272–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabir, F., Katayama, S., Tanji, N. et al. Antimicrobial effects of chlorogenic acid and related compounds. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 57, 359–365 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4056-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4056-6