Abstract
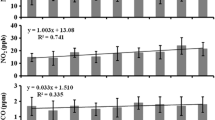
Ambient ammonia gas (NH3(g)) was continuously measured for one year, from March 2018 to February 2019, using a passive sampling method in a source-specific monitoring campaign in Hanoi, Vietnam, providing an unprecedented picture of the spatiotemporal characteristics of NH3(g) in this city. The four survey sites (three urban and one rural) were representative of a typical downtown area, a polluted river, a crossroad, and a rural area. Regarding spatial distribution, a distinctly high concentration (79.8 ± 61.2 ppb) was indicated at the polluted river, an important source unheard of in urban areas, followed by the crossroad (38.6 ± 18.8 ppb) and the downtown (36.5 ± 20.0 ppb); the lowest concentration (35.6 ± 36.0 ppb) was observed in the rural area. Seasonal variation was thoroughly discussed, together with meteorological parameters as driving factors. The strong dependence of NH3(g) concentration on the change in temperature and relative humidity at polluted river and rural area due to the strong impact of these meteorological factors on the volatilization of NH3(g) from wastewater and agriculture, respectively, causes the highest concentration in summer at these sites. The NH3(g) intensely emitted from the polluted river in summer was, furthermore, transferred to the surrounding area under the impact of the local wind direction. However, basically, in downtown, the concentration was higher in the cooler seasons than in the warmer seasons, which was found different compared with the conventional results in most of former studies, suggesting the major impact of vehicular emission on the rise of NH3(g) in urban area.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Alebic-Juretic A (2008) Airborne ammonia and ammonium within the Northern Adriatic area, Croatia. Environ Pollut 154:439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.11.029
Backes AM, Aulinger A, Bieser J, Matthias V, Quante M (2016) Ammonia emissions in Europe, part II: how ammonia emission abatement strategies affect secondary aerosols. Atmos Environ 126:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.039
Bajwa KS, Aneja VP, Pal Arya S (2006) Measurement and estimation of ammonia emissions from lagoon–atmosphere interface using a coupled mass transfer and chemical reactions model, and an equilibrium model. Atmos Environ 40:275–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2005.12.076
Behera SN, Sharma M, Aneja VP, Balasubramanian R (2013) Ammonia in the atmosphere: a review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8092–8131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2051-9
Borsari V, de Assunção JV (2017) Ammonia emissions from a light-duty vehicle. Transp Res Part D Transp Environ 51:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2016.12.008
Chang Y, Zou Z, Deng C, Huang K, Collett JL, Lin J, Zhuang G (2016) The importance of vehicle emissions as a source of atmospheric ammonia in the megacity of Shanghai. Atmos Chem Phys 16:3577–3594. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-3577-2016
Cohen DD, Crawford J, Stelcer E, Bac VT (2010) Characterisation and source apportionment of fine particulate sources at Hanoi from 2001 to 2008. Atmos Environ 44:320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.10.037
Dai XR, Saha CK, Ni JQ, Heber AJ, Blanes-Vidal V, Dunn JL (2015) Characteristics of pollutant gas releases from swine, dairy, beef, and layer manure, and municipal wastewater. Water Res 76:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.02.050
Department of Transport (2017) Hanoi Portal. https://hanoi.gov.vn/tintuc_sukien/-/hn/ZVOm7e3VDMRM/3/2798413/40/40/16.html;jsessionid=KuWRCqBcBnxV7SWBVBs1t-Fa.app2?doAsUserId=_viewTinTucId%3D122202. Last access: 27 Oct, 2021
General Statistics Office (2016) Area, population and population density. https://www.gso.gov.vn/px-web-2/?pxid=V0201&theme=D%C3%A2n%20s%E1%BB%91%20v%C3%A0%20lao%20%C4%91%E1%BB%99ng. Last access: 24 Aug 2021
Ha TD, Hung LV, Duc T, Hai M, Anh TT (2020) Forecast of water quality of Tolich river based on scenarios of Hanoi sewerage planning by using model QUAL2K. Vietnam J Sci Technol 58:75–83. https://doi.org/10.15625/2525-2518/58/3A/14269
Heeb NV, Forss A-M, Brühlmann S, Lüscher R, Saxer CJ, Hug P (2006) Three-way catalyst-induced formation of ammonia—velocity- and acceleration-dependent emission factors. Atmos Environ 40(31):5986–5997. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2005.12.035
Hien PD, Hangartner M, Fabian S, Tan PM (2014) Concentrations of NO2, SO2, and benzene across Hanoi measured by passive diffusion samplers. Atmos Environ 88(2):66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.01.036
Huai T, Durbin TD, Miller JW, Pisano JT, Sauer CG, Rhee SH, Norbeck JM (2003) Investigation of NH3 emissions from new technology vehicles as a function of vehicle operating conditions. Environ Sci Technol 37:4841–4847. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030403+
Khuriganova OI, Obolkin VA, Golobokova LP, Bukin YS, Khodzher TV (2019) Passive sampling as a low-cost method for monitoring air pollutants in the Baikal Region (Eastern Siberia). Atmosphere. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10080470
Kobara H, Takeuchi K, Ibusuki T (2007) Effect of relative humidity on aerosol generation through experiments at low concentrations of gaseous nitric acid and ammonia. Aerosol Air Qual Res 7(2):193–204. https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2006.10.0023
Kulmala M, Korhonen P, Napari I, Karlsson A, Berresheim H, O’Dowd CD (2002) Aerosol formation during PARFORCE: ternary nucleation of H2SO4, NH3, and H2O. J Geophys Res 107(D19):8111. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JD000900
Lee HS, Kang C-M, Kang B-W, Kim H-K (1999) Seasonal variations of acidic air pollutants in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos Environ 33:3143–3152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00382-3
Livingston C, Rieger P, Winer A (2009) Ammonia emissions from a representative in-use fleet of light and medium-duty vehicles in the California South Coast Air Basin. Atmos Environ 43:3326–3333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.04.009
McMurry PH, Fink M, Sakurai H, Stolzenburg MR, Mauldin IL, Smith J, Eisele F, Moore K, Sjostedt S, Tanner D, Huey LG, Nowak JB, Edgerton E, Voisin D (2005) A criterion for new particle formation in the sulfur-rich Atlanta atmosphere. J Geophys Res 110:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD005901
Meng ZY, Lin WL, Jiang XM, Yan P, Wang Y, Zhang YM, Jia XF, Yu XL (2011) Characteristics of atmospheric ammonia over Beijing, China. Atmos Chem Phys 11(12):6139–6151. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-6139-2011
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (2014) National Environmental Status Report 2013: Atmospheric environment (in Vietnamese)
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (2016) National Environmental Status Report 2011–2015. Chapter 5: Atmospheric Environment, 101–116 (in Vietnamese)
Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (2017) National Environmental Status Report 2016. Chapter 2: Atmospheric Environment, 25–45 (in Vietnamese)
Nguyen DV, Sato H, Hamada H, Yamaguchi S, Hiraki T, Nakatsubo R, Murano K, Aikawa M (2021) Symbolic seasonal variation newly found in atmospheric ammonia concentration in urban area of Japan. Atmos Environ 244:117943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117943
Ni J-Q, Heber AJ, Sutton AL, Kelly DT (2009) Mechanisms of gas releases from swine wastes. Trans ASABE 52(6):2013–2025. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.29203
Parkinson J, Tayler K, Mark O (2007) Planning and design of urban drainage systems in informal settlements in developing countries. Urban Water J 4(3):137–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/15730620701464224
Perrino C, Catrambone M, Bucchianico DMDA, Allegrini I (2002) Gaseous ammonia in the urban area of Rome, Italy and its relationship with traffic emissions. Atmos Environ 36:5385–5394. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00469-7
Reche C, Viana M, Karanasiou A, Cusack M, Alastuey A, Artinano B, Revuelta MA, Lopez-Mahía P, Blanco-Heras G, Rodríguez S, Sanchez de la Campa A, Fernandez-Camacho R, Gonzalez-Castanedo Y, Mantilla E, Tang YS, Querol X (2015) Urban NH3 levels and sources in six major Spanish cities. Chemosphere 119:769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.097
Thom DT (2013) Nghiên cứu sự biến động đất nông nghiệp do ảnh hưởng của quá trình công nghiệp hóa và đô thị hóa huyện Sóc Sơn, thành phố Hà Nội
Tucci CEM (2001) Chapter 2, Urban drainage issues in developing countries. In: Maksimovic C, Tucci CEM (eds) Urban drainage in specific climates, v. I: Urban drainage in humid tropics. IHP-V|Technical Documents in Hydrology|No. 40, vol. 1. UNESCO, Paris
Wang C, Yin S, Bai L, Zhang X, Gu X, Zhang H, Lu Q, Zhang R (2018a) High-resolution ammonia emission inventories with comprehensive analysis and evaluation in Henan, China, 2006–2016. Atmos Environ 193:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.08.063
Wang R, Ye X, Liu Y, Li H, Yang X, Chen J, Gao W, Yin Z (2018b) Characteristics of atmospheric ammonia and its relationship with vehicle emissions in a megacity in China. Atmos Environ 182:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.03.047
Whitehead JD, Longley ID, Gallagher MW (2007) Seasonal and diurnal variation in atmospheric ammonia in an urban environment measured using a quantum cascade laser absorption spectrometer. Water Air Soil Pollut 183:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9381-5
Wu S-P, Dai L-H, Wei Y, Zhu H, Zhang Y-J, Schwab JJ, Yuan C-S (2018) Atmospheric ammonia measurements along the coastal lines of Southeastern China: Implications for inorganic nitrogen deposition to coastal waters. Atmos Environ 177:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.12.040
Xu P, Koloutsou-Vakakis S, Rood MJ, Luan S (2017) Projections of NH3 emissions from manure generated by livestock production in China to 2030 under six mitigation scenarios. Sci Total Environ 607:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.258
Yao X, Hu Q, Zhang L, Evans GJ, Godri KJ, Ng AC (2013) Is vehicular emission a significant contributor to ammonia in the urban atmosphere? Atmos Environ 80:499–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.08.028
Zhang CL, Geng XS, Wang H, Zhou L, Wang BG (2017) Emission factor for atmospheric ammonia from a typical municipal wastewater treatment plant in South China. Environ Pollut 220:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.082
Zhang Y, Tang A, Wang D, Wang Q, Benedict K, Zhang L, Liu D, Li Y, Collett JL Jr, Sun Y, Liu X (2018) The vertical variability of ammonia in urban Beijing, China. Atmos Chem Phys 18:16385–16398. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-16385-2018
Zhang X, Murakami T, Wang J, Aikawa M (2021) Sources, species and secondary formation of atmospheric aerosols and gaseous precursors in the suburb of Kitakyushu, Japan. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143001
Zhao ZQ, Bai ZH, Winiwarter W, Kiesewetter G, Heyes C, Ma L (2017) Mitigating ammonia emission from agriculture reduces PM2.5 pollution in the Hai River Basin in China. Sci Total Environ 609:1152–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.240
Zhou C, Zhou H, Holsen TM, Hopke PK, Edgerton ES, Schwab JJ (2019) Ambient ammonia concentrations across New York State. J Geophys Res Atmosp 124(14):8287–8302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD030380
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Sumitomo Foundation (Grant No. 173025).
Funding
This work was supported by the Sumitomo Foundation (Grant No. 173025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DVN was involved in the investigation (sample preparation) at all sites, conceptualization, chemical analysis, statistical analysis, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization, software. LKN contributed to the investigation sampling sites initially. DAT helped in the investigation (sample acquisition) at Hanoi urban site. MHD contributed to the investigation (sample acquisition) at rural site. HTN contributed to the project co-administration and resources. MA was involved in the project co-administration, funding acquisition, supervision, conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, visualization, resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors participated in the preparation of the manuscript.
Consent to publication
All authors consent for publication.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: U.W. Tang.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Van Nguyen, D., Nguyen, L.K., Tran, D.A. et al. Seasonal variation of NH3 concentration and its controlling factors in Hanoi, Vietnam, depending on the site classification. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 8277–8286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04567-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04567-0