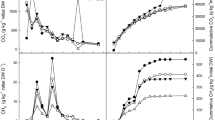
Abstract
An increase in the generation of organic waste with no adequate means of disposal has become a worldwide problem. Composting is an eco-friendly method of organic waste disposal and also producing organic fertilizer. Different methods have been applied by researchers to improve the agronomic value of compost. In this study, a mixture experimental design was used to optimize the proportions of poultry litter, vegetable waste, and corn stalk during composting to enhance the agronomic value. A total of 10 treatments with different proportions of substrate mix were observed for 30 days. Temperature, moisture content, NH4+/NO3–, electric conductivity, organic matter content, and pH were monitored. Germination index was used to determine the maturity and phytotoxicity of the compost mix. The results indicated that organic matter degradation followed a first-order kinetic pattern. The statistical model showed that the special cubic model explained the variation in the trend of germination index with R2 = 0.9827. The simplex–centroid mixture design predicted that the best substrate proportions that would produce a final compost with low phytotoxicity and high agronomic value were poultry litter = 57.58%, vegetable waste = 4.01% and corn stalk = 38.41%. The follow-up experiments validated the model predictions. The outcome of this study when implemented would be of great importance in regards to plant phytotoxicity and sustainable agriculture. Co-composting of different organic waste is a good method of improving the agronomic value of compost.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah N, Chin NL (2010) Simplex-centroid mixture formulation for optimised composting of kitchen waste. Bioresour Technol 101:8205–8210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.05.068
Adhikari BK, Barrington S, Martinez J, King S (2009) Effectiveness of three bulking agents for food waste composting. Waste Manag 29(1):197–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.04.001
Bremner JM (1965) Inorganic forms of Nitrogen. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil. Analysis Part 2 Am. Soc. of Agro. Madison, Wis., vol 9, pp 1179–1237
Cesaro A, Conte A, Belgiorno SA, Siciliano A, Guida M (2019) The evolution of compost stability and maturity during the full-scale treatment of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. J Environ Manag 232:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.121
Chang R, Guo Q, Chen Q, Bernal MP, Wang Q, Li Y (2019) Effect of initial material bulk density and easily-degraded organic matter content on temperature changes during composting of cucumber stalk. J Environ Sci 80:306–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.10.004
Cornell JA (2002) Experiment with mixtures: designs, models and the analysis of mixture data, 3rd edn. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., USA, p 680
Duan M, Gu J, Wang X, Li Y, Zhang S, Yin Y, Zhang R (2018) Effects of genetically modified cotton stalks on antibiotic resistance genes, intI1, and intI2 during pig manure composting. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:637–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.023
Ermolaev E, Jarvis A, Sundberg C, Smårs S, Pell M, Jönsson H (2015) Nitrous oxide and methane emissions from food waste composting at different temperatures. Waste Manag 46:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.08.021
Fernández FJ, Sánchez-Arias V, Rodríguez L, Villaseñor J (2010) Feasibility of composting combinations of sewage sludge, olive mill waste and winery waste in a rotary drum reactor. Waste Manag 30(10):1948–1956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.04.007
Ge J, Huang G, Huang J, Zeng J, Han L (2015) Mechanism and kinetics of organic matter degradation based on particle structure variation during pig manure aerobic composting. Hazard Mater 292:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.010
Gupta G, Borowiec J, Okoh J (1997) Toxicity identification of poultry litter aqueous leachate. PoultSci 76:1364–1367. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/76.10.1364
Gupta D, Singh RS, Sachan A, Vidyarthi AS, Gupta A (2012) A re-appraisal on intensification of biogas production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16(7):4908–4916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.05.005
He Z, Lin H, Hao J, Kong X, Tian K, Bei Z, Tian X (2018) Impact of vermiculite on ammonia emission and organic matter decomposition of food waste during composting. Bioresour Technol 263:548–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.031
Iqbal MK, Shafiq T, Ahmed K (2010) Characterization of bulking agents and its effects on physical properties of compost. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1913–1919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.030
Jain MS, Kalamdhad AS (2019) Drum composting of nitrogen-rich Hydrilla verticillata with carbon-rich agent: Effects on composting physics and kinetics. J Environ Manag 231:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.111
Jain MS, Jambhulkar R, Kalamdhad AS (2018) Biochar amendment for batch composting of nitrogen rich organic waste: effect on degradation kinetics, composting physics and nutritional properties. Bioresour Technol 253:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.038
Jalili M, Mokhtari M, Eslami H, Abbasi F, Ghanbari R, Ebrahimi AA (2019) Toxicity evaluation and management of co-composting pistachio wastes combined with cattle manure and municipal sewage sludge. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:798–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.056
Jiang J, Kang K, Wang C, Sun X, Dang S, Wang N, Wang Y, Zhang C, Yan G, Li Y (2018) Elevation of total greenhouse gas emission during sewage sludge composting by different dicyandiamide added forms: Mixture surface broadcasting and their combination. Waste Manag 81:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.10.003
Kalamdhad AS, Singh YK, Ali M, Khwairakpam M, Kazmi AA (2009) Rotary drum composting of vegetable waste and tree leaves. Bioresour Technol 100:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.030
Kawai K, Tasaki T (2016) Revisiting estimates of municipal solid waste generation per capita and their reliability. J Mater Cycles Waste 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-015-0355-1
Komilis D, Evangelou A, Voudrias E (2011) Monitoring and optimizing the co-composting of dewatered sludge: a mixture experimental design approach. J Environ Manag 92(9):2241–2249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.04.012
Kulikowska D (2016) Kinetics of organic matter removal and humification progress during sewage sludge composting. Waste Manag 49:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.01.005
Kumar A, Alaimo CP, Horowitz R, Mitloehner FM, Kleeman MJ, Green PG (2011) Volatile organic compound emissions from green waste composting, characterization and ozone formation. Atmos Environ 45(10):1841–1848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.01.014
Lim SL, Lee LH, Wu TY (2016) Sustainability of using composting and vermicomposting technologies for organic solid waste biotransformation: recent overview, greenhouse gases emissions and economic analysis. J Clean Prod 111:262–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.083
Lopez-Cano I, Roig A, Cayuela ML, Alburquerque JA, Sánchez-Monedero MA (2016) Biochar improves N cycling during composting of olive mill wastes and sheep manure. Waste Manag 49:553–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.12.031
Luo Y, Liang J, Zeng G, Chen M, Mo D, Li G, Zhang D (2017) Seed germination test for toxicity evaluation of compost: its roles, problems and prospects. Waste Manag 71:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.09.023
Makan A, Assobhei O, Mountadar M (2013) Effect of initial moisture content on the in-vessel composting under air pressure of organic fraction of municipal solid waste in Morocco. Iran J Environ Health 10:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1735-2746-10-3
Marshall RE, Farahbakhsh K (2013) Systems approaches to integrated solid waste management in developing countries. Waste Manag 33(4):988–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.12.023
Mejias L, Komilis D, Gea T, Sánchez A (2017) The effect of airflow rates and aeration mode on the respiration activity of four organic wastes: Implication on the composting process. Waste Manag 65:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.04.008
Mohee R, Driver MFB, Sobratee N (2008) Transformation of spent broiler litter from exogenous matter to compost in a sub-tropical context. Bioresour Technol 99(1):128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.11.040
Mozhiarasi V, Speier CJ, Rose PMB, Mondal MM, Pragadeesh S, Weichgrebe D, Srinivasan SV (2019) Variation in generation of vegetable, fruit and flower market waste and effects on biogas production, exergy and energy contents. J Mater Cycles Waste 21:713–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00828-2
Muhammad J, Khan S, Lei M, Khan MA, Nawab J, Rashid A, Ullah S, Khisro SB (2020) Application of poultry manure in agriculture fields leads to food plant contamination with potentially toxic elements and causes health risk. Environ Technol Innov 19:100909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100909
Oktiawan W, Zaman B, Purwono (2018) Use of germination bioassay to test compost maturity in Tekelan village. Web Conf 31:05012. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20183105012
Onwosi CO, Igbokwe VC, Odimba JN, Eke IE, Nwankwoala MO, Iroh IN, Ezeogu LI (2017) Composting technology in waste stabilization: on the methods, challenges and future prospects. J Environ Manag 190:140–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.051
Paradelo R, Eden M, Martinez I, Kellerde T, Houot S (2019) Soil physical properties of a Luvisol developed on loess after 15 years of amendment with compost. Soil till Res 191:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.04.003
Petric I, Helic A, Avdic EA (2012) Evolution of process parameters and determination of kinetics for co-composting of organic fraction of municipal solid waste with poultry manure. Bioresour Technol 117:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.046
Růžičková J, Raclavská H, Kucbel M, Grobelak A, Šafář M, Raclavský K, Švédová B, Juchelková D, Moustakas K (2021) The potential environmental risks of the utilization of composts from household food waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:24663–24679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09916-5
Sharma D, Yadav KD, Kumar S (2018) Biotransformation of flower waste composting: optimization of waste combinations using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 270:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.036
Siles-Castellano AB, López MJ, López-González JA, Suárez-Estrella F, Jurado MM, Estrella-González MJ, Moreno J (2020) Comparative analysis of phytotoxicity and compost quality in industrial composting facilities processing different organic wastes. J Clean Prod 252:119820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119820
Solaiman ZM, Yang H, Archdeacon D, Tippett O, Tibi M, Whiteley AS (2019) Humus-rich compost increases lettuce growth, nutrient uptake, mycorrhizal colonisation, and soil fertility. Pedosphere 29(2):170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(19)60794-0
Sun D, Lan Y, Xu EG, Meng J, Chen W (2016) Biochar as a novel niche for culturing microbial communities in composting. Waste Manag 54:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.05.004
Tabrika I, Mayad EH, Furze JN, Zaafrani M, Azim K (2021) Optimization of tomato waste composting with integration of organic feedstock. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12303-9
Testolin RC, Feuzer-Matos AJ, Cotelle S, Adani F, Janke L, Poyer-Radetski G, Pereira AC, Ariente-Neto R, Somensi CA, Radetski CM (2021) Using textile industrial sludge, sewage wastewater, and sewage sludge as inoculum to degrade recalcitrant textile dyes in a co-composting process: an assessment of biodegradation efficiency and compost phytotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28(36):49642–49650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14211-y
Wang S, Zeng Y (2018) Ammonia emission mitigation in food waste composting: a review. Bioresour Technol 248:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.050
Waqas M, Nizami AS, Aburiazaiza AS, Barakat MA, Ismail IMI, Rashid MI (2018) Optimization of food waste compost with the use of biochar. J Environ Manag 216:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.015
Witek-Krowiak A, Chojnacka K, Podstawczyk D, Dawiec A, Pokomeda K (2014) Application of response surface methodology and artificial neural network methods in modelling and optimization of biosorption process. Bioresour Technol 160:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.021
Wu TY, Lim SL, Lim PN, Shak KPY (2014) Biotransformation of biodegradable solid wastes into organic fertilizers using composting or/and vermicomposting. Chem Eng Trans 39:1579–1584. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1439264
Zakarya AI, Khalib BNS, Ramzi MN (2018) Effect of pH, temperature and moisture content during composting of rice straw burning at different temperature with food waste and effective microorganism. Web Conf 34:02019. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20183402019
Zhang H, Schuchardt F, Li G, Yang J, Yang Q (2013) Emission of volatile sulfur compounds during composting of municipal solid waste (MSW). Waste Manag 33(4):957–963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2012.11.008
Zhou Y, Selvam A, Wong JW (2016) Effect of Chinese medicinal herbal residues on microbial community succession and anti-pathogenic properties during co-composting with food waste. Bioresour Technol 217:190–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.080
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Uchenna C. Nduka for his kind assistance in data statistical analysis.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.N. Ezugworie contributed to validation, methodology, and writing—original draft. O.C. Okeh performed writing—original draft. C.O. Onwosi contributed to conceptualization, supervision, validation, methodology, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Maryam Shabani.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezugworie, F.N., Okeh, O.C. & Onwosi, C.O. Reducing compost phytotoxicity during co-composting of poultry litter, vegetable waste, and corn stalk: mixture experimental design approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 2699–2712 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04161-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04161-4