Abstract
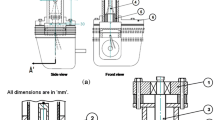
In this study, reciprocating motion of the piston in a single-cylinder, two-stroke, spark-ignition engine was achieved with a novel rhombic drive mechanism to reduce friction losses, vibration and the lateral forces of the piston on the cylinder compared to conventional engine with slider-crank mechanism. Three-dimensional model of the prototype two-stroke engine with rhombic drive mechanism was prepared in Solidworks software according to kinematic relations, and 3D assembly strength analysis was carried out with inertia relief method in Abaqus and Hypermesh software. According to the finite element model, the most critical component was determined as gear pins and endurance limit for the mechanism was satisfied. Then, the prototype of the single-cylinder, two-stroke, and spark-ignition engine with rhombic drive mechanism was manufactured. The engine was tested at different engine speeds from 1700 to 3000 rpm at stoichiometric air/fuel ratio. In the tests, performance characteristics of the engine and CO, HC, NO and CO2 emissions were obtained. Prototype rhombic-driven engine provided 0.98 Nm output torque at 2400 rpm and 0.3 kW output power at 3000 rpm. Maximum thermal efficiency was obtained as 23.55%. In total, about 11% weight reduction was achieved when compared with a mass-production engine with the same swept volume and compression ratio. This engine is expected to stand for an alternative range extender engine to use on light/unmanned aviation vehicles and small size agricultural applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy F (2011) The effect of opium poppy oil diesel fuel mixture on engine performance and emissions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(1):57–62
Aksoy F, Solmaz H, Karabulut H, Cinar C, Ozgoren YO, Polat S (2016) A thermodynamic approach to compare rhombic-drive and crank-drive mechanisms for a beta type Stirling Engine. Appl Therm Eng 93:359–367
Ali Y, Hrairi M, Kattan I (2012) Potential for improving vehicle fuel efficiency and reducing the environmental pollution via fuel ionization. Int J Environ Sci Technol 9:495–502
Antonelli E, Nuccio P, Dongiovanni C, Marzano MR (2004) A new GDI 2-stroke engine to meet future emission limits: the design and prototype architecture, SAE 32-0041
Ausserer JK, Polanka MD, Baranski JA, Grinstead KD, Litke PJ (2017) Measurement of loss pathways in small, two-stroke internal- combustion engines. SAE Int J Eng 10:128–143
Blair GP (1996) Design and simulation of two-stroke engines. Society of Automotive Engineers Inc, Warrandale, PA
Boretti A, Jiang S (2015) Two-stroke direct injection jet ignition engines for unmanned aerial vehicles. SAE technical paper 01-2424, https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-2424
Cantore G, Mattarelli E, Rinaldini CA (2014) A new design concept for 2-Stroke aircraft diesel engines. Energy Procedia 45:739–748
Carlucci AP, Ficarella A, Laforgia D, Renna A (2015) Supercharging system behaviour for high altitude operation of an aircraft 2-stroke Diesel engine. Energy Convers Manag 101:470–480
Cheng YJY (2010) Numerical model for predicting thermodynamic cycle and thermal efficiency of a beta-type stirling engine with rhombic drive mechanism. Renew Energy 35:2590–2601
Cheng CH, Yu YJ (2011) Dynamic Simulation of a beta-type Stirling engine with cam-drive mechanism via the combination of the thermodynamic and dynamic models. Renew Energy 36:714–725
Cheng CH, Yu YJ (2012) Combining dynamic and thermodynamic models for dynamic simulation of a beta-type stirling engine with rhombic drive mechanism. Renew Energy 37:161–173
Dube A, and Ramesh A (2016) Influence of injection parameters on the performance and emissions of a direct injection two stroke SI engine. SAE technical paper 01-1052, https://doi.org/10.4271/2016-01-1052
Ferguson CR, Kirkpatrick AT (2014) Internal combustion engine applied thermosciences. Wiley, New Jersey
Gultekin E (2019) Design and development of a two-stroke engine with rhombic drive mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Turkish Aeronautical Association, Institute of Science and Technology, Ankara, Turkey
Hassani EH, Boutammachte N, Knorr J, Hannaoui EM (2013) Study of a low temperature stirling engine driven by a rhombic drive mechanism. Int J Energy Environ Eng 4:40
Heywood JB (1988) Internal combustion engine fundamentals. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
https://www.neander-motors.com/en/state-of-the-art/neandersolution (2017) Neander Motor Vehicles AG. Accessed 19 April 2019
Jia B, Wang Y, Smallbone A, Roskilly AP (2018) Analysis of the scavenging process of a two-stroke free-piston engine based on the selection of scavenging ports or valves. MDPI Energies 11:324. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020324
Karabulut H, Aksoy F, Ozturk E (2009) Thermodynamic analysis of a β type stirling engine with a displacer driving mechanism by means of a lever. Renew Energy 34:202–208
Mattarelli E, Rinaldini CA (2017) Commercial vehicles: New diesel engine concept for euro VI and beyond. SAE technical paper 26-0034, https://doi.org/10.4271/2017-26-0034
Morton R, Riviere R, Geyer S (2017) Understanding limits to the mechanical efficiency of opposed piston engines. SAE technical paper 01-1026, https://doi.org/10.4271/2017-01-1026
Newton K, Steeds W, Garrett TK (1983) The motor vehicle, 10th edn, Butterworths, England
Pohjalainen T, Larmi M (2015) Novel crank mechanism increasing engine efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions. SAE technical paper, No. 01-1259, https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-1259
Pulkrabek WW (2014) Engineering fundamentals of the internal combustion engine. Pearson Education Limited, England
Rucker RD (2000) An analysis of the parallel combustion two-stroke engine. SAE 01-1022, https://doi.org/10.4271/2000-01-1022
Savioli T, Zardin B, Borghi M (2017) Development of a 2-stroke GDI engine. Energy Procedia 126:1091–1098
Shankar RK, Priyanka EB, Saravanan B (2015) Performance analysis of gasoline direct injection in two-stroke spark-ignition engines. Int J Adv Res Electr Electron Instrum Eng 4:4940–4947
Shendage DJ, Kedare SB, Bapat SL (2011) An analysis of beta type stirling engine with rhombic drive mechanism. Renew Energy 36:289–297
Solmaz H, Karabulut H (2014) Performance comparison of a novel configuration of beta-type stirling engines with rhombic drive engine. Energy Convers Manag 78:627–633
Warren S, Yang D (2013) Design of rotary engines from the apex seal profile (Abbr.: rotary engine design by apex seal). Mech Mach Theory 64:200–209
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge to Chairperson of Automotive Engineering Department in Gazi University due to utilization permit of the laboratories.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Fatih ŞEN.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gultekin, E., Cinar, C. & Okur, M. Design, manufacturing and testing of a prototype two-stroke engine with rhombic drive mechanism. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 455–462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02488-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02488-z