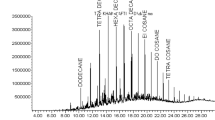
Abstract
Comparative study on the petroleum crude oil degradation potential of microbes from petroleum-contaminated soil and non-contaminated soil was performed in the present paper. Three samples were employed to conduct the evaluation, of which two are from the petroleum-contaminated soil of Yanchang oil field, and one is from non-contaminated soil of Northwest University Campus, Xi’an. The bacterial plate counts in sample No. 1 of the petroleum-contaminated soil were 6.0 × 102 and the bacterial plate counts in sample No. 2 of the petroleum-contaminated soil were 4.0 × 103, while the bacterial plate counts in sample No. 3 of non-petroleum-contaminated were 6.0 × 104. Petroleum-degrading microbes were isolated from Bushnell Haas mineral salt medium and 16 bacterial strains and two fungal strains from PCS sample No. 1, five bacterial strains and one fungal strain from PCS sample No. 2, and 17 bacterial strains and one fungal strain from garden soil, respectively. For primary screening of potential petroleum-degrading microbes, 2, 6-dichlorophenol indophenol test was carried out and nine bacterial strains from PCS No. 1 and four bacterial strains from garden soil showed the potential petroleum-degrading activity. The petroleum degradation percentage of mixture of 13 bacteria was 47.57%, and it was higher than that of four fungi and the combined mixture (13 bacteria and four fungi). Study showed that the microbes isolated from non-contaminated soil had the good petroleum degradation potential.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebusoye SA et al (2007) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in polluted tropical stream. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(8):1149–1159
Adegbola GM, Eniola KIT, Opasola OA (2014) Isolation and identification of indigenous hydrocarbon tolerant bacteria from soil contaminated with used engine oil in Ogbomoso, Nigeria. Adv Appl Sci Res 5(3):420–422
Adel EE et al (2012) In vitro screening for oil degrading bacteria and evaluation of their biodegradation potential for hydrocarbon. Afr J Microbiol Res 6(49):7534–7544
Afifi A, Motamedi H, Alizadeh B, Leilavi H (2015) Isolation and identification of oil degrading bacteria from oil sludge in Abadan oil refinery. Environ Exp Biol 13:13–18
Allamin IA et al (2014) Distribution of hydrocarbon degrading fungi in soil in Kukawa, Bornostate, Nigeria. Merit Res J Environ Sci Toxicol 2(7):135–140
Arpita G, Sheetal S (2015) Study of oil degrading bacteria isolated from oil contaminated sites. Int J Res Appl Sci Eng Technol (IJRASET) 3(II):345–349
Bharti P, Irafan M (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa is present in crude oil contaminated sites of Barmer Region (India). J Bioremediat Biodegrad 2(5):1–2
Bidoia ED, Montagnolli RN, Lpes PRM (2010) Microbiol biodegradation potential of hydrocarbons evaluated bycolorimetric technique: a case study. In: Mendez-Vilas A (ed) Microbes in Applied Research: Current Advances andChallenges. World Scientific Publishing, pp 162–166
Chukwura EI et al (2016) Hydrocarbon degradation potentials of fungi associated with oil-contaminated soil from selected mechanic workshops in Awka, Anambra State, Nigeria. Front Environ Microbiol 2(6):38–44
Daniel OT (2011) Bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil- a case study at Newmont Ghana-Gold limited-Ahafo Kenyasi. Master Thesis
Das N, Chandran P (2010) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants. An overview. Biotechnol Res Int 7(6):1–13
Ganesh A, Lin J (2009) Diesel degradation and biosurfactant production by gram - positive isolates. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 8(21):5847–5854
Head IM et al (2006) Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(3):173–182
Henry R, Walther III (2014) Clean up techniques used for coastal oil spills: an analysis of spills occurring in Santa Barbara, California, Prince William Sound, Alaska, The sea of Japan, and The gulf coast. Master’s projects and capstones. 104. https://repository.usfca.edu/capstone/104
Joshi RA, Pandey GB (2011) Screening of petroleum degrading bacteria from cow dung. Res J Agri Sci 2:69–71
Kubota K, Koma D, Matsumiya Y, Chung S, Kubo M (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of long-chain hydrocarbondegradation bacteria and evaluation of their hydrocarbon–degradation by the 2,6-DCPIP assay. Biodegradation 19:749–757
Kumari N et al (2013) Isolation, identification and characterization of oil degrading bacteria isolated from contaminated sites of Barmer, Rajasthan. Int J Biotechnol Bioeng Res 4(5):429–436
Mahjoubi M et al (2013) Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria isolated from petroleum contaminated sites in Tunisia; isolation, identification and characterization of the biotechnological potential. New Biotechnol 30(6):723–733
Mamitha KS, Grasian I, Albert HS (2013) Isolation and Identification of hydrocarbon degrading bacteria from Ennore creek. Bioinformation 9(3):150–157 ISSN 0973-2063 (online) 0973-8894 (print)
Martins FF et al (2012) Evolution of crude oil degradation by Yarrowia lipolytica. Chem Eng Trans 27:223–228. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1227038
Mohsenzaheh F, Rad AC, Akbari M (2012) Evaluation of oil removal efficiency and enzymatic activity in some fungal strains for bioremediation of petroleum-polluted soils. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 9(26):1–8
Obi LU et al (2016) Isolation and characterization of crude oil sludge degrading bacteria, vol 5:1946. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3617-z
Okoh AI, Trejo-Hernandez MR (2006) Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon polluted systems: exploiting the bioremediation strategies. Afr J Biotechnol 5:2520–2525
Olajire AA, Essien JP (2014) Aerobic degradation of petroleum components by microbial consortia. J Pet Environ Biotechnol 5(5):1000195
Panda SK et al (2013) Isolation and identification of petroleum hydrocarbon degrading microorganisms from oil contaminated environment. Int J Environ Sci 3(5):1–8
Patil TD et al (2012) Bioremediation of complex hydrocarbons using microbial consortium isolated from diesel oil polluted soil. Pelagia Res Libr Der Chem Sin 3(4):953–958
Roy S et al (2002) Survey of petroleum degrading bacteria in coastal waters of Sunderban Biosphere Reserve. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:575–581
Sandhu SS et al (2016) Determination of hydrocarbon degrading potentiality of indigenous fungal isolates. Int J Environ Sci 6(6):1163–1172
Selvakumar S et al (2014) Rapid screening of crude oil degrading bacteria isolated from oil contaminated areas. Sci Tech J 1(3):24–27
Silva DM et al (2011) Identification of fungi of the genus Aspergillus section Nigri using polyphasic. Braz J Microbiol 42:761–773
Uzoamaka GO et al (2009) Hydrocarbon degradation potentials of indigenous fungal isolates from petroleum contaminated soils. Phys Nat Sci 3(1):1–6
Varjani SJ, Upasani VN (2013) Comparative studies on bacterial consortia for hydrocarbon degradation. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 2(10):5377–5383
Xenia ME, Refugio RV (2016) Microorganisms metabolisms during bioremediation of oil contaminated soils. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 7:2
Xu J (2012) Bioremediation of crude oil contaminated soil by petroleum-degrading active bacteria. In: Romero-Zerón L (ed) Introduction to enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes and bioremediation of oil-contaminated sites, pp 207–244. ISBN 978-953-51-0629-6. http://www.intechopen.com/books/introduction-to-enhanced-oil-recovery-eor-processes-and-bioremediation-of-oil-contaminated-sites/bioremediation-of-oil-contaminated-soil-by-highly-petroleum-degrading-bacteria
Yakimov MM et al (2007) Obligate oil-degrading marine bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18(3):257–266
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully thank the Ministry of Science and Technology of China for financial support. Ms Chaochao Xie and Na Zhang are acknowledged for helping with this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Necip Atar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ra, T., Zhao, Y. & Zheng, M. Comparative study on the petroleum crude oil degradation potential of microbes from petroleum-contaminated soil and non-contaminated soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 7127–7136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2114-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2114-z