Abstract
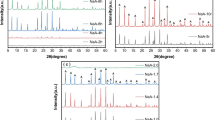
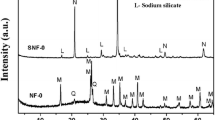
In this work, rice husk ash was used as silica source to synthesize NaX zeolite potentially suitable for CO2 adsorption. The produced material, denoted NaX-RHA, was characterized employing X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and gas adsorption porosimetry, in order to verify the occurred production of well-crystallized NaX zeolite with a significant degree of purity. CO2 adsorption isotherms on NaX-RHA were volumetrically evaluated in the 298–348 K temperature range up to standard pressure, revealing performances that are higher than those reported for commercial similar substrates. The experimental data regarding CO2 adsorption on NaX-RHA were very satisfyingly fitted by the semiempirical Sips model. Analyzing the best fitting values of model parameters allowed to conclude that the synthesized adsorbent could be quite suitable for applications like CO2 capture from flue gas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aprea P, Caputo D, Gargiulo N, Iucolano F, Pepe F (2010) Modeling carbon dioxide adsorption on microporous substrates: comparison between Cu-BTC metal-organic framework and 13X zeolitic molecular sieve. J Chem Eng Data 55:3655–3661
Arenillas A, Smith KM, Drage TC, Snape CE (2005) CO2 capture using some fly ash-derived carbon materials. Fuel 84:2204–2210
Barth-Wirsching U, Höller H, Klammer D, Konrad B (1993) Synthetic zeolites formed from expanded perlite: type, formation conditions and properties. Miner Petrol 48:275–294
Bedard RL (2010) Synthesis of zeolites and manufacture of zeolitic catalysts and adsorbents. In: Kulprathipanja S (ed) Zeolites in industrial separation and catalysis. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 61–83
Bhatia S (1990) Zeolite catalysts: principles and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Camacho BCR, Ribeiro RPPL, Esteves IAAC, Mota JPB (2015) Adsorption equilibrium of carbon dioxide and nitrogen on the MIL-53(Al) metal organic framework. Sep Purif Technol 141:150–159
Choi S, Drese JH, Jones CW (2009) Adsorbent materials for carbon dioxide capture from large anthropogenic point sources. Chemsuschem 2:796–854
Dalai AK, Rao MS (1985) Synthesis of NaX zeolite using silica from rice husk ash. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 24:465–468
Dalai AK, Pradhan NC, Rao MS, Gokhale KVGK (2005) Synthesis and characterization of NaX and Cu-exchanged NaX zeolites from silica obtained from rice husk ash. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 12:227–234
Do DD (1998) Adsorption analysis: equilibria and kinetics. Imperial College Press, London
Gargiulo N, Caputo D, Colella C (2007) Preparation and characterization of polyethylenimine-modified mesoporous silicas as CO2 sorbents. Stud Surf Sci Catal 170:1938–1943
Gargiulo N, Aprea P, Caputo D, Eić M, Huang Q, Colella C (2009) Adsorption and diffusion of carbon dioxide in polyethylenimine-modified SBA-15 silicas. In: Acierno D, D’Amore A, Caputo D, Cioffi R (eds) Special topics on materials science and technology—an Italian Panorama. Brill, Leiden, pp 213–220
Gargiulo N, Pepe F, Caputo D (2012) Modeling carbon dioxide adsorption on polyethylenimine-functionalized TUD-1 mesoporous silica. J Colloid Interface Sci 367:348–354
Gargiulo N, Peluso A, Aprea P, Pepe F, Caputo D (2014a) CO2 Adsorption on polyethylenimine-functionalized SBA-15 mesoporous silica: isotherms and modeling. J Chem Eng Data 59:896–902
Gargiulo N, Pepe F, Caputo D (2014b) CO2 adsorption by functionalized nanoporous materials: a review. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14:1811–1822
Gargiulo N, Macario A, Iucolano F, Giordano G, Caputo D (2015a) Modeling the adsorption of CO2/N2 mixtures on siliceous nanoporous materials. Sci Adv Mater 7:258–263
Gargiulo N, Verlotta A, Peluso A, Aprea P, Caputo D (2015b) Modeling the performances of a CO2 adsorbent based on polyethylenimine-functionalized macro-/mesoporous silica monoliths. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 215:1–7
Ghasemi Z, Younesi H (2012) Preparation of free-template nanometer-sized Na–A and –X zeolites from rice husk ash. Waste Biomass Valoriz 3:61–74
Gokhale KVGK, Dalai AK, Rao MS (1986) Thermal characteristics of synthetic sodium zeolites prepared with silica from rice-husk ash. J Therm Anal 31:33–39
Grajciar L, Čejka J, Zukal A, Otero Areán C, Turnes Palomino G, Nachtigall P (2012) Controlling the adsorption enthalpy of CO2 in zeolites by framework topology and composition. Chemsuschem 5:2011–2022
Halmann MM, Steinberg M (1999) Greenhouse gas carbon dioxide mitigation: science and technology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hasan MMF, Baliban RC, Elia JA, Floudas CA (2012) Modeling, simulation, and optimization of postcombustion CO2 capture for variable feed concentration and flow rate. 1. Chemical absorption and membrane processes. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:15642–15664
Jadhav PD, Chatti RV, Biniwale RB, Labhsetwar NK, Devotta S, Rayalu SS (2007) Monoethanol amine modified zeolite 13X for CO2 adsorption at different temperatures. Energy Fuels 21:3555–3559
Khummongkol P, Anuwattana R (2009) Synthesis of zeolites from industrial wastes. In: Wong TW (ed) Handbook of zeolites: structure, properties and applications. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, pp 469–498
Kim J, Lin L-C, Swisher JA, Haranczyk M, Smit B (2012) Predicting large CO2 adsorption in aluminosilicate zeolites for postcombustion carbon dioxide capture. J Am Chem Soc 134:18940–18943
Kongkachuichay P, Lohsoontorn P (2006) Phase diagram of zeolite synthesized from perlite and rice husk ash. ScienceAsia 32:13–16
Lechert H, Staelin P (2001) FAU—Linde Type X. In: Robson H, Lillerud KP (eds) Verified synthesis of zeolitic materials, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 150–152
Lee J-S, Kim J-H, Kim J-T, Suh J-K, Lee J-M, Lee C-H (2002) Adsorption equilibria of CO2 on zeolite 13X and zeolite X/activated carbon composite. J Chem Eng Data 47:1237–1242
Lowell S, Shields JE, Thomas MA, Thommes M (2004) Characterization of Porous Solids and Powders: Surface Area, Pore Size and Density. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Martra G, Coluccia S, Davit P, Gianotti E, Marchese L, Tsuji H, Hattori H (1999) Acidic and basic sites in NaX and NaY faujasites investigated by NH3, CO2 and CO molecular probes. Res Chem Intermed 25:77–93
Oreggioni GD, Brandani S, Luberti M, Baykan Y, Friedrich D, Ahn H (2015) CO2 capture from syngas by an adsorption process at a biomass gasification CHP plant: its comparison with amine-based CO2 capture. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control 35:71–81
Pillai RS, Peter SA, Vir Jasra R (2012) CO2 and N2 adsorption in alkali metal ion exchanged X-Faujasite: grand canonical Monte Carlo simulation and equilibrium adsorption studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 162:143–151
Querol X, Moreno N, Umaña JC, Alastuey A, Hernández E, López-Soler A, Plana F (2002) Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash: an overview. Int J Coal Geol 50:413–423
Santasnachok C, Kurniawan W, Hinode H (2015) The use of synthesized zeolites from power plant rice husk ash obtained from Thailand as adsorbent for cadmium contamination removal from zinc mining. J Environ Chem Eng 3:2115–2126
Shen Y, Zhao P, Shao Q (2014) Porous silica and carbon derived materials from rice husk pyrolysis char. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 188:46–76
Sips R (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495
Siriwardane RV, Shen M-S, Fisher EP, Poston JA (2001) Adsorption of CO2 on molecular sieves and activated carbon. Energy Fuels 15:279–284
Song W, Justice RE, Jones CA, Grassian VH, Larsen SC (2004) Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption properties of nanocrystalline ZSM-5. Langmuir 20:8301–8306
Structure Commission of the International Zeolite Association (2007) Framework type FAU. Database of zeolite structures. http://izasc.ethz.ch/fmi/xsl/IZA-SC/mat_xrd.xsl?-db=crystal_data&-lay=web&STC=FAU&-find. Accessed 16 Nov 2016
Thuadaij P, Nuntiya A (2012) Preparation and characterization of faujasite using fly ash and amorphous silica from rice husk ash. Procedia Eng 32:1026–1032
Victor DG, Zhou D, Ahmed EHM, Dadhich PK, Olivier JGJ, Rogner H-H, Sheikho K, Yamaguchi M (2014) Climate change 2014: mitigation of climate change. In: Edenhofer O, Pichs-Madruga R, Sokona Y, Farahani E, Kadner S, Seyboth K, Adler A, Baum I, Brunner S, Eickemeier P, Kriemann B, Savolainen J, Schlömer S, von Stechow C, Zwickel T, Minx JC (eds) Contribution of working group III to the 5th assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, pp 111–150
Wang Q, Luo J, Zhong Z, Borgna A (2011) CO2 capture by solid adsorbents and their applications: current status and new trends. Energy Environ Sci 4:42–55
Wu Y-J, Yang Y, Kong X-M, Li P, Yu J-G, Ribeiro AM, Rodrigues AE (2015) Adsorption of Pure and Binary CO2, CH4, and N2 Gas Components on Activated Carbon Beads. J Chem Eng Data 60:2684–2693
Yusof AM, Nizam NA, Abd Rashid NA (2010) Hydrothermal conversion of rice husk ash to faujasite-types and NaA-type of zeolites. J Porous Mater 17:39–47
Zukal A, Pulido A, Gil B, Nachtigall P, Bludský O, Rubeš M, Čejka J (2010) Experimental and theoretical determination of adsorption heats of CO2 over alkali metal exchanged ferrierites with different Si/Al ratio. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:6413–6422
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the help provided by Dr. Benedetto De Vito (ACLabs—Laboratori di Chimica Applicata, Dipartimento di Ingegneria Chimica, dei Materiali e della Produzione Industriale, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II) for performing SEM investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Agnieszka Galuszka.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gargiulo, N., Shibata, K., Peluso, A. et al. Reinventing rice husk ash: derived NaX zeolite as a high-performing CO2 adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 1543–1550 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1534-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1534-5