Abstract
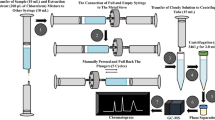
A salt-induced homogenous dispersive solid phase extraction method combined with an ionic liquid based-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction was developed for the extraction of two aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin and streptomycin) form milk samples prior to their determination by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. For this purpose, 15 mL milk sample mixed with 300 mg trichloroacetic acid to precipitate the sample proteins. After vortexing (1 min) and centrifugation (for 3 min at 5000 rpm), the supernatant was transferred into another test tube. After adjusting the solution pH at 10, polyvinylpyrrolidone (75 mg) was dissolved in it. The homogenous phase was broken by adding sodium chloride (20%, w/v) and polyvinylpyrrolidone was precipitated as fine particles which acted as a sorbent. After centrifugation, the supernatant phase was discarded and the analytes were eluted from the sorbent surface using 1.25 mL methanol. Subsequently, methanol was mixed with 85 µL trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride and the mixture was quickly injected into sodium chloride solution (10%, w/v). After a few seconds, the extraction solvent collected on the top of the solution was used in determination of the analytes. Under optimal conditions calibration curves of the analytes were linear in the range of 1–500 ng mL−1. Also, limits of detection and quantification were 0.29 and 0.18 ng mL−1; and 1.0 and 0.61 ng mL−1 for gentamicin and streptomycin, respectively. The extraction recoveries were 87 and 93% for gentamicin and streptomycin, respectively. Acceptable relative standard deviations ≤ 6.1% were also obtained. At last, the studied antibiotics were successfully determined in milk samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SI-HDSP:
-
Salt-induced-homogenous dispersive solid phase extraction
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometer
- PVP:
-
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
- ER:
-
Enrichment factor
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- IL:
-
Ionic liquids
References
J. Otte, U. Pica-Ciamarra, S. Morzaria, Front. Vet. Sci. 6, 37 (2019)
D. Schar, A. Sommanustweechai, R. Laxminarayan, V. Tangcharoensathien, PLoS Med. 15, e1002521 (2018)
M. Mahmudul Hassan, M.E. El Zowalaty, A. Lundkvist, J.D. Arhult, M.R. Khan Nayem, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 111, 141 (2021)
H. Yang, L. Paruch, X. Chen, A. Eerde, H. Skomedal, Y. Wang, D. Liu, J.L. Clarke, Front Vet Sci. 6, 136 (2019)
B.K. Bansal, N.S. Bajwa, S.S. Randhawa, R. Ranjan, P.S. Dhaliwal, Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 43, 323 (2011)
G. Lu, Q. Chen, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, L. Zhu, Food Res. Int. 147, 110450 (2021)
Codex Alimentarius Commission (2012), Maximum residue limits for veterinary drugs in foods updated as at the 35th session of the Codex Alimentarius Commission, http://www.codexalimentarius.org/standards/veterinary-drugs-mrls/en/. Accessed 15 Sept 2021
S.E. Mashana, C. Sindato, M.L. Matee, L.E.G. Mboera, Antibiotics 10, 1 (2021)
Y.M. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhou, Z.F. Liu, Q. Meng, X.S. Feng, Food Rev. Int. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129.2021.1952423
X. Wang, S. Yang, Y. Li, J. Zhang, Y. Jin, W. Zhao, Y. Zhang, J. Huang, P. Wang, C. Wu, J. Zhou, J. Chromatogr. A 1542, 28 (2018)
J. Wang, Q. Zhao, N. Jiang, W. Li, L. Chen, X. Lin, Z. Xie, L. Youa, Q. Zhang, J. Chromatogr. A 1458, 24 (2017)
S. Ji, F. Zhang, X. Luo, B. Yang, G. Jin, J. Yan, X. Liang, J. Chromatogr. A 1313, 113 (2013)
J. Bazzan Arsand, L. Jank, M.T. Martins, R. Barcellos Hoff, F. Barreto, T. Mara Pizzolato, C. Sirtori, Talanta 154, 38 (2016)
A. Moehbbi, A. Jouyban, M.A. Farajazdeh, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, M. Nemati, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 210, 114552 (2022)
M. Locatelli, M. Teresa Ciavarella, D. Paolino, C. Celia, E. Fiscarelli, G. Ricciottif, A. Pompilio, G. Di Bonaventura, R. Grande, G. Zengin, L. Di Marzio, J. Chromatogr. A 1419, 58 (2015)
A. Jouyban, M.A. Farajzadeh, M. Nemati, A.A. Alizadeh Nabil, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Microchem. J. 154, 104631 (2020)
M.A. Farajzadeh, A. Mohebbi, H. Fouladvand, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Microchem. J. 155, 104795 (2020)
J. Wu, G. Lu, X. Huang, Microchem. J. 159, 105549 (2020)
T. Yao, K. Du, Food Chem. 331, 127342 (2020)
K. Köseoğlu, H.I. Ulusoy, E. Yilmaz, M. Soylak, J. Food Compost. Anal. 90, 103482 (2020)
T. Liu, P. Cao, J. Geng, J. Li, M. Wang, M. Wang, X. Li, D. Yin, Food Chem. 142, 358 (2014)
A. Grover, I. Mohiuddin, A.K. Malik, J.S. Aulakh, D. Kukkar, K.H. Kim, Chemosphere 264, 128429 (2021)
S. Büyüktiryaki, R. Keçili, C.M. Hussain, Trends Anal. Chem. 127, 115893 (2020)
M. Rajabi, M. Hemmati, J. Mol. Liq. 324, 114997 (2021)
A. Jouyban, M. Nemati, M.A. Farazajdeh, A. Yazdani, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Microchem. J. 172, 106932 (2022)
E. Zahiri, J. Khandaghi, M.A. Farajzadeh, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, J. Chromatogr. A 1627, 461390 (2020)
A. Mohebbi, M.A. Farajzadeh, S. Yaripour, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Excli J. 17, 952 (2018)
M.A. Farajzadeh, A. Mohebbi, H. Fouladvand, M.R. Afshar Mogaddam, Microchem. J. 155, 104795 (2020)
D. Rajalingam, C. Loftis, J.J. Xu, T.K.S. Kumar, Trichloroacetic acid-induced protein precipitation involves the reversible association of a stable partially structured intermediate. Protein Sci. 18, 980 (2009)
https://www.ich.org/page/multidisciplinary-guidelines. Accessed 29 Nov 2021
Acknowledgements
The financial support of Food and Drug Safety Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Science for the study under Grant No. 66127 is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jouyban, A., Nemati, M., Farajzadeh, M.A. et al. Homogenous dispersive solid phase extraction combined with ionic liquid based-dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of gentamicin and streptomycin from milk prior to HPLC-MS/MS analysis. J IRAN CHEM SOC 19, 4309–4316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02606-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02606-8