Abstract
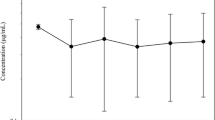
Elimination of erythromycin in milk following intramammary therapy of specific mastitis in cows was studied. Five cows received therapy in one quarter (G1), and eight in two quarters with five milked twice (G2) and three thrice a day (G3). Dose infused was 300 mg/quarter 12 h × 5 times. The drug concentrations in milk were determined using microbial assay technique with Micrococcus luteus as the test organism. Considerable variations occurred in the excretion of drug; levels for treated quarters being 8.25 to 37.61 μg/ml at first milking that declined rapidly at 24 h and no drug activity was observed beyond 36 h post treatment. In total, about 6–25% of the last infused dose appeared in the milk. Drug crossed to 1/15 quarter (G1), 6/10 quarters (G2) and all the six untreated quarters (G3). Crossover levels were significantly higher in mastitic quarters and for G3 cows, but duration of excretion remained same in all cases. It seems that crossover of erythromycin to untreated quarters is related to the udder health and dose infused.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Bovimast from Indo-Biocare Ltd., Vadodara, India.
References
Arret, B., Johnson, D.P. and Kirshbaum, A., 1971. Outline of details of microbiological assay of antibiotics: Second revision. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 60, 1689–1694.
Bajwa, N.S., Bansal, B.K., Dua, K. and Mavi, P.S., 2005. Effect of erythromycin in specific mastitis and quality of milk in cows. Indian Veterinary Journal, 82, 728–730.
Bajwa, N.S., Bansal, B.K., Srivastava, A.K. and Ranjan, R., 2007. Pharmacokinetic profile of erythromycin after intramammary administration in lactating dairy cows with specific mastitis. Veterinary Research Communications, 31, 603–610.
Ballarini, G., 2001. Drug therapy of bovine mastitis and pharmacokinetics. Obiettivi-e-documenti-veterinari, 22, 27–31.
Bansal, B.K., Hamann J., Classens I., Kroemker, V. and Singh, K.B., 2003. Distribution of oxacillin in serum and milk of treated and untreated quarters in cows following intramammary infusion. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, supplement 98, 231.
Cattell, M.B., Dinsmore, R.P., Belschner, A.P., Carmen, J. and Goodell, G., 2001. Environmental gram-positive mastitis treatment: In vitro sensitivity and bacteriologic cure. Journal of Dairy Science, 84, 2036–2043.
Gehring, R. and Smith, G.W., 2006. An overview of factors affecting the disposition of intramammary preparations used to treat bovine mastitis. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 29, 237–241.
Getahun, K., Kelay, B., Bekana, M., and Lobago, F. 2008. Bovine mastitis and antibiotic resistance patterns in Selalle smallholder dairy farms, central Ethiopia. Tropical Animal Health Production, 40, 261–268.
Hamann, J. and Heeschen, W., 1995. Preliminary studies on cephalosporin concentrations in milk after intramammary infusion to lactating cows, in relation to dose, milking frequency and the compound used. Tierärztliche Umschau, 50, 782–874, 787–788.
Hogan, S. J., Gonzalez, R. N., Harmon, R. J., Nickerson, S. C., Oliver, S. P., Pankey, J. W. and Smith, L. K., 1999. Laboratory Handbook on Bovine Mastitis, National Mastitis Council, Inc., WD Hoard, Fort Atkinson, USA.
International Dairy Federation, 1987. Definition and guidelines for diagnosis of bovine mastitis. IDF- Bulletin No. 211, pp 8–16.
Knappstein, K., Suhren, G. and Walte, H.G., 2003. Influence of milking frequency on withdrawal period after application of beta -lactam antibiotic-based drugs. Analytica-Chimica-Acta, 483, 241–249.
Knappstein, K., Suhren, G. and Walte, H. G., 2006. Influence of milking frequencies in automatic milking systems on excretion characteristics of different antibiotics in milk. Kieler Milchwirtschaftliche Forschungsberichte, 57, 215–261.
Malvisi, J., Anfossi, P., Zaghini, A. and Stracciari, G. L., 1991. Oxytetracycline, neomycin and oleandomycin in serum and milk of healthy and mastitic cows after intramammary infusion of a combined preparation. Archivio-Veterinario-Italiano, 42, 36–47.
Milashki, S., Donev, B. and Doneva, M., 1990. Release of lincomycin and gentamicin in milk after intramammary infusion of drug Lincogen in cows with mastitis. Veterinarna Sbirka, 88, 45–46.
Moretain, J.P. and Boisseau, J., 1989. Excretion of penicillins and cephalexin in bovine milk following intramammary administration. Food Additives and Contaminants, 6, 79–90.
Nord, K., 1990. Can frequent milking after local intramammary antibiotic treatment for mastitis be recommended? Norsk Veterinaertidsskrift, 102, 655–660.
Nouws, J.F.M. and Ziv, G., 1979. Distribution and residues of macrolide antibiotics in normal dairy cows. Archive fur Lebensmittelhygience, 30, 202–208.
Radostits, O.M., Gay, C.C., Blood, D.C. and Hinchcliff, K.W., 2000. Veterinary Medicine, 9th Ed., Book Power formerly ELBS printers, London, pp. 603–700.
Romnee, J.M., 1995. Determination of residues after antibiotics therapy. In: Symposium on residues of antimicrobial drugs and other inhibitors in milk. Kiel, Germany, 28–31 August, 1995. pp 102–103.
Rule, R., Quiroga, G., Buschiazzo, H., Lacchini, R. and Mordujovich, P., 1998. Rate of decline of cefotaxime and ceftazidime in milk following intramammary administration to healthy and mastitic dairy cows. Veterinary Record, 143, 310–311.
Shephard, R.W., Malmo, J. and Pfeiffer D.U., 2000. A clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment of lactating cows with high somatic cell counts in their milk. Australian Veterinary Journal, 78, 763-768.
Smith, G.W., Gehring, R., Riviere, J.E., Yeatts, J.L. and Baynes, R.E., 2004. Elimination kinetics of ceftiofur hydrochloride after intramammary administration in lactating dairy cows. Journal of American Veterinary Medical Association, 224, 1827–1830.
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W. G., 1989. Statistical Methods, 9th Ed., Iowa State University Press.
Stockler, R.M., Morin, D.E., Lantz, R.K. and Constable, P.D. 2009. Effect of milking frequency and dosing interval on the pharmacokinetics of cephapirin after intramammary infusion in lactating dairy cows. Journal Dairy Reserach, 92, 4262-4275.
Suhren, G., Knappstein, K. and Walte, H.G., 2005. Influence of milking frequencies on excretion of antibiotics following intramammary administration of a multi-component drug. Milchwissenschaft, 60, 356–358.
Sweeney, R.W., Fennell, M.A., Smith, C.M. and Bardalaye, P.C., 1996. Systemic absorption of gentamicin following intramammary administration to cows with mastitis. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 19, 155–157.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, B.K., Bajwa, N.S., Randhawa, S.S. et al. Elimination of erythromycin in milk after intramammary administration in cows with specific mastitis: relation to dose, milking frequency and udder health. Trop Anim Health Prod 43, 323–329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9692-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9692-1