Abstract
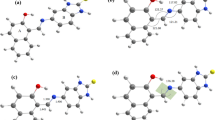
Albumin which is the most abundant drug carrier protein in plasma controls the distribution aspect of drug pharmacokinetics. The aim of this study has been to elucidate the concurrent binding behavior of indomethacin/ibuprofen/heme to HSA under the effect of aspirin-mediated protein acetylation and also to explore the esterase-like catalytic property of the unmodified/modified proteins, as binary or ternary systems, by using various spectroscopic and molecular docking techniques. We found that aspirin-based modification of HSA affects the protein conformation as well as ligand binding at sites I–III. Decrease in pNPA-mediated esterase activity of HSA in different reversible inhibition modes, upon the protein–ligand interactions, was also documented, an issue that may receive considerable attention for computational prodrug design in near future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Khodarahmi, S.A. Karimi, M.R.A. Kooshk, S.A. Ghadami, S. Ghobadi, M. Amani, Comparative spectroscopic studies on drug binding characteristics and protein surface hydrophobicity of native and modified forms of bovine serum albumin: possible relevance to change in protein structure/function upon non-enzymatic glycation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 89, 177–186 (2012)
I. Petitpas, T. Grüne, A.A. Bhattacharya, S. Curry, Crystal structures of human serum albumin complexed with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Mol. Biol. 314, 955–960 (2001)
I. Petitpas, C.E. Petersen, C.-E. Ha, A.A. Bhattacharya, P.A. Zunszain, J. Ghuman, N.V. Bhagavan, S. Curry, Structural basis of albumin–thyroxine interactions and familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100, 6440–6445 (2003)
M. Wardell, Z. Wang, J.X. Ho, J. Robert, F. Ruker, J. Ruble, D.C. Carter, The atomic structure of human methemalbumin at 1.9 Å. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 291, 813–819 (2002)
J. Ghuman, P.A. Zunszain, I. Petitpas, A.A. Bhattacharya, M. Otagiri, S. Curry, Structural basis of the drug-binding specificity of human serum albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 353, 38–52 (2005)
N. Bijari, Y. Shokoohinia, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, S. Ranjbar, S. Parvaneh, M. Moieni-Arya, R. Khodarahmi, Spectroscopic study of interaction between osthole and human serum albumin: identification of possible binding site of the compound. J. Lumin. 143, 328–336 (2013)
N. Moradi, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, S. Ghobadi, M. Shahlaei, R. Khodarahmi, Spectroscopic study of drug-binding characteristics of unmodified and pNPA-based acetylated human serum albumin: does esterase activity affect microenvironment of drug binding sites on the protein? J. Lumin. 160, 351–361 (2015)
J. Zhang, H.-H. Sun, Y.-Z. Zhang, L.-Y. Yang, J. Dai, Y. Liu, Interaction of human serum albumin with indomethacin: spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies. J. Solut. Chem. 41, 422–435 (2012)
S. Ranjbar, Y. Shokoohinia, S. Ghobadi, N. Bijari, S. Gholamzadeh, N. Moradi, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, A. Aghaei, R. Khodarahmi, Studies of the interaction between isoimperatorin and human serum albumin by multispectroscopic method: identification of possible binding site of the compound using esterase activity of the protein. Sci. World J. 2013, 305081 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/305081
G. Zhang, N. Zhao, L. Wang, Fluorescence spectrometric studies on the binding of puerarin to human serum albumin using warfarin, ibuprofen and digitoxin as site markers with the aid of chemometrics. J. Lumin. 131, 2716–2724 (2011)
X.M. He, D.C. Carter, Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 358, 209–215 (1992)
Y. Ozeki, Y. Kurono, T. Yotsuyanagi, K. Ikeda, Effects of drug binding on the esterase activity of human serum albumin: inhibition modes and binding sites of anionic drugs. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 28, 535–540 (1980)
G. Sudlow, D. Birkett, D. Wade, Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 12, 1052–1061 (1976)
F. Ge, C. Chen, D. Liu, B. Han, X. Xiong, S. Zhao, Study on the interaction between theasinesin and human serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Lumin. 130, 168–173 (2010)
Y.-S. Li, Y.-S. Ge, Y. Zhang, A.-Q. Zhang, S.-F. Sun, F.-L. Jiang, Y. Liu, Interaction of coomassie brilliant blue G250 with human serum albumin: probing of the binding mechanism and binding site by spectroscopic and molecular modeling methods. J. Mol. Struct. 968, 24–31 (2010)
S. Nafisi, G.B. Sadeghi, A. PanahYab, Interaction of aspirin and vitamin C with bovine serum albumin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 105, 198–202 (2011)
B. Bojko, A. Sułkowska, M. Maciążek, J. Rownicka, F. Njau, W. Sułkowski, Changes of serum albumin affinity for aspirin induced by fatty acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 42, 314–323 (2008)
J. Hirsh, E.W. Salzman, L. Harker, V. Fuster, J.E. Dalen, J.A. Cairns, R. Collins, Aspirin and other platelet active drugs: relationship among dose, effectiveness, and side effects. CHEST J. 95, 12S–18S (1989)
H. Watanabe, S. Tanase, K. Nakajou, T. Maruyama, U. Kragh-Hansen, M. Otagiri, Role of Arg-410 and Tyr-411 in human serum albumin for ligand binding and esterase-like activity. Biochem. J. 349, 813–819 (2000)
F. Yang, C. Bian, L. Zhu, G. Zhao, Z. Huang, M. Huang, Effect of human serum albumin on drug metabolism: structural evidence of esterase activity of human serum albumin. J. Struct. Biol. 157, 348–355 (2007)
K.M.K. Sand, M. Bern, J. Nilsen, H.T. Noordzij, I. Sandlie, J.T. Andersen, Unraveling the interaction between FcRn and albumin: opportunities for design of albumin-based therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 5, 682 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00682
P. Ascenzi, M. Fasano, Allostery in a monomeric protein: the case of human serum albumin. Biophys. Chem. 148, 16–22 (2010)
O.H. Lowry, N.J. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr, R.J. Randall, Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
H. Svensson, Fractionation of serum with ammonium sulfate and water dialysis, studied by electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 139, 805–825 (1941)
J.H. Bergloef, S. Eriksson, J. Curling, Chromatographic preparation and in vitro properties of albumin from human plasma. J. Appl. Biochem. 5, 282–292 (1982)
R.F. Chen, Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J. Biol. Chem. 242, 173–181 (1967)
M.S. Liyasova, L.M. Schopfer, O. Lockridge, Reaction of human albumin with aspirin in vitro: mass spectrometric identification of acetylated lysines 199, 402, 519, and 545. Biochem. Pharmacol. 79, 784–791 (2010)
G.E. Means, M.L. Bender, Acetylation of human serum albumin by p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry 14, 4989–4994 (1975)
Y. Pocker, J. Stone, The catalytic versatility of erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase. III. Kinetic studies of the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochemistry 6, 668–678 (1967)
S.L. Snyder, P.Z. Sobocinski, An improved 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid method for the determination of amines. Anal. Biochem. 64, 284–288 (1975)
X. Wu, J. Liu, Q. Wang, W. Xue, X. Yao, Y. Zhang, J. Jin, Spectroscopic and molecular modeling evidence of clozapine binding to human serum albumin at subdomain IIA. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 79, 1202–1209 (2011)
R.L. Joseph, R. Lakowicz, Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy (Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 1999)
M. Eftink, C. Ghiron, Exposure of tryptophanyl residues and protein dynamics. Biochemistry 16, 5546–5551 (1977)
X.-Z. Feng, Z. Lin, L.-J. Yang, C. Wang, C.-L. Bai, Investigation of the interaction between acridine orange and bovine serum albumin. Talanta 47, 1223–1229 (1998)
H.-N. Hou, Z.-D. Qi, Y.-W. OuYang, F.-L. Liao, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, Studies on interaction between Vitamin B12 and human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 47, 134–139 (2008)
H.M. Berman, J. Westbrook, Z. Feng, G. Gilliland, T.N. Bhat, H. Weissig, I.N. Shindyalov, P.E. Bourne, The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 235–242 (2000)
D. van der Spoel, E. Lindahl, B. Hess, the GROMACS development team, GROMACS User Manual Version 4.6. 7 (2014)
D.M.F. Van Aalten, R. Bywater, J.B. Findlay, M. Hendlich, R.W. Hooft, G. Vriend, PRODRG: a program for generating molecular topologies and unique molecular descriptors from coordinates of small molecules. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 10, 255–262 (1996)
H.J. Berendsen, J.P. Postma, W.F. van Gunsteren, J. Hermans, Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration, in Intermolecular Forces, ed. by B. Pullman (Springer, Berlin, 1981), pp. 331–342
R. Fletcher, M.J. Powell, A rapidly convergent descent method for minimization. Comput. J. 6, 163–168 (1963)
G. Bussi, D. Donadio, M. Parrinello, Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 126, 014101 (2007)
R. Martoňák, A. Laio, M. Parrinello, Predicting crystal structures: the Parrinello–Rahman method revisited. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 075503 (2003)
B. Hess, H. Bekker, H.J. Berendsen, J.G. Fraaije, LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 18, 1463–1472 (1997)
T. Darden, D. York, L. Pedersen, Particle mesh Ewald: an N· log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 98, 10089–10092 (1993)
H. Grubmüller, H. Heller, A. Windemuth, K. Schulten, Generalized Verlet algorithm for efficient molecular dynamics simulations with long-range interactions. Mol. Simul. 6, 121–142 (1991)
L.-J. Ball, C.M. Goult, J.A. Donarski, J. Micklefield, V. Ramesh, NMR structure determination and calcium binding effects of lipopeptide antibiotic daptomycin. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2, 1872–1878 (2004)
G.M. Morris, R. Huey, W. Lindstrom, M.F. Sanner, R.K. Belew, D.S. Goodsell, A.J. Olson, AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 30, 2785–2791 (2009)
N.A. Kratochwil, W. Huber, F. Müller, M. Kansy, P.R. Gerber, Predicting plasma protein binding of drugs: a new approach. Biochem. Pharmacol. 64, 1355–1374 (2002)
S.K. Chaturvedi, E. Ahmad, J.M. Khan, P. Alam, M. Ishtikhar, R.H. Khan, Elucidating the interaction of limonene with bovine serum albumin: a multi-technique approach. Mol. BioSyst. 11, 307–316 (2015)
N. Zaidi, M.R. Ajmal, G. Rabbani, E. Ahmad, R.H. Khan, A comprehensive insight into binding of hippuric acid to human serum albumin: a study to uncover its impaired elimination through hemodialysis. PloS ONE 8, e71422 (2013)
B.M. Baker, K.P. Murphy, [14] Prediction of binding energetics from structure using empirical parameterization. Methods Enzymol. 295, 294–315 (1998)
P.D. Ross, S. Subramanian, Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 20, 3096–3102 (1981)
Y. Kurono, T. Maki, T. Yotsuyanagi, K. Ikeda, Esterase-like activity of human serum albumin: structure-activity relationships for the reactions with phenyl acetates and p-nitrophenyl esters. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 27, 2781–2786 (1979)
A. Sułkowska, Interaction of drugs with bovine and human serum albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 614, 227–232 (2002)
S. Esmaeili, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, K. Khaledian, H. Adibi, S. Rouhani, R. Khodarahmi, Degradation products of the artificial azo dye, Allura red, inhibit esterase activity of carbonic anhydrase II: A basic in vitro study on the food safety of the colorant in terms of enzyme inhibition. Food Chem. 213, 494–504 (2016)
H. Lineweaver, D. Burk, The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 56, 658–666 (1934)
Y. Wang, H. Yu, X. Shi, Z. Luo, D. Lin, M. Huang, Structural mechanism of ring-opening reaction of glucose by human serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 15980–15987 (2013)
M. Siah, M.H. Farzaei, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, H. Adibi, S.S. Arab, M.R. Rashidi, R. Khodarahmi, Inhibition of guinea pig aldehyde oxidase activity by different flavonoid compounds: an in vitro study. Bioorg. Chem. 64, 74–84 (2016)
H. Rimac, Ž. Debeljak, M. Bojić, L. Miller, Displacement of drugs from human serum albumin: from molecular interactions to clinical significance. Curr. Med. Chem. 24, 1930–1947 (2017)
A. Jangholi, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, S.S. Arab, G. Riazi, F. Mokhtari, M. Poorebrahim, H. Mahdiuni, B.I. Kurganov, A.A. Moosavi-Movahedi, R. Khodarahmi, Appraisal of role of the polyanionic inducer length on amyloid formation by 412-residue 1N4R Tau protein: a comparative study. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 609, 1–19 (2016)
M. Kiselev, I. Gryzunov, G. Dobretsov, M. Komarova, Size of a human serum albumin molecule in solution. Biofizika 46, 423–427 (2001)
M. Shahlaei, B. Rahimi, M.R. Ashrafi-Kooshk, K. Sadrjavadi, R. Khodarahmi, Probing of possible olanzapine binding site on human serum albumin: combination of spectroscopic methods and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Lumin. 158, 91–98 (2015)
U. Kragh-Hansen, V.T.G. Chuang, M. Otagiri, Practical aspects of the ligand-binding and enzymatic properties of human serum albumin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25, 695–704 (2002)
O. Lockridge, W. Xue, A. Gaydess, H. Grigoryan, S.-J. Ding, L.M. Schopfer, S.H. Hinrichs, P. Masson, Pseudo-esterase activity of human albumin slow turnover on tyrosine 411 and stable acetylation of 82 residues including 59 lysines. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 22582–22590 (2008)
O. Phuangsawai, S. Hannongbua, M.P. Gleeson, Elucidating the origin of the esterase activity of human serum albumin using QM/MM calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 118, 11886–11894 (2014)
P. Ascenzi, A. Di Masi, G. Fanali, M. Fasano, Heme-based catalytic properties of human serum albumin. Cell Death Discov. 1, 15025 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Research Council of Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran, for the financial supports (Grant No. 93102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was performed in partial fulfillment of the requirements for M.Sc. degree of M. Almasi, in Department of Clinical Biochemistry and Medical Biology Research Center, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaeili, S., Almasi, M., Vaisi-Raygani, A. et al. Exploring the interaction between “site-markers, aspirin and esterase-like activity” ternary systems on the human serum albumin: direct evidence for modulation of catalytic activity of the protein in different inhibition modes. J IRAN CHEM SOC 15, 555–573 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1256-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-017-1256-0