Abstract
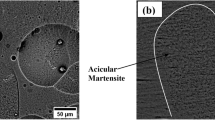
In the present study, Ti-Cu-based alloys were provided by the simultaneous application of both reactive melt infiltration and liquid phase sintering techniques. In order to apply the reactive melt infiltration technique, stearic acid was added at 10, 15, and 20% by weight as the pore forming agent in titanium. Cold-pressed samples were subjected to two different sintering temperatures (1100 and 1200 °C), and melt copper was provided to leak between the titanium particles, natural pores, and the pores forming upon the vaporization of stearic acid. According to the microstructure results, two types of microstructure (eutectoid and hypereutectoid) formed. Eutectoid structure consists of formation of α-Ti + Ti2Cu. The presence of Ti2Cu intermetallic phase caused an increase in hardness. While the increase in the sintering temperature increased transverse rupture strength, the increased amount of copper caused a decrease due to pore formation (natural pores and pores produced). According to the morphology of the surface of fracture, brittle transgranular and partially ductile fractures occurred in the samples. In summary, it was found that 20% Cu amount and 1200 °C were the most suitable in terms of hardness and relative density, while pure titanium had the highest TRS value at 1200 °C.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Kikuchi, Y. Takada, S. Kiyosue, M. Yoda, M. Woldu, Z. Cai, O. Okuno, T. Okabe, Mechanical properties and microstructures of cast Ti-Cu alloys. Dent. Mater. 19, 174–181 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0109-5641(02)00027-1
C. Leyens, M. Peters, Titanium and titanium alloys: fundamentals and applications (John Wiley & Sons, USA, 2003) https://doi.org/10.1002/3527602119
Y.M. Ahmed, K.S.M. Sahari, M. Ishak, B.A. Khidhir, Titanium and its alloy. Int. J. Sci. Res. 3, 1351–1361 (2014)
Y. Alshammari, F. Yang, L. Bolzoni, Yield of binary Ti-Cu and Ti-Mn alloys produced via powder metallurgy. Appl. Mech. Mater. 884, 49–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.884.49
Y. Takada, O. Okuno, Corrosion characteristics of α-Ti and Ti2Cu composing Ti-Cu alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 24, 610–616 (2005). https://doi.org/10.4012/dmj.24.610
X. Yao, Q.Y. Sun, L. Xiao, J. Sun, Effect of Ti2Cu precipitates on mechanical behavior of Ti-2.5 Cu alloy subjected to different heat treatments. J. Alloys Compd. 484, 196–202 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.04.095
S.M. Javadhesari, S. Alipour, M.R. Akbarpour, Biocompatibility, osseointegration, antibacterial and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ti-Cu alloy as a new orthopedic material. Colloids Surf. B Colloid Surf. B. 189, 110889 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110889
Y. Xu, J. Jiang, Z. Yang, Q. Zhao, Y. Chen, Y. Zhao, The effect of copper content on the mechanical and tribological properties of hypo-hyper-and eutectoid Ti-Cu alloys. Materials. 13, 3411 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153411
H. Paul, R. Chulist, M.M. Miszczyk, G. Cios, A. Galka, W. Skuza, P. Petrzak, I. Mania, Interfacial reactions and structural properties of explosively welded titanium/copper plates. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 770, 012033 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/770/1/012033
C.D. Bohórquez, S.P. Pérez, A. Sarmiento, M.E. Mendoza, Effect of temperature on morphology and wear of a Cu-Ti-TiC MMC sintered by abnormal glow discharge. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 026501 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab6e3b
J. Wanga, S. Zhang, Z. Sun, H. Wang, L. Ren, K. Yang, Optimization of mechanical property, antibacterial property and corrosion resistance of Ti-Cu alloy for dental implant. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 2336–2344 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2019.03.044
M. Takahashi, M. Kikuchi, Y. Takada, O. Okuno, Mechanical properties and microstructures of dental cast Ti-Ag and Ti-Cu alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 21, 270–280 (2002). https://doi.org/10.4012/dmj.21.270
C. Ohkubo, I. Shimura, T. Aoki, S. Hanatani, T. Hosoi, M. Hattori, Y. Oda, T. Okabe, Wear resistance of experimental Ti-Cu alloys. Biomaterials. 24, 3377–3381 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00157-1
Q.Y. Sun, Z.T. Yu, R.H. Zhu, Dynamic fracture toughness of Ti-2.5 Cu alloy strengthened with nano-scale particles at room and low temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 483, 131–134 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.11.171
S.H. Huo, M. Qian, G.B. Schaffer, E. Crossin, (2011) Aluminium powder metallurgy. In: Fundamentals of Aluminium Metallurgy, Woodhead Publishing Series in Metals and Surface Engineering, 655-701 (2011), https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857090256.3.655
P.E. de Jongh, T.M. Eggenhuisen, Melt infiltration: an emerging technique for the preparation of novel functional nanostructured materials. Adv. Mater. 25(46), 6672–6690 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201301912
R. Dong, W. Zhu, C. Zhao, Y. Zhang, F. Ren, Microstructure, mechanical properties, and sliding wear behavior of spark plasma sintered Ti-Cu alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 49, 6147–6160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4953-0
O. Taguchi, Y. Iijima, Diffusion of copper, silver and gold in α-titanium. Philos. Mag. A. 72, 1649–1655 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1080/01418619508243935
C.B. Yi, Z.Y. Ke, L. Zhang, J. Tan, Y.H. Jiang, Z. He, Antibacterial Ti-Cu alloy with enhanced mechanical properties as implant applications. Mater. Res. Express. 7, 105404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abc371
A.M.M. Gariba, S. Islak, H.R.H. Hraam, M. Akkaş, Microstructural and mechanical properties of Ti-B4C/CNF functionally graded materials. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 11, 736–745 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-022-00900-8
T. Luangvaranunt, P. Pripanapong, Pin-on-disc wear of precipitation hardened titanium–copper alloys fabricated by powder metallurgy. Mater. Trans. 53, 518–523 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M2011293
S. Islak, Ö. Küçük, Ö. Eski, C. Özorak, M. Akkaş, The effect of CNT content and sintering temperature on some properties of CNT-reinforced MgAl composites. Sci. Sint. 49, 347–357 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2298/SOS1704347I
Y. Alshammari, F. Yang, L. Bolzoni, Low-cost powder metallurgy Ti-Cu alloys as a potential antibacterial material. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 95, 232–239 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.04.004
K.H. Min, S.P. Kang, D.G. Kim, Y. Do Kim, Sintering characteristic of Al2O3-reinforced 2xxx series Al composite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 400, 150–153 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.03.070
H.R.H. Hraam, Investigation of the microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium-based-material produced by powder metallurgy technique (Institute of Science Kastamonu University, Turkey, 2021)
L. Bolzoni, F. Yang, M. Paul, Development and characterisation of low-cost powder metallurgy Ti-Cu-Fe alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 24, 2678–2687 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.03.178
K.N. Campo, C.C.D. Freitas, É.S.N. Lopes, S.C. Moon, R. Dippenaar, R. Caram, Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti-Cu alloys produced by semisolid processing. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 32(11), 3578–3586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(22)66040-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hraam, H.R.H., Islak, S. & Gariba, A.M.M. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Cu-Based Materials Produced by Using Reactive Melt Infiltration and Liquid Phase Sintering Techniques. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 12, 662–671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-023-00978-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-023-00978-8