Abstract
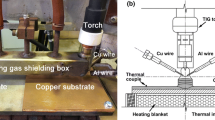
In this work, Cu-6.5% Al alloy was deposited by wire arc additive manufacturing based on cold metal transfer (CMT) welding process, through separate feeding of pure Cu and Al wires into a molten pool, onto a 3-mm pure copper plate. The deposited alloy was homogenized by heat treatment at 800 °C (2 h) and evaluated for their microstructure using optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy, and mechanical properties. The paper discusses the structure-mechanical property correlation under both as-fabricated and heat-treated condition. Results reveal that (1) the CMT welding process is efficient in making Cu-Al alloy with target chemical composition, (2) heat treatment improved solid solution strengthening effect, which improved the hardness, and (3) heat treatment improved tensile strength properties and ductility of the alloy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.X. Ren, Q. Wang, J.P. Hou, Z.J. Zhang, H.J. Yang, Z.F. Zhang, Exploring the strength and ductility improvement of Cu-Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 786, 139441 (2020)
Z. Li, K.G. Pradeep, Y. Deng, D. Raabe, C.C. Tasan, Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature. 534(7606), 227 (2016)
G. Liu, G.J. Zhang, F. Jiang, X.D. Ding, Y.J. Sun, J. Sun, E. Ma, Nanostructured high-strength molybdenum alloys with unprecedented tensile ductility. Nat. Mater. 12(4), 344 (2013)
D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, L.V. Louzguina-Luzgina, H. Kato, A. Inoue, Investigation of Ti-Fe-Co bulk alloys with high strength and enhanced ductility. Acta Mater. 53(7), 2009 (2005)
R. Liu, Y.Z. Tian, Z.J. Zhang, P. Zhang, X.H. An, Z.F. Zhang, Exploring the fatigue strength improvement of Cu-Al alloys. Acta Mater. 144, 613 (2018)
N. Tsuji, Y. Ito, Y. Saito, Y. Minamino, Strength and ductility of ultrafine grained aluminum and iron produced by ARB and annealing. Scripta Mater. 47(12), 893 (2002)
H.B. Ma, K.X. Ren, R.F. Qiu, H.X. Shi, Growth behavior of intermetallic compounds at Cu/Al solid state interface. Cailiao Rechuli Xuebao Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 40(7), 60 (2019)
B. Dong, Z. Pan, C. Shen, Y. Ma, H. Li, Fabrication of copper-rich Cu-Al alloy using the wire-arc additive manufacturing process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 48(6), 3143 (2017)
Y. Wang, X. Chen, S. Konovalov, C. Su, A.N. Siddiquee, N. Gangil, In-situ wire-feed additive manufacturing of Cu-Al alloy by addition of silicon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 487, 1366–1375 (2019)
R. Uscinowicz, Impact of temperature on shear strength of single lap Al-Cu bimetallic joint. Compos. B Eng. 44(1), 344 (2013)
L. M. Dimaté Castellanos: Resistencia a La Corrosión En Recubrimientos Comerciales Metaceram 25050 y Proxon 21071 Producidos Con El Sistema de Proyección Térmica Por Llama, 2011
T. Gustmann, A. Neves, U. Kühn, P. Gargarella, C.S. Kiminami, C. Bolfarini, J. Eckert, S. Pauly, Influence of processing parameters on the fabrication of a Cu-Al-Ni-Mn shape-memory alloy by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 11, 23 (2016)
K.R.W. Xuesong Gao, G.A. Faria, W. Zhang, Numerical analysis of non-spherical particle effect on molten pool dynamics in laser-powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Comput. Mater. Sci. 179(15), 109648 (2020)
B. Cong, J. Ding, S. Williams, Effect of arc mode in cold metal transfer process on porosity of additively manufactured Al-6.3%Cu alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 76(9–12), 1593 (2015)
Y. Wang, S. Konovalov, X. Chen, Y. Ivanov, S. Jayalakshmi, R.A. Singh, Research on Cu-6.6%Al-3.2%Si alloy by dual wire arc additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Eng. Perfor. 30(3), 1694 (2021)
K. Liu, X. Chen, Q. Shen, Z. Pan, R.A. Singh, S. Jayalakshmi, S. Konovalov, Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of deep cryogenic treated Cu-Al-Si alloy fabricated by cold metal transfer (CMT) process. Mater. Charact. 159, 110011 (2020)
X.H. An, S. Qu, S.D. Wu, Z.F. Zhang, Effects of stacking fault energy on the thermal stability and mechanical properties of nanostructured Cu-Al alloys during thermal annealing. J. Mater. Res. 26(3), 407 (2011)
D. Wu, W. Lin Wang, L. Gang Zhang, Z. Yu Wang, K. Chao Zhou, L. Bin Liu, New high-strength Ti-Al-V-Mo alloy: from high-throughput composition design to mechanical properties. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 26, 1151 (2019)
C. Shen, Z. Pan, D. Cuiuri, B. Dong, H. Li, In-depth study of the mechanical properties for Fe3Al based iron aluminide fabricated using the wire-arc additive manufacturing process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 669, 118 (2016)
J. Hu, Y.N. Shi, X. Sauvage, G. Sha, K. Lu, Grain boundary stability governs hardening and softening in extremely fine nanograined metals. Science. 355(6331), 1292 (2017)
J. Tao, G. Chen, W. Jian, J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X. Zhu, T.G. Langdon, Materials science and engineering a anneal hardening of a nanostructured Cu-Al alloy processed by high-pressure torsion and rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 628, 207 (2015)
Y. Wang, S. Konovalov, X. Chen, V.B. Deev, E.S. Prusov, Deformation behavior of Cu-6.5 wt% Al alloy under quasi-static tensile loading. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30(8), 1–7 (2021)
T.S. Srivatsan, A review of fractography: observing, measuring, and interpreting fracture surface topography, D. Hull. Mater. Manuf. Process. 24, 10–11 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grant No. 51975419 and Foreign Experts Bureau Project of China under Grant Nos. QN20200116001 and G20200116018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Su, C. & Konovalov, S. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cu-6.5%Al Alloy Deposited by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 10, 634–641 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-021-00781-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-021-00781-3