Abstract
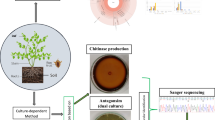
Chlorella is an autotrophic and eukaryotic microorganism that photosynthesizes using chlorophyll. In the last few decades, green algae (Chlorophyceae) have been evaluated as highly effective biofertilizers in agriculture. Representatively Chlorella vulagris, C. pyrenoidosa, and Scenedesmus obliquus were developed as eco-friendly and effective biofertilizers for many crops. Recently, C. fusca strain CHK0059 has been reported to greatly improve the productivity of various crops, but the mode of action of C. fusca CHK0059 as a biofertilizer and biocontrol agent has remained unveiled. The purpose of this study was to evaluate how the strawberry’s phenotype was altered and unveil microbiota community shifting by the C. fusca CHK0059 treatment using 16 S rRNA sequencing and metagenomic analyses. Total chlorophyll contents per leaf area were 4.38 µg/cm² in the control and 6.47 µg/cm² in the C. fusca CHK0059 treated group, the rate was 47.71% higher than in untreated strawberries. Microbiota communities in the crown endosphere, and root endosphere were not significantly affected by C. fusca CHK0059 treatment. However, the strawberry rhizosphere microbiota community responded, and microbiota metabolic pathways were also alerted by C. fusca CHK0059. These results provide a new approach to the value and mechanism of microalgae in organic farming.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed in this study are present in the manuscript and available in the public database.
References
Adam M (1999) The promotive effect of the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum on the growth of some crop plants. Acta Microbiol Pol 48:163–171
Adeleke BS, Babalola OO (2021) Biotechnology overview of agriculturally important endophytic fungi. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 62:507–520
Andersen RA (2005) Algal culturing techniques. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, C.A., USA, pp 239–287
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Becker EW (1994) Microalgae: biotechnology and microbiology. Cambridge studies in Biotechnology
Cho G, Jo GS, Lee Y, Kwak Y (2022) Effect of Scenedesmus sp. CHK0059 on strawberry microbiota community. J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:862–868
Elhafiz A, GaurA, Hamdany N, Osman M, Lakshmi TVR (2015) Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella pyrenoidosa live cells appear to be promising sustainable biofertilizer to grow rice, lettuce, cucumber and eggplant in the UAE soils. Rece Res Sci Technol 7:14–21. https://doi.org/10.19071/rrst.2015.v7.2919
Han S, Kim M, Lee J, Ban H, Seung J, Kim T (2010) Agricultural outlook 2010 (I). Korea Rural Economic Institute (KREI) Seoul, Korea
Ibrahim I, Elbaily Z (2020) A review: importance of chlorella and different applications. Alex J Vet Sci 65:16–34. https://doi.org/10.5455/ajvs.94847
Jeong HW, Kim HM, Lee HR, Kim HM, Hwang SJ (2020) Growth of Astragalus membranaceus during nursery period as affected by different plug tray cell size, number of seeds per cell, irrigation interval, and EC level of nutrient solution. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 38:210–217
Kim MJ, Shim CK, Ko BG, Kim J (2014) Effect of Chlorella vulgaris CHK0008 fertilization on enhancement of storage and freshness in organic strawberry and leaf vegetables. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 32:872–878. https://doi.org/10.7235/hort.2014.14107
Kim MJ, Shim CK, Kim YK, Hong SJ, Park JH, Han EJ, Jee HJ, Lee SB, Kim SC (2015) Effect of Chlorella sp. on improving antioxidant activities and growth promotion in organic soybean sprout cultivation. Korean J Org Agric 23:939–950. https://doi.org/10.11625/KJOA.2015.23.4.939
Kim MJ, Shim CK, Kim YK, Hong SJ, Park JH, Han EJ, Kim SC et al (2016) Effect of fresh chlorella powder on improving qualities and storage condition of organic soybean tofu. Korean J Food Preserv 23:832–838. https://doi.org/10.11002/kjfp.2016.23.6.832
Kim SJ, Ko EJ, Hong JK, Jeun YC (2018) Ultrastructures of Colletotrichum orbiculare in cucumber leaves expressing systemic acquired resistance mediated by Chlorella fusca. Plant Pathol J 34:113–120. https://doi.org/10.5423/PPJ.OA.09.2017.0204
Kim MJ, Shim CK, Ko BG, Kim J (2020) Effect of the microalga Chlorella fusca CHK0059 on strawberry PGPR and biological control of Fusarium wilt disease in non-pesticide hydroponic strawberry cultivation. J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:708–716. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.2001.01015
Lee SM, Ryu CM (2021) Algae as new kids in the beneficial plant microbiome. Front Plant Sci 12:91. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.599742
Lee YJ, Ko YJ, Jeun YC (2016) Illustration of disease suppression of anthracnose on cucumber leaves by treatment with Chlorella fusca. Res Plant Dis 22:257–263. https://doi.org/10.5423/RPD.2016.22.4.257
Lee YJ, Kim SJ, Jeun YC (2017) Ultra-structural observations of Colletotrichum orbiculare on cucumber leaves pre-treated with Chlorella fusca. Res Plant Dis 23:42–48. https://doi.org/10.5423/RPD.2017.23.1.42
Lee SM, Kim SK, Lee N, Ahn CY, Ryu CM (2020a) D-Lactic acid secreted by Chlorella fusca primes pattern‐triggered immunity against Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis. Plant J 102:761–778. 10.1111/tpj.14661
Lee SM, Lee B, Shim CK, Chang YK, Ryu CM (2020b) Plant anti-aging: Delayed flower and leaf senescence in Erinus alpinus treated with cell-free Chlorella cultivation medium. Plant Signal Behav 15:1763005. 10.1080/15592324.2020b.1763005
Liu J, Chen F (2016) Biology and industrial applications of Chlorella: advances and prospects. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 153:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2014_286
Lundberg DS, Yourstone S, Mieczkowski P, Jones CD, Dangl JL (2013) Practical innovations for high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2634
Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (2015) Agriculture, food and rural affairs statistics yearbook, Sejong, Korea
Park JE, Hwang S (2010) Effect of precooling and storage temperatures on the post-harvest management of the fruits in ‘Maehyang’ and ‘Soogyeong’ strawberries for export. J Bio-Environ Cont 19:366–371
Parker MS, Mock T, Armbrust EV (2008) Genomic insights into marine microalgae. Annu Rev Genet 42:619–645. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091417
Sanmukh S, Bruno B, Ramakrishnan U, Khairnar K, Swaminathan S (2014) Bioactive compounds derived from microalgae showing antimicrobial activities. J Aquac Res Devel 5:2–24. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9546.1000224
Seo HS, Kim CH (2016) Agricultural outlook modeling 2016. Korea Rural Economic Institute (KREI) Seoul, Korea
Stirk WA, Balint P, Tarkowska D, Novak O, Maroti G, Ljung K, Tureckova V, Strnad M, Ordog V, van Staden J (2014) Effect of light on growth and endogenous hormones in Chlorella minutissima (Trebouxiophyceae). Plant Physiol Biochem 79:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.03.005
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Rural Development Administration (PJ015641).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL, GC, and GSJ performed field experiments and data analyses. YL and GC prepared the figures and tables. GC and YK designed the experiment and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Seon-In Yeom.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y., Cho, G., Jo, G.S. et al. Effect of microalgae Chlorella fusca CHK0059 on the microbiota community in nursery strawberry. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 64, 547–556 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00490-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-022-00490-y