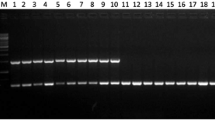
Abstract
Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) is a plant pathogen of cruciferous crops that causes black rot disease throughout the world. At present, based on the host–pathogen interactions among differential cultivars of Brassica crops, 11 pathogenic Xcc races have been identified, but the race identification method based on host–pathogen interactions is time-consuming. However, early and rapid detection of the pathogen could reduce economic loss by allowing appropriate control measures against black rot disease to be taken more quickly. In this study, a PCR-based molecular marker has been developed for identifying the Xcc race 1 and Xcc race 2 bacterial strains together. The specificity of the marker was tested by PCR using 8 available Xcc races, X. campestris strains, and other bacteria. Upon amplification, a polymorphic band was observed in the PCR amplicon with a size of 1523 bp and 929 bp in Xcc races 1 and 2, respectively. A deletion of 594 bp conferred the specificity in Xcc race 2 compared to race 1. The identified PCR-based molecular marker clearly discriminated the Xcc race 1 and race 2 from other races when tested in artificially infected cabbage leaves. Thus, PCR-based development of an Xcc race 1- and 2-specific marker could be a valuable tool for the accurate detection of Xcc race 1 and 2 together for implementing control measures more quickly.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afrin KS, Rahim MA, Rubel MH, Natarajan S, Song J-Y, Kim H-T, Park J-I, Nou I-S (2018) Development of race-specific molecular marker for Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris race 3, the causal agent of black rot of crucifers. Can J Plant Sci 98:1119–1125
Alberto L (2015) Evaluation of resistance on cabbage varieties resistance against Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Mozambique. Int J Agric Crop Sci 8:723–731
Ballard E, Dietzgen R, Sly L, Gouk C, Horlock C, Fegan M (2011) Development of a Bio-PCR protocol for the detection of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni. Plant Dis 95:1109–1115
Berg T, Tesoriero L, Hailstones D (2005) PCR-based detection of Xanthomonas campestris pathovars in Brassica seed. Plant Pathol 54:416–427
Chen J-H, Hsieh Y-Y, Hsiau S-L, Lo T-C, Shau C-C (1999) Characterization of insertions of IS476and two newly identified insertion sequences, IS1478 and IS1479, in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. J Bacteriol 181:1220–1228
Cruz J, Tenreiro R, Cruz L (2017) Assessment of diversity of Xanthomonas campestris pathovars affecting cruciferous plants in Portugal and disclosure of two novel X. campestris pv. campestris races. J Plant Pathol 99:403–414
Darling AE, Miklós I, Ragan MA (2008) Dynamics of genome rearrangement in bacterial populations. PLoS Genet 4:e1000128
Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT (2010) progressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 5:e11147
FAOSTAT (2017) http://www.fao.org/home/en/. Accessed 18 Jan 2019
Fargier E, Manceau C (2007) Pathogenicity assays restrict the species Xanthomonas campestris into three pathovars and reveal nine races within X. campestris pv. campestris. Plant Pathol 56:805–818
Kałużna M, Pulawska J, Waleron M, Sobiczewski P (2014) The genetic characterization of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis, the causal agent of walnut blight in Poland. Plant Pathol 63:1404–1416
Kamoun S, Kamdar HV, Tola E, Kado CI (1992) A vascular hypersensitive response: role of the hrpK locus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 5:22–33
Kim BS (1986) Testing for detection of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in crucifer seeds and seed disinfection. Korean J Plant Pathol 2:96–101
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. Transl Res 44:301–307
Liu W, Li L, Khan MA, Zhu F (2012) Popular molecular markers in bacteria. Mol Genet Microbiol Virol 27:103–107
Martinelli F, Scalenghe R, Davino S, Panno S, Scuderi G, Ruisi P, Villa P, Stroppiana D, Boschetti M, Goulart LR (2015) Advanced methods of plant disease detection. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 35:1–25
Raeside C, Gaffé J, Deatherage DE, Tenaillon O, Briska AM, Ptashkin RN, Cruveiller S, Médigue C, Lenski RE, Barrick JE (2014) Large chromosomal rearrangements during a long-term evolution experiment with Escherichia coli. MBio 5:e01377-01314
Rubel MH, Robin AHK, Natarajan S, Vicente JG, Kim H-T, Park J-I, Nou I-S (2017) Whole-genome re-alignment facilitates development of specific molecular markers for races 1 and 4 of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, the cause of black rot disease in Brassica oleracea. Int J Mol Sci 18:2523
Schaad NW, Cheong S, Tamaki S, Hatziloukas E, Panopoulos NJ (1995) A combined biological and enzymatic amplification (BIO-PCR) technique to detect Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola in bean seed extracts. Phytopathology 85:243–246
Shitikov EA, Bespyatykh JA, Ischenko DS, Alexeev DG, Karpova IY, Kostryukova ES, Isaeva YD, Nosova EY, Mokrousov IV, Vyazovaya AA (2014) Unusual large-scale chromosomal rearrangements in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing B0/W148 cluster isolates. PLoS ONE 9:e84971
Singh D, Raghavendra B, Rathaur PS, Singh H, Raghuwanshi R, Singh R (2014) Detection of black rot disease causing pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris by bio-PCR from seeds and plant parts of cole crops. Seed Sci Technol 42:36–46
Singh D, Rathaur P, Vicente J (2016) Characterization, genetic diversity and distribution of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races causing black rot disease in cruciferous crops of India. Plant Pathol 65:1411–1418
Song E-S, Kim S-Y, Noh T-H, Cho H, Chae S-C, Lee B-M (2014) PCR-based assay for rapid and specific detection of the new Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae K3a race using an AFLP-derived marker. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:732–739
Vicente JG, Holub EB (2013) Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (cause of black rot of crucifers) in the genomic era is still a worldwide threat to brassica crops. Mol Plant Pathol 14:2–18
Vicente JG, Conway J, Roberts S, Taylor J (2001) Identification and origin of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races and related pathovars. Phytopathology 91:492–499
Zhu L, Wang Q, Tang P, Araki H, Tian D (2009) Genomewide association between insertions/deletions and the nucleotide diversity in bacteria. Mol Biol Evol 26:2353–2361
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Center for Horticultural Seed Development (Golden Seed Project No. 213007-05-3-SB510) of the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs in the Republic of Korea (MAFRA). We thank Dr Joana G. Vicente, University of Warwick, United Kingdom for providing Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races (1–7), Xci and Xcr isolates. Authors also thank to Dr. Pilar Soengas for giving Xcc race 8 strain. We thank the Korean Agriculture Culture Collection (KACC), Korea and the ICMP collection from New Zealand for providing isolates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Sung-Chur Sim.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubel, M.H., Natarajan, S., Nath, U.K. et al. Development of a marker for detection of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris races 1 and 2 in Brassica oleracea. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 60, 511–517 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00143-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00143-7