Abstract
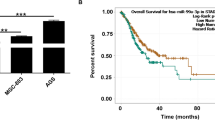
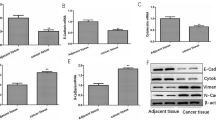
Recently, the dysregulation of circRNAs has been increasingly implicated in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Among these circRNAs, circMAN1A2 has been highlighted for the up-regulated expression in NPC, whereas the underlying mechanisms have not been clearly established. Thus, the aim of this study was to delineate the tumor-supporting role of circMAN1A2 in the oncogenesis and metastases of NPC. We validated through qRT-PCR that circMAN1A2 was highly expressed in NPC tissues and NPC cells. Survival analysis through Kaplan–Meier method showed that the overall survival, disease-free survival, and distant metastasis-free survival of patients was negatively correlated with the expression of circMAN1A2. Then, gain- and loss-of function assays demonstrated that circMAN1A2 knockdown could impede the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT in NPC cells. Further, we conducted dual luciferase reporter gene, RIP, and RNA pull down assays, unveiling that circMAN1A2 functioned as a sponge of miR-135a-3p, and miR-135a-3p targeted UBR5. Additionally, UBR5 interacted with ATMIN to foster the ubiquitination of ATMIN, thereby expediting the malignant behaviors of NPC cells as well as the lung and inguinal lymph node metastases of NPC tumors in vivo. Together, our study uncovered the tumor-initiating and pro-metastatic role of circMAN1A2-miR-135a-3p-UBR5-ATMIN axis in NPC regulation that may be a potential therapeutic target for human NPC.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Bruce JP, Yip K, Bratman SV, Ito E, Liu FF. Nasopharyngeal cancer: molecular landscape. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(29):3346–55.
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2019;394(10192):64–80.
Liu Y, He S, Wang XL, Peng W, Chen QY, Chi DM, et al. Tumour heterogeneity and intercellular networks of nasopharyngeal carcinoma at single cell resolution. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):741.
Bruce JP, To KF, Lui VWY, Chung GTY, Chan YY, Tsang CM, et al. Whole-genome profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals viral-host co-operation in inflammatory NF-kappaB activation and immune escape. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4193.
Yang J, Zhu D, Liu S, Shao M, Liu Y, Li A, et al. Curcumin enhances radiosensitization of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating circRNA network. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59(2):202–14.
Lin X, Wang S, Lin K, Zong J, Zheng Q, Su Y, et al. Competitive endogenous RNA landscape in Epstein-Barr virus associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 782473.
Tao M, Zheng M, Xu Y, Ma S, Zhang W, Ju S. CircRNAs and their regulatory roles in cancers. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):94.
Cao YZ, Sun JY, Chen YX, Wen CC, Wei L. The roles of circRNAs in cancers: perspectives from molecular functions. Gene. 2021;767: 145182.
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T, et al. CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):90.
Fan CM, Wang JP, Tang YY, Zhao J, He SY, Xiong F, et al. circMAN1A2 could serve as a novel serum biomarker for malignant tumors. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(7):2180–8.
Wu H, Liu Y, Duan H, Fan X, Wang Y, Song J, et al. Identification of differentially expressed circular RNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2020;29(4):483–92.
Zhu D, Shao M, Yang J, Fang M, Liu S, Lou D, et al. Curcumin enhances radiosensitization of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via mediating regulation of tumor stem-like cells by a CircRNA network. J Cancer. 2020;11(8):2360–70.
Lei F, Lei T, Huang Y, Yang M, Liao M, Huang W. Radio-susceptibility of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: focus on Epstein-Barr Virus, MicroRNAs, long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2020;13(3):192–205.
Duan S, Dong X, Hai J, Jiang J, Wang W, Yang J, et al. MicroRNA-135a-3p is downregulated and serves as a tumour suppressor in ovarian cancer by targeting CCR2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:712–20.
Zhou H, Guo W, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zha R, Ding J, et al. MicroRNA-135a acts as a putative tumor suppressor by directly targeting very low density lipoprotein receptor in human gallbladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(8):956–65.
Zhao X, Sun Z, Li H, Jiang F, Zhou J, Zhang L. MiR-135a-5p modulates biological functions of thyroid carcinoma cells via targeting VCAN 3′-UTR. Cancer Biomark. 2017;20(2):207–16.
Wang LX, Kang ZP, Yang ZC, Ma RX, Tan Y, Peng XB, et al. MicroRNA-135a inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation through targeting interleukin-17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(6):2232–8.
Zhang K, Zhang X, Cai Z, Zhou J, Cao R, Zhao Y, et al. A novel class of microRNA-recognition elements that function only within open reading frames. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018;25(11):1019–27.
Chung GT, Lung RW, Hui AB, Yip KY, Woo JK, Chow C, et al. Identification of a recurrent transforming UBR5-ZNF423 fusion gene in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pathol. 2013;231(2):158–67.
Krishnan A, Berthelet J, Renaud E, Rosigkeit S, Distler U, Stawiski E, et al. Proteogenomics analysis unveils a TFG-RET gene fusion and druggable targets in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2056.
Beltran AP, Benitez E, Rondon M, Ariza YV, Aristizabal FA, Briceno I. Association of DEAR1 tagging single nucleotide polymorphisms with breast cancer in a sample of Colombian population: a case control study. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2020;14:1178223420904939.
Wang M, Liu G, Shan GP, Wang BB. In vivo and in vitro effects of ATM/ATR signaling pathway on proliferation, apoptosis, and radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017;32(6):193–203.
Zhang T, Cronshaw J, Kanu N, Snijders AP, Behrens A. UBR5-mediated ubiquitination of ATMIN is required for ionizing radiation-induced ATM signaling and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(33):12091–6.
Chan SY, Choy KW, Tsao SW, Tao Q, Tang T, Chung GT, et al. Authentication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumor lines. Int J Cancer. 2008;122(9):2169–71.
Zhang H, Tsao SW, Jin C, Strombeck B, Yuen PW, Kwong YL, et al. Sequential cytogenetic and molecular cytogenetic characterization of an SV40T-immortalized nasopharyngeal cell line transformed by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 gene. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2004;150(2):144–52.
Huang DP, Ho JH, Poon YF, Chew EC, Saw D, Lui M, et al. Establishment of a cell line (NPC/HK1) from a differentiated squamous carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Int J Cancer. 1980;26(2):127–32.
Cheung ST, Huang DP, Hui AB, Lo KW, Ko CW, Tsang YS, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666–1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int J Cancer. 1999;83(1):121–6.
Zhan Y, Chen Z, Li Y, He A, He S, Gong Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA DANCR promotes malignant phenotypes of bladder cancer cells by modulating the miR-149/MSI2 axis as a ceRNA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):273.
Hua Q, Jin M, Mi B, Xu F, Li T, Zhao L, et al. LINC01123, a c-Myc-activated long non-coding RNA, promotes proliferation and aerobic glycolysis of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-199a-5p/c-Myc axis. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):91.
Yang R, Xing L, Zheng X, Sun Y, Wang X, Chen J. The circRNA circAGFG1 acts as a sponge of miR-195-5p to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression through regulating CCNE1 expression. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):4.
Li M, Li Y, Yu M. CircRNA ZNF609 Knockdown suppresses cell growth via modulating miR-188/ELF2 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:2399–409.
Liu R, Zhou M, Zhang P, Zhao Y, Zhang Y. Cell proliferation and invasion is promoted by circSERPINA3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating miR-944/MDM2 axis. J Cancer. 2020;11(13):3910–8.
Wei H, Liu D, Sun J, Mao Y, Zhao L, Zhu W, et al. Circular RNA circ_0008450 upregulates CXCL9 expression by targeting miR-577 to regulate cell proliferation and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;110: 104288.
Zhao ZJ, Shen J. Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol. 2017;14(5):514–21.
Wang M, Ji YQ, Song ZB, Ma XX, Zou YY, Li XS. Knockdown of lncRNA ZFAS1 inhibits progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by sponging miR-135a. Neoplasma. 2019;66(6):939–45.
Wang H, Zhou Y, Oyang L, Han Y, Xia L, Lin J, et al. LPLUNC1 stabilises PHB1 by counteracting TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination to inhibit NF-kappaB activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 2019;38(25):5062–75.
Kanu N, Behrens A. ATMINistrating ATM signalling: regulation of ATM by ATMIN. Cell Cycle. 2008;7(22):3483–6.
Shen M, Xu Z, Xu W, Jiang K, Zhang F, Ding Q, et al. Inhibition of ATM reverses EMT and decreases metastatic potential of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells through JAK/STAT3/PD-L1 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):149.
Pearson SJ, Roy Sarkar T, McQueen CM, Elswood J, Schmitt EE, Wall SW, et al. ATM-dependent activation of SIM2s regulates homologous recombination and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 2019;38(14):2611–26.
Funding
This study was supported by 2019 Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Plan Joint Construction Project (No. LHGJ20190058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DKY conceived and designed research. QQD performed experiments. JW interpreted results of experiments. JYZ analyzed data. SNZ prepared figures. YJZ drafted paper. DKY and PHL edited and revised manuscript. All authors read and approved final version of manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Approval number: 2016-KY-142). All patients or legal guardians provided written informed consents. Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (Approval number: KY-2021-0728) and performed in accordance with Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, QQ., Li, PH., Wang, J. et al. CircMAN1A2 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via enhancing the ubiquitination of ATMIN through miR-135a-3p/UBR5 axis. Human Cell 36, 657–675 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00831-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00831-0