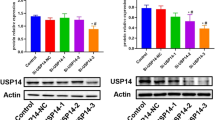
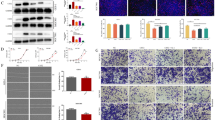
Abstract
Resistance to chemotherapy drugs is a major factor affecting the surgical outcome and prognosis of osteosarcoma patients. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play an important role in tumor resistance to chemotherapy. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of circRNA circ-chitinase 3-like 1.2 (CHI3L1.2) in resistance to cisplatin chemotherapy in osteosarcoma. We found that circ-CHI3L1.2 levels were higher in cisplatin-resistant cells than in their parent cells. circ-CHI3L1.2 knockdown decreased the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of cisplatin and the expression levels of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multidrug-resistance protein 1 (MRP1), and glutathione-S-transferase Pi1 (GSTP1), and promoted apoptosis of cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma cells. In addition, circ-CHI3L1.2 knockdown induced mesenchymal to epithelial transition (MET) and suppressed cell migration and invasion. The competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism indicated that circ-CHI3L1.2 targets the micro-RNA (miR)-340-5p-lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase β (LPAATβ) axis, and inhibition of miR-340-5p alleviates the effect of circ-CHI3L1.2 knockdown. In conclusion, circ-CHI3L1.2 levels were increased in cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma cells and circ-CHI3L1.2 knockdown sensitized cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma cells to cisplatin through the miR-340-5p-LPAATβ axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNA
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
- ceRNA:
-
Competitive endogenous RNA
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- miR-NC:
-
Negative control miRNA
- CCK8:
-
Cell counting Kit-8
- IC50:
-
Inhibitory concentration 50
- GSTs:
-
Glutathione S-transferases
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7–30.
Robl B, Pauli C, Botter SM, Bode-Lesniewska B, Fuchs B. Prognostic value of tumor suppressors in osteosarcoma before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:379. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1397-4.
Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, Lewis VO, Gorlick R. Current and future therapeutic approaches for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018;18(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737140.2018.1413939.
Sakamoto A, Iwamoto Y. Current status and perspectives regarding the treatment of osteo-sarcoma: chemotherapy. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2008;3(3):228–31.
Geng H, Brennan S, Milne TA, Chen WY, Li Y, Hurtz C, et al. Integrative epigenomic analysis identifies biomarkers and therapeutic targets in adult B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(11):1004–23.
Lindner K, Eichelmann AK, Matuszcak C, Hussey DJ, Haier J, Hummel R. Complex Epigenetic Regulation of Chemotherapy Resistance and Biohlogy in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma via MicroRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):499.
Segal-Bendirdjian E, Jacquemin-Sablon A. Cisplatin resistance in a murine leukemia cell line associated with defect of apoptosis. Bull Cancer. 1996;83(5):371–8.
Suzuki H, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E, Niinuma T, Kai M. Relationship between noncoding RNA dysregulation and epigenetic mechanisms in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;927:109–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-1498-7_4.
Xin Z, Ma Q, Ren S, Wang G, Li F. The understanding of circular RNAs as special triggers in carcinogenesis. Brief Funct Genomics. 2017;16(2):80–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elw001.
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M, Glavač D. Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer biomarkers. Int J Genom. 2017;2017:6218353. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6218353.
Ji W, Qiu C, Wang M, Mao N, Wu S, Dai Y. Hsa_circ_0001649: a circular RNA and potential novel biomarker for colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(1):122–6.
Zhang S, Zeng X, Ding T, Guo L, Li Y, Ou S, et al. Microarray profile of circular RNAs identifies hsa_circ_0014130 as a new circular RNA biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2878. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21300-5.
Gao D, Zhang X, Liu B, Meng D, Fang K, Guo Z, et al. Screening circular RNA related to chemotherapeutic resistance in breast cancer. Epigenomics. 2017;9(9):1175–88.
Xiong W, Ai YQ, Li YF, Ye Q, Chen ZT, Qin JY, et al. Microarray analysis of circular RNA expression profile associated with 5-fluorouracil-based chemoradiation resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Biomed Res Int. 2017;8421614(10):1.
Ji Q, Zhang C, Sun X, Li Q. Circular RNAs function as competing endogenous RNAs in multiple types of cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(1):23–30.
Song L, Duan P, Gan Y, Li P, Zhao C, Xu J, et al. Silencing LPAATbeta inhibits tumor growth of cisplatin-resistant human osteosarcoma in vivo and in vitro. Int J Oncol. 2017;50(2):535–44. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3820.
Song L, Zhou Z, Gan Y, Li P, Xu Y, Zhang Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 causes cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma through inducing the LPAATbeta/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by sponging the miR-340-5p. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):9656–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28244.
Song L, Duan P, Gan Y, Li P, Zhao C, Xu J, et al. MicroRNA-340-5p modulates cisplatin resistance by targeting LPAATbeta in osteosarcoma. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017;50(5): e6359. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431x20176359.
Phatak P, Donahue J. Biotinylated micro-RNA pull down assay for identifying miRNA targets. Bio-Protoc. 2017. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2253.
Liu Y-C, Li J-R, Sun C-H, Andrews E, Chao R-F, Lin F-M, et al. CircNet: a database of circular RNAs derived from transcriptome sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D209–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv940.
Muriithi W, Macharia LW, Heming CP, Echevarria JL, Nyachieo A, Filho PN, et al. ABC transporters and the hallmarks of cancer: roles in cancer aggressiveness beyond multidrug resistance. Cancer Biol Med. 2020;17(2):253–69. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0284.
Amawi H, Sim HM, Tiwari AK, Ambudkar SV, Shukla S. ABC transporter-mediated multidrug-resistant cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1141:549–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7647-4_12.
Fletcher JI, Williams RT, Henderson MJ, Norris MD, Haber M. ABC transporters as mediators of drug resistance and contributors to cancer cell biology. Drug Resist Updates. 2016;26:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2016.03.001.
Chatterjee A, Gupta S. The multifaceted role of glutathione S-transferases in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018;433:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.06.028.
Yu X, Yustein JT, Xu J. Research models and mesenchymal/epithelial plasticity of osteosarcoma. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-021-00600-w.
Guarino M, Rubino B, Ballabio G. The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology. 2007;39(3):305–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/00313020701329914.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Clinical Science Foundation of Army Medical University (no. 2018XLC3018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ and QZ participated in the design of the study, most experiment, and writing the draft manuscript. FL and RZ carried out the statistical analysis. J-zX and JX were involved in the cell culture. FD and LS participated in the design of the study and the revision of draft manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhou, Q., Luo, F. et al. Circular RNA circ-CHI3L1.2 modulates cisplatin resistance of osteosarcoma cells via the miR-340-5p/LPAATβ axis. Human Cell 34, 1558–1568 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00564-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00564-6