Abstract
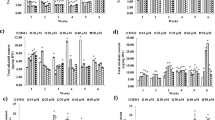
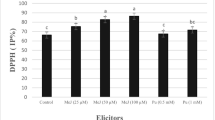
Digitalis purpurea L. is a perennial medicinal herb containing high concentrations of secondary metabolites like cardiac glycosides with extensive therapeutic use. This study aimed to evaluate the induction of secondary metabolites in D. purpurea by applying polyamines as elicitors in suspension cultures. Toward this aim, different explants of D. purpurea including leaf, petiole, and root were first cultured in MS30 medium, then, the potential of callus formation was investigated by applying 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), benzylaminopurine (BAP), and naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) hormones as inducers. The induction of secondary metabolites by different elicitors in suspension cell culture was assessed by applying 50 and 100 mg.L−1 of putrescine (PUT), spermidine (SPD), and spermine (SPM), and 50, 100, and 200 μM concentrations of Methyl jasmonate (MJ), respectively. All the experiments were performed as factorial in a completely randomized design (CRD) with three replications. Results showed that the application of hormone on leaf explants had a significant effect on callus induction. The highest fresh and dry weights of callus were obtained by leaf explant with 2 mg.L−1 BAP and 0.5 mg.L−1 2,4-D. Moreover, SPD and MJ significantly increased the phenol content, antioxidant activities, cardenolides, and digitoxin contents of the callus in suspension cell culture at the concentrations of 100 mg.L−1 and 50 µM, respectively in compared to control. Therefore, the application of SPD and MJ in suspension culture had an inhibitory and additive effect on the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites of D. purpurea.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BAP:
-
Benzylaminopurine
- NAA:
-
Naphthaleneacetic acid
- MJ:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- PUT:
-
Putrescine
- SPD:
-
Spermidine
- SPM:
-
Spermine
- CRD:
-
Completely randomized design
References
Adil M, Ren X, Kang DI, Jeong BR (2018) Effect of explant type and plant growth regulators on callus induction, growth and secondary metabolites production in Cnidium officinale Makino. Mol Biol Rep 45(6):1919–1927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4340-3
Ali AMA, El-Nour MEM, Yagi SM (2018) Total phenolic and flavonoids contents and antioxidant activity of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) rhizome, callus and callus treated with some elicitors. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16(2):677–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.03.003
Angelova Z, Georgiev S, Roos W (2006) Elicitation of plants. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equipment 20(2):72–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2006.10817345
Bonfill M, Palazon J, Cusido RM, Pinol MT, Morales C (1996) Effect of auxin and phenobarbital on the ultrastructure and digitoxin content in Digitalis purpurea tissue culture. Can J Bot 74:378–382. https://doi.org/10.1139/b96-047
Bhusare BP, John CK, Bhatt VP, Nikam TD (2020) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in leaf and root explants of Digitalis lanata Ehrh: Direct and indirect method. S Afr J Bot 130:356–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.01.012
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset CLWT (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lwt-Food Sci Technol 28(1):5–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (2000) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, p 1280
Chang CC, Yang MH, Wen HM, Chern JC (2002) Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J Food Drug Anal 10(3):178–182. https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.2748
Coste A, Vlase L, Halmagyi A, Deliu C, Coldea G (2011) Effects of plant growth regulators and elicitors on production of secondary metabolites in shoot cultures of Hypericum hirsutum and Hypericum maculatum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 106(2):279–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9919-5
Dias MI, Sousa MJ, Alves RC, Ferreira IC (2016) Exploring plant tissue culture to improve the production of phenolic compounds: a review. Ind Crop Prod 82:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.12.016
Espinosa-Leal CA, Puente-Garza CA, García-Lara S (2018) In vitro plant tissue culture: means for production of biological active compounds. Planta 248:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2910-1
Gómez Plaza E, Bautista Ortín AB, Ruiz García Y, Fernández Fernández JI, Gil Muñoz R (2017) Effect of elicitors on the evolution of grape phenolic compounds during the ripening period. J Sci Food Agric 97(3):977–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7823
Gorelick J, Bernstein N (2014) Elicitation: An underutilized tool in the development of medicinal plants as a source of therapeutic secondary metabolites. Adv Agron 124:201–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800138-7.00005-X
Gurel S, Gurel E, Kaya Z (2001) Callus development and indirect shoot regeneration from seedling explants of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) cultured In Vitro. Turk J Botany 25:25–33. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2013.168.178
Ghasemi K, Ghasemi Y, Ebrahimzadeh MA (2009) Antioxidant activity, phenol and flavonoid contents of 13 citrus species peels and tissues. Pak J Pharm Sci 22(3):277–281
Hagimori M, Matsumoto T, Obi Y (1983) Effects of mineral salts, initial pH and precursors on digitoxin formation by shoot-forming cultures of Digitalis purpurea L. grown in liquid media. Agric Biol Chem 47:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1983.10865678
Hosseini SZ, Jelodar NB, Rahimian H, Ranjbar G (2015) Effect of different concentrations of kinetin and 2,4, D on callus induction of citrus rootstock (Citrus sp.). Appl Biotechnol Rep 7(2):1045–1050
Khanpour- Ardestani N, Sharifi M, Behmanesh M (2015) Effect of methyl jasmonate on antioxidant enzyme activities, phenolic and flavonoid compounds in Scrophularia striata cell culture. Journal of Plant Research (iranian Journal of Biology) 27(5):840–853 ((In Persian))
Khawar K, Sarhin E, Sevimay C, Cocu S, Parmaksiz I, Uranbey S, Ipek A, Kaya M, Sancak C, Ozcan S (2005) Adventitious shoot regeneration and micropropagation of Plantago lanceolata L. Period Biol 107(1):113–116
Kintzios S, Adamopoulou M, Pistola E, Delki K, Drossopoulos J (2002) Studies on the physiological function of in vitro produced antioxidants from sage (Salvia officinalis L.): effects on cell growth and metabolism. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 9(2–3):229–233. https://doi.org/10.1300/J044v09n02_33
Krizek DT, Kramer GF, Upadhyaya A, Mirecki RM (1993) UV-B response of cucumber seedlings grown under metal halide and high pressure sodium/deluxe lamps. Physiol Plant 88(2):350–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1993.tb05509.x
Kumar O, Subba Tata S, Rupavati T (2010) In vitro induction of callusogenesis in chili peppers (Capsicum Annuum L.). Int J Curr Res 3:42–45
Mulabagal V, Tsay HS (2004) Plant cell cultures-an alternative and efficient source for the production of biologically important secondary metabolites. Int J Appl Sci Eng 2(1):29–48. https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2003504
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Namdeo AG (2007) Plant cell elicitation for production of secondary metabolites: a review. Phcog Rev 1(1):69–79
Neibaur I, Gallo M, Altpeter F (2008) The effect of auxin type and cytokinin concentration on callus induction and plant regeneration frequency from immature inflorescence segments of seashore paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum Swartz). Cell Dev Biol Plant 44:480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-008-9143-0
Olmstead RG, de Pamphilis CW, Wolfe AD, Young ND, Elisons WJ, Reeves PA (2001) Disintegration of the Scrophulariaceae. Am J Bot 88(2):348–361
Pakseresht G, Kahrizi D, Mansouri M, Ghorbani T, Kazemi N (2016) Study of callus induction and cell culture to secondary metabolite production in Hyssopus officinalis L. JRPS 5(2):104–111
Patel H, Krishnamurthy R (2013) Elicitors in plant tissue culture. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 2(2):60–65
Piri KH, Nazarian F (2001) Plant Tissue Culture. Abu Ali Sina University Press, Hamedan
Pitta-Alvarez SI, Spollansky TC, Giulietti AM (2000) The influence of different biotic and abiotic nitrogen metabolism of growing spinach. Biol Trace Element Res 110(2):179–190. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020507o
Poulev A, O’Neal JM, Logendra S, Pouleva RB, Timeva V, Garvey AS, Gleba D, Jenkins IS, Halpern BT, Kneer R, Cragg GM (2003) Elicitation, a new window into plant chemodiversity and phytochemical drug discovery. J Med Chem 46(12):2542–2547. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm020359t
Radman R, Saez T, Bucke C, Keshavarz T (2003) Elicitation of plants and microbial cell systems. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 37(1):91–102. https://doi.org/10.1042/BA20020118
Rao SR, Ravishankar G (2002) Plant cell cultures: chemical factories of secondary metabolites. Biotechnol 20:101–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0734-9750(02)00007-1
Sahraroo A, Babalar M, Mirjalili MH, Moghaddam MRF, Ebrahimi SN (2014) In-vitro callus induction and rosmarinic acid quantification in callus culture of Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad (Lamiaceae). Iran J Pharm Res 13(4):1447–1456. https://doi.org/10.22037/IJPR.2014.1570
Saravanan S, Nadarajan N (2005) Effect of media supplements on in vitro response of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Genotypes. Res J Agric Biol Sci 1(1):98–100
Savita V, Virk GS, Nagpal A (2010) Effect of explant type and different plant growth regulators on callus induction and plantlet regeneration in Citrus jambhiri Lush. Environ We Int j Sci Tech 5:97–106
Singleton VL, Rossi JA (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic phosphotungstic acid reagents. AJEV 16:144–158
Trejo-Tapia G, Balcazar-Aguilar JB, Martínez-Bonfil B, Salcedo-Morales G, Jaramillo-Flores M, Arenas-Ocampo ML, Jiménez-Aparicio A (2008) Effect of screening and subculture on the production of betaxanthins in Beta vulgaris L. var.‘Dark Detroit’callus culture. IFSET 9(1):32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2007.04.009
Vasconsuelo A, Boland R (2007) Molecular aspects of the early stage of elicitation of secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Sci 172:861–875
Verma SK, Das AK, Cingoz GS, Gurel E (2016) In vitro culture of Digitalis L. (Foxglove) and the production of cardenolides: An up-to-date review. Ind Crop Prod 94:20–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.08.031
Zhao J, Davis LC, Verpoorte R (2005) Elicitor signal transduction leading to production of plant secondary metabolites. Biotechnol Adv 23(4):283–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.01.003
Zhou FF, Wang Z, Shi LY, Niu JJ, Shang WQ, He D, He SL (2016) Effects of different medium composition and exogenous hormones on browning of tree Peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.) callus in tissue Culture. Flower Res J 24(2):96–102. https://doi.org/10.11623/frj.2016.24.2.03
Acknowledgements
We thank the research group of the Department of Cultivation and Development of Medicinal Plants for making their laboratory facilities and equipment available to us in the Institute of Medicinal Plants, ACECR, Karaj, Iran, and Department of Horticulture, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM carried out the experiment and collected available literature and prepared the first draft of the manuscript with support from VA, and PM, FR, and AM analyzed the statistical data and verified the accuracy of the tests; VA designed the model and the computational framework and he was also responsible for the correspondence; PM and FR and AM edited the manuscript as phytochemical consultants.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the accuracy and integrity of the paper content.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rad, M.M., Abdossi, V., Moradi, P. et al. Phytochemical changes of Digitalis purpurea L. in response to polyamines and methyl jasmonate application in callus culture. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 31, 310–319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-021-00678-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-021-00678-w