Abstract
Purpose
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) that possess the ability of self-renewal and multi-potency have been shown to drive tumor progression and metastasis. The majority of recent studies has focused on potential molecules targeting CSCs so as to develop novel strategies for efficient cancer treatment or protection. Here, we show how alpha-lipoic acid (LA), an endogenous mitochondrial anti-oxidant, affects the CSC-like phenotypes of human non-small cell lung cancer-derived H23, H292 and H460 cells.
Methods
CSC-like phenotypes were verified by anchorage-independent growth, three-dimensional (3D) spheroid formation and the expression of CSC markers. Enriched CSC populations were used to confirm the effects of LA. Protein ubiquitination and degradation were assessed using immunoprecipitation.
Results
We found that treatment with LA reduced the CSC-like phenotype, as indicated by a decreased expression of known CSC markers (CD133, CD44, ALDH1A1, Oct-4 and Nanog) in H460 cells. In addition, we found that LA reduced the CSC-related abilities of anchorage-independent growth and 3D spheroid formation, and suppressed factors related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, such as E-cadherin, Vimentin, Slug and Snail. Mechanistically, we found that LA suppresses CSC through depletion of the cellular stemness proteins β-catenin and Oct-4 via decreasing the level of active (phosphorylated) Akt. This resulted in the induction of GSK3β-dependent β-catenin ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation and a decrease in the stabilized (phosphorylated) form of Oct-4. The effects of LA on the CSC-like phenotypes were confirmed in CSC enriched H460, H292 and H23 non-small cell lung cancer-derived cells.
Conclusion
Our data are indicative for a novel regulatory role and underlying mechanism of LA in the negative regulation of a CSC-like phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer-derived cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.F. Sun, Y.H. Hu, L.P. Xiong, X.Y. Tu, J.H. Zhao, S.S. Chen, J. Song, X.Q. Ye, Enhanced expression of stem cell markers and drug resistance in sphere-forming non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8, 6287–6300 (2015)
C. Samardzija, M. Quinn, J.K. Findlay, N. Ahmed, Attributes of Oct4 in stem cell biology: perspectives on cancer stem cells of the ovary. J. Ovarian Res. 5, 37 (2012). doi:10.1186/1757-2215-5-37
A. Merlos-Suarez, F.M. Barriga, P. Jung, M. Iglesias, M.V. Cespedes, D. Rossell, M. Sevillano, X. Hernando-Momblona, V. da Silva-Diz, P. Munoz, H. Clevers, E. Sancho, R. Mangues, E. Batlle, The intestinal stem cell signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts disease relapse. Cell stem Cell 8, 511–524 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.02.020
S. Slawek, K. Szmyt, M. Fularz, J. Dziudzia, M. Boruczkowski, J. Sikora, M. Kaczmarek, Pluripotency transcription factors in lung cancer-a review. Tumour Biol. (2015). doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4407-x
K. Vazquez-Santillan, J. Melendez-Zajgla, L. Jimenez-Hernandez, G. Martinez-Ruiz, V. Maldonado, NF-kappaB signaling in cancer stem cells: a promising therapeutic target? Cell. Oncol. 38, 327–339 (2015). doi:10.1007/s13402-015-0236-6
N. Bhummaphan, P. Chanvorachote, Gigantol suppresses cancer stem cell-like phenotypes in lung cancer cells. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 836564 (2015). doi:10.1155/2015/836564
D. Raha, T.R. Wilson, J. Peng, D. Peterson, P. Yue, M. Evangelista, C. Wilson, M. Merchant, J. Settleman, The cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase is required to maintain a drug-tolerant tumor cell subpopulation. Cancer Res. 74, 3579–3590 (2014). doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-13-3456
Q.W. Zhao, Y.W. Zhou, W.X. Li, B. Kang, X.Q. Zhang, Y. Yang, J. Cheng, S.Y. Yin, Y. Tong, J.Q. He, H.P. Yao, M. Zheng, Y.J. Wang, Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Oct4 is associated with the proliferation of stemlike cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 33, 1621–1629 (2015). doi:10.3892/or.2015.3752
H. Wang, G. Zhang, H. Zhang, F. Zhang, B. Zhou, F. Ning, H.S. Wang, S.H. Cai, J. Du, Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype and cancer stem cell-like properties in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells through AKT/beta-catenin/Snail signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 723, 156–166 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.004
Y. Lin, Y. Yang, W. Li, Q. Chen, J. Li, X. Pan, L. Zhou, C. Liu, C. Chen, J. He, H. Cao, H. Yao, L. Zheng, X. Xu, Z. Xia, J. Ren, L. Xiao, L. Li, B. Shen, H. Zhou, Y.J. Wang, Reciprocal regulation of Akt and Oct4 promotes the self-renewal and survival of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell. 48, 627–640 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.08.030
E.M. Verheyen, C.J. Gottardi, Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling by Protein Kinases. Dev. Dyn. 239, 34–44 (2010). doi:10.1002/dvdy.22019
Y. Teng, X. Wang, Y. Wang, D. Ma, Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cancer stem cells in lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 392, 373–379 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.028
M.K. Mohammed, C. Shao, J. Wang, Q. Wei, X. Wang, Z. Collier, S. Tang, H. Liu, F. Zhang, J. Huang, D. Guo, M. Lu, F. Liu, J. Liu, C. Ma, L.L. Shi, A. Athiviraham, T.C. He, M.J. Lee, Wnt/beta-catenin signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal, tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 3, 11–40 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2015.12.004
J.A. Mayr, R.G. Feichtinger, F. Tort, A. Ribes, W. Sperl, Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 37, 553–563 (2014). doi:10.1007/s10545-014-9705-8
F.A. Moura, K.Q. de Andrade, J.C. dos Santos, M.O. Goulart, Lipoic Acid: its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 15, 458–483 (2015)
U. Wenzel, A. Nickel, H. Daniel, Alpha-Lipoic acid induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells by increasing mitochondrial respiration with a concomitant O2 − generation. Apoptosis 10, 359–368 (2005). doi:10.1007/s10495-005-0810-x
K. van de Mark, J.S. Chen, K. Steliou, S.P. Perrine, D.V. Faller, Alpha-lipoic acid induces p27Kip-dependent cell cycle arrest in non-transformed cell lines and apoptosis in tumor cell lines. J. Cell. Physiol. 194, 325–340 (2003). doi:10.1002/jcp.10205
P. Puchsaka, C. Chaotham, P. Chanvorachote, alpha-Lipoic acid sensitizes lung cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents and anoikis via integrin beta1/beta3 downregulation. Int. J. Oncol. 49, 1445–1456 (2016). doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3624
P. Chanvorachote, S. Luanpitpong, Iron induces cancer stem cells and aggressive phenotypes in human lung cancer cells. Am. J. Phys. Cell Physiol. 310, C728–C739 (2016). doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00322.2015
C. Ninsontia, P.P. Phiboonchaiyanan, C. Kiratipaiboon, P. Chanvorachote, Zinc suppresses stem cell properties of lung cancer cells through protein kinase C-mediated beta-catenin degradation. Am. J. Phys. Cell Phys. 312, C487–c499 (2017). doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00173.2016
S.A. Mani, W. Guo, M.-J. Liao, E.N. Eaton, A. Ayyanan, A.Y. Zhou, M. Brooks, F. Reinhard, C.C. Zhang, M. Shipitsin, The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133, 704–715 (2008)
H.M. Xu, B. Liao, Q.J. Zhang, B.B. Wang, H. Li, X.M. Zhong, H.Z. Sheng, Y.X. Zhao, Y.M. Zhao, Y. Jin, Wwp2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets transcription factor Oct-4 for ubiquitination. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 23495–23503 (2004). doi:10.1074/jbc.M400516200
A. Ashworth, G. Rodrigues, G. Boldt, D. Palma, Is there an oligometastatic state in non-small cell lung cancer? A systematic review of the literature. Lung Cancer 82, 197–203 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.07.026
P. Chen, J. Li, Y.C. Chen, H. Qian, Y.J. Chen, J.Y. Su, M. Wu, T. Lan, The functional status of DNA repair pathways determines the sensitization effect to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. 39, 511–522 (2016). doi:10.1007/s13402-016-0291-7
Y.L. Chen, T.Y. Yang, K.C. Chen, C.L. Wu, S.L. Hsu, C.M. Hsueh, Hypoxia can impair doxorubicin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting MRP1 and P-gp expression and boosting the chemosensitizing effects of MRP1 and P-gp blockers. Cell. Oncol. 39, 411–433 (2016). doi:10.1007/s13402-016-0285-5
Y.X. Bao, X.D. Zhao, H.B. Deng, C.L. Lu, Y. Guo, X. Lu, L.L. Deng, Schedule-dependent cytotoxicity of sunitinib and TRAIL in human non-small cell lung cancer cells with or without EGFR and KRAS mutations. Cell. Oncol. 39, 343–352 (2016). doi:10.1007/s13402-016-0278-4
M. Yamasaki, M. Iwase, K. Kawano, Y. Sakakibara, M. Suiko, M. Ikeda, K. Nishiyama, alpha-Lipoic acid suppresses migration and invasion via downregulation of cell surface beta1-integrin expression in bladder cancer cells. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 54, 18–25 (2014). doi:10.3164/jcbn.13-57
G. Simbula, A. Columbano, G.M. Ledda-Columbano, L. Sanna, M. Deidda, A. Diana, M. Pibiri, Increased ROS generation and p53 activation in α-lipoic acid-induced apoptosis of hepatoma cells. Apoptosis 12, 113–123 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10495-006-0487-9
Y. Wei, Y. Jiang, F. Zou, Y. Liu, S. Wang, N. Xu, W. Xu, C. Cui, Y. Xing, Y. Liu, B. Cao, C. Liu, G. Wu, H. Ao, X. Zhang, J. Jiang, Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by CD133-p85 interaction promotes tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 6829–6834 (2013). doi:10.1073/pnas.1217002110
R. Jiang, X. Niu, Y. Huang, X. Wang, beta-Catenin is important for cancer stem cell generation and tumorigenic activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 48, 229–237 (2016). doi:10.1093/abbs/gmv134
J. Li, B.P. Zhou, Activation of beta-catenin and Akt pathways by Twist are critical for the maintenance of EMT associated cancer stem cell-like characters. BMC Cancer 11, 49 (2011). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-49
P. De Sarno, X. Li, R.S. Jope, Regulation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3β phosphorylation by sodium valproate and lithium. Neuropharmacology 43, 1158–1164 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(02)00215-0
F. Amri, I. Ghouili, M. Amri, A. Carrier, O. Masmoudi-Kouki, Neuroglobin protects astroglial cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic cell death. J. Neurochem. 140, 151–169 (2017). doi:10.1111/jnc.13876
H. Zhou, D. Li, C. Shi, T. Xin, J. Yang, Y. Zhou, S. Hu, F. Tian, J. Wang, Y. Chen, Effects of Exendin-4 on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in vitro. Sci. Rep. 5, 12898 (2015). doi:10.1038/srep12898
Y. Xiao, X. Li, Y. Cui, J. Zhang, L. Liu, X. Xie, H. Hao, G. He, M.C. Kander, M. Chen, Z. Liu, C.M. Verfaillie, H. Zhu, M. Lei, Z. Liu, Hydrogen peroxide inhibits proliferation and endothelial differentiation of bone marrow stem cells partially via reactive oxygen species generation. Life Sci. 112, 33–40 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2014.07.016
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Rachadapisek Sompote Fund for Postdoctoral Fellowship, Grant for International Research Integration: Chula Research Scholar, Ratchadaphiseksomphot Endowment Fund and Pharmaceutical Sciences Research Fund, Chulalongkorn University, and Mr. Krich Rajprasit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
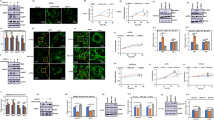
LA inhibits the expression of CSC markers, self-renewal transcription factors, EMT-associated proteins and up-stream signaling proteins. H460 cells were treated with LA (5 μM) for 12, 24 and 48 h. After treatment, (A, C) the expression levels of CD133, CD44, ALDH1A1, E-cadherin, Vimentin, Slug and Snail were determined by Western blotting and the relative protein levels were quantified by densitometry. (B, D, E, F) Dose-dependent effect of LA on the expression of CSC markers, self-renewal transcription factors, EMT-associated proteins, and up-stream signaling proteins in H460 cells after LA (0–5 μM) treatment for 48 h. After treatment, the expression levels of CD133, CD44, ALDH1A1, Oct-4, p-Oct-4, Nanog, E-cadherin, Vimentin, Slug, Snail, β-catenin, p-Akt (Ser 473), Akt, p-GSK3β (Ser 9) and GSK3β were determined by Western blotting, and the relative protein levels quantified by densitometry. (G) Cell lysate of the parental wild type cells (WT) and CSC-enriched cells were prepared and analyzed for CD133, CD44, ALDH1A1, Oct-4, p-Oct-4 and Nanog by immunoblotting, and the relative protein levels quantified by densitometry. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 versus non-treated control. # p < 0.05 versus non-treated wild type control. (GIF 123 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
LA inhibits CSC-related proteins in H292 and H23 cell lines. The cells were treated with LA (0–5 μM) for 48 h. After treatment, (E-J) the expression levels of CD133, CD44, ALDH1A1, Oct-4, p-Oct-4, Nanog, β-catenin, p-Akt (Ser 473), Akt, p-GSK3β (Ser 9) and GSK3β were determined by Western blotting, and the relative protein levels quantified by densitometry. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05 versus the untreated control. (GIF 72 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phiboonchaiyanan, P.P., Chanvorachote, P. Suppression of a cancer stem-like phenotype mediated by alpha-lipoic acid in human lung cancer cells through down-regulation of β-catenin and Oct-4. Cell Oncol. 40, 497–510 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0339-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0339-3