Abstract
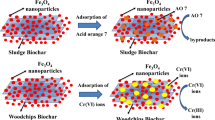
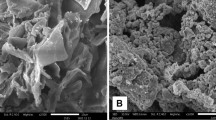
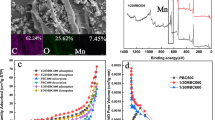
The purpose of this study was to remove Cr(III) ions from aqueous solution using biochar@Fe3O4@SDS nanocomposite. Biochar@Fe3O4@SDS was synthesized as a novel adsorbent by chemical co-precipitation method. The structural features of the nanocomposite were investigated using energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), dynamic light scattering (DLS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses. The BET surface area and the mean pore diameter of the biochar@Fe3O4@SDS were 102.04 m2/g and 169.49°A, respectively, indicating the high porosity of the aforementioned nanocomposite. DLS and XRD analyses showed that the mean particle size and crystal size of biochar@Fe3O4@SDS are 78.9 nm and 28 nm, respectively. Also, the highest Cr(III) removal efficiency (99.5%) using biochar@Fe3O4@SDS was obtained at pH = 9, contact time = 40 min, temperature = 55 ºC, the Cr(III) ion concentration = 10 mg/L, and the nanocomposite dosage = 2 g/L. Moreover, the maximum sorption capacity obtained from the Langmuir model was 120.48 mg/g, which is a significant value compared to previous studies for Cr(III) removal. Furthermore, the isotherm study indicated that the Cr(III) sorption process using the aforementioned nanocomposite followed the Freundlich models due to the higher correlation coefficient (0.986). Also, the pseudo-second order kinetic model with a correlation coefficient of 1 was better fitted than the pseudo-first order model with experimental data. Subsequently, the thermodynamic study demonstrated that the sorption process of Cr(III) ions using biochar@Fe3O4@SDS is favorable, feasible, spontaneous, and endothermic.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Kali A, Amar A, Loulidi I et al (2022) Characterization and adsorption capacity of four low-cost adsorbents based on coconut, almond, walnut, and peanut shells for copper removal. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02564-4
Zhang S, Wang J, Zhang Y et al (2021) Applications of water-stable metal-organic frameworks in the removal of water pollutants: a review. Environ Pollut 291:118076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118076
Zhang L, Wang L, Zhang Y et al (2022) The performance of electrode ultrafiltration membrane bioreactor in treating cosmetics wastewater and its anti-fouling properties. Environ Res 206:112629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112629
Yu S, Tang H, Zhang D et al (2021) MXenes as emerging nanomaterials in water purification and environmental remediation. Sci Total Environ 811:152280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152280
Liu W, Huang F, Liao Y et al (2008) Treatment of CrVI-Containing Mg(OH)2 Nanowaste. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(30):5619–5622. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200800172
Liu W, Zheng J, Ou X et al (2018) Effective extraction of Cr(VI) from hazardous gypsum sludge via controlling the phase transformation and chromium species. Environ Sci Technol 52(22):13336–13342. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02213
Dai L, Wang Z, Guo T et al (2022) Pollution characteristics and source analysis of microplastics in the Qiantang River in southeastern China. Chemosphere 293:133576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133576
Liu W, Li J, Zheng J et al (2020) Different pathways for Cr(III) oxidation: implications for Cr(VI) reoccurrence in reduced chromite ore processing residue. Environ Sci Technol 54(19):11971–11979. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c01855
Almeida JC, Cardoso CED, Tavares DS et al (2019) Chromium removal from contaminated waters using nanomaterials – a review. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 118:277–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.005
Basu A, Behera SS, Dash S et al (2019) A study on removal of Cr(III) from aqueous solution using biomass of Cymbopogon flexuosus immobilized in sodium alginate beads and its use as hydrogenation catalyst. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 102:118–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.05.012
Yao L, Selmi A, Esmaeili H (2021) A review study on new aspects of biodemulsifiers: production, features and their application in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 284:131364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131364
Hu M, Wang Y, Yan Z et al (2021) Hierarchical dual-nanonet of polymer nanofibers and supramolecular nanofibrils for air filtration with a high filtration efficiency, low air resistance and high moisture permeation. J Mater Chem A 9(24):14093–14100. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA01505B
Qiu M, Liu L, Ling Q et al (2022) Biochar for the removal of contaminants from soil and water: a review. Biochar 4:19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-022-00146-1
Tian X, Yang R, Chen T et al (2022) Removal of both anionic and cationic dyes from wastewater using pH-responsive adsorbents of L-lysine molecular-grafted cellulose porous foams. J Hazard Mater 426:128121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128121
Rodríguez Correa C, Ngamying C, Klank D et al (2018) Investigation of the textural and adsorption properties of activated carbon from HTC and pyrolysis carbonizates. Biomass Conv Bioref 8:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-017-0280-8
Naeem MA, Imran M, Amjad M et al (2019) Batch and column scale removal of cadmium from water using raw and acid activated wheat straw biochar. Water 11(7):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071438
Law XN, Cheah WY, Chew KW et al (2022) Microalgal-based biochar in wastewater remediation: its synthesis, characterization and applications. Environ Res 204:111966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111966
Lucaci AR, Bulgariu D, Ahmad I (2019) Potential use of biochar from various waste biomass as biosorbent in Co (II) removal processes. Water 11(8):1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11081565
Abshirini Y, Foroutan R, Esmaeili H (2019) Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from Ziziphus spina–christi leaf. Mater Res Express 6(4):045607. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aafb45
Lucaci AR, Bulgariu D, Bulgariu L (2021) In situ functionalization of iron oxide particles with alginate: a promising biosorbent for retention of metal ions. Polymers 13(20):3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203554
Liu X, Pang H, Liu X et al (2021) Orderly porous covalent organic frameworks-based materials: superior adsorbents for pollutants removal from aqueous solutions. The Innovation 2(1):100076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100076
Keshavarz M, Foroutan R, Papari F et al (2021) Synthesis of CaO/Fe2O3 nanocomposite as an efficient nanoadsorbent for the treatment of wastewater containing Cr (III). Sep Sci Technol 56(8):1328–1341. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2020.1778727
Shi C, Wu Z, Yang F, Tang Y (2021) Janus particles with pH switchable properties for high-efficiency adsorption of PPCPs in water. Solid State Sci 119:106702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2021.106702
Sobhanardakani S, Zandipak R, Cheraghi M (2016) Synthesis of DNPH/SDS/Fe3O4 nanoparticles for removal of Cr (VI) ions from aqueous solution. Avicenna J Environ Health Eng 3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.17795/ajehe-7789
Tamjidi S, Esmaeili H (2019) Chemically modified CaO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite by sodium dodecyl sulfate for Cr (III) removal from water. Chem Eng Technol 42(3):607–616. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201800488
Esmaeili H, Tamjidi S (2020) Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of natural clay/Fe3O4/graphene oxide for enhance removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(25):31652–31664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09448-y
Awual MR (2015) A novel facial composite adsorbent for enhanced copper (II) detection and removal from wastewater. Chem Eng J 266:368–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.094
Awual MR (2019) Efficient phosphate removal from water for controlling eutrophication using novel composite adsorbent. J Clean Prod 228:1311–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.325
Veloso CH, Filippova IV, Ouvrard S, Araujo AC (2020) Adsorption of polymers onto iron oxides: equilibrium isotherms. J Mater Res Technol 9(1):779–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.11.018
Kabir MM, Akter MM, Khandaker S et al (2022) Highly effective agro-waste based functional green adsorbents for toxic chromium (VI) ion removal from wastewater. J Mol Liq 347:118327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.118327
Rambabu K, Thanigaivelan A, Bharath G et al (2021) Biosorption potential of Phoenix dactylifera coir wastes for toxic hexavalent chromium sequestration. Chemosphere 268:128809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128809
Sheikh TA, Rahman MM, Asiri AM et al (2018) 4-Hexylresorcinol sensor development based on wet-chemically prepared Co3O4@ Er2O3 nanorods: a practical approach. J Ind Eng Chem 66:446–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2018.06.012
Silva VAJ, Andrade PL, Silva MPC et al (2013) Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with fucan polysaccharides. J Magn Magn Mater 343:138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.04.062
Burks T, Avila M, Akhtar F et al (2014) Studies on the adsorption of chromium(VI) onto 3-Mercaptopropionic acid coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 425:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.03.025
Takmil F, Esmaeili H, Mousavi SM et al (2020) Nano-magnetically modified activated carbon prepared by oak shell for treatment of wastewater containing fluoride ion. Adv Powder Technol 31(8):3236–3245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.06.015
Pontremoli C, Boffito M, Fiorilli S et al (2018) Hybrid injectable platforms for the in situ delivery of therapeutic ions from mesoporous glasses. Chem Eng J 340:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.073
Zhang P, Hao M, Mao X et al (2020) Effects of W6+ substitution on crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Li3Mg2NbO6 ceramics. Ceram Int 46(13):21336–21342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.229
Yan W, Cao M, Fan S et al (2021) Multi-yolk ZnSe/2(CoSe2)@NC heterostructures confined in N-doped carbon shell for high-efficient sodium-ion storage. Compos B Eng 213:108732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108732
Faiyas APA, Vinod EM, Joseph J et al (2010) Dependence of pH and surfactant effect in the synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and its properties. J Magn Magn Mater 322(4):400–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.09.064
Fu Y, Chen H, Guo R (2021) Extraordinary strength-ductility in gradient amorphous structured Zr-based alloy. J Alloys Compd 888:161507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161507
Awual MR (2019) Mesoporous composite material for efficient lead (II) detection and removal from aqueous media. J Environ Chem Eng 7(3):103124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103124
Wanliang Z, Manli Z, Hongying C et al (2016) Experimental study on cleaning and detoxification of chromium in construction waste. Procedia Environ Sci 31:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.033
Awual MR (2019) Novel ligand functionalized composite material for efficient copper (II) capturing from wastewater sample. Compos B Eng 172:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.05.103
Baijnath L, Gautam V, Yadav V (2014) A comparative study of the removal efficiency of calcium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide as recipitating agents for chromium (III). J Civ Eng Environ Technol 1(1):17–20
Manirethan V, Raval K, Rajan R et al (2018) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by melanin nanopigment obtained from marine source: Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Environ Manage 214:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.084
Hasan MM, Shenashen MA, Hasan MN et al (2021) Natural biodegradable polymeric bioadsorbents for efficient cationic dye encapsulation from wastewater. J Mol Liq 323:114587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114587
Chowdhury MF, Khandaker S, Sarker F et al (2020) Current treatment technologies and mechanisms for removal of indigo carmine dyes from wastewater: a review. J Mol Liq 318:114061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114061
Panda H, Tiadi N, Mohanty M, Mohanty C (2017) Studies on adsorption behavior of an industrial waste for removal of chromium from aqueous solution. S Afr J Chem Eng 23:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2017.05.002
Xu D, Liu J, Ma T et al (2022) Coupling of sponge fillers and two-zone clarifiers for granular sludge in an integrated oxidation ditch. Environ Technol Innov 26:102264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.102264
Munjur HM, Hasan MN, Awual MR et al (2020) Biodegradable natural carbohydrate polymeric sustainable adsorbents for efficient toxic dye removal from wastewater. J Mol Liq 319:114356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114356
Zhao J, Liu J, Wang W et al (2016) Highly efficient removal of bivalent heavy metals from aqueous systems by magnetic porous Fe3O4-MnO2: Adsorption behavior and process study. Chem Eng J 304:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.07.003
Gupta VK, Ali I (2004) Removal of lead and chromium from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—a sugar industry waste. J Colloid Interface Sci 271(2):321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2003.11.007
Mohan D, Singh KP, Singh VK (2006) Trivalent chromium removal from wastewater using low cost activated carbon derived from agricultural waste material and activated carbon fabric cloth. J Hazard Mater 135(1–3):280–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.11.075
Li Q, Zhai J, Zhang W et al (2007) Kinetic studies of adsorption of Pb(II), Cr(III) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution by sawdust and modified peanut husk. J Hazard Mater 141(1):163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.109
Wu Y, Zhang S, Guo X, Huang H (2008) Adsorption of chromium(III) on lignin. Bioresour Technol 99(16):7709–7715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.069
Yang S, Li L, Pei Z et al (2014) Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics of Cr(III) on graphene oxide. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 457:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.05.062
Gonçalves AC, Nacke H, Schwantes D et al (2017) Adsorption mechanism of chromium (III) using biosorbents of Jatropha curcas L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(27):21778–21790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9749-z
Singh NB, Nagpal G, Agrawal S (2018) Water purification by using adsorbents: a review. Environ Technol Innov 11:187–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.006
Rambabu K, Bharath G, Banat F, Show PL (2020) Biosorption performance of date palm empty fruit bunch wastes for toxic hexavalent chromium removal. Environ Res 187:109694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109694
Yegane Badi M, Azari A, Pasalari H et al (2018) Modification of activated carbon with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite for removal of ceftriaxone from aquatic solutions. J Mol Liq 261:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shima Shiraghaei Koutenaei: Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, software.
Gholamhossein Vatankhah: Conceptualization, methodology, supervision.
Hossein Esmaeili: Conceptualization, Data curation and methodology. Writing-review and editing, Project administration, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No approval was required. This manuscript is the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere.
Consent to participate
All authors contributed to this work.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiraghaei Koutenaei, S., Vatankhah, G. & Esmaeili, H. Ziziphus spina-christi leaves biochar decorated with Fe3O4 and SDS for sorption of chromium (III) from aqueous solution. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 14, 10251–10264 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03029-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03029-4