Abstract
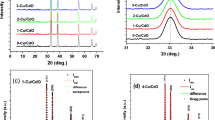
This study investigated the impact of the post-deposition annealing (PDA) process on the material and electrical properties of copper oxide (Cu2O) and nickel oxide (NiO) thin films deposited on a silicon carbide (SiC) substrate. Through radiofrequency (RF) sputtering, these films were subjected to PDA in a nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) gas environment. Remarkably, the Cu2O films resisted phase transition following the N2 PDA process but exhibited a transition to cupric oxide (CuO) after undergoing the O2 PDA process. The symmetry of Cu 2p in the as-deposited Cu2O film was excellent; however, the phase-transformed CuO films exhibited an increase in binding energy and the emergence of satellite peaks. The Ni 2p exhibited various defects, such as nickel vacancies (VNi) and interstitial oxygen (Oi), in response to the different PDA atmospheres. The rectification ratios of the N2-annealed Cu2O and NiO devices were determined as 1.50 × 107 and 4.01 × 106, respectively, signifying a substantial enhancement by a factor of approximately 789 for the Cu2O/SiC device and 124 for the NiO/SiC device relative to their non-annealed counterparts. The findings of this study indicate that meticulous control of deposition for potential p-type materials such as Cu2O and NiO can significantly improve the performance in applications involving high-throughput and low-cost electronics.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
She, X., Huang, A.Q., Lucia, O., Ozpineci, B.: Review of silicon carbide power devices and their applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64, 8193–8205 (2017)
Alok, D., Baliga, B.J., McLarty, P.K.: A simple edge termination for silicon carbide devices with nearly ideal breakdown voltage. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 15, 394–395 (1994)
Itoh, A., Kimoto, T., Matsunami, H.: High performance of high-voltage 4H-SiC Schottky barrier diodes. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 16, 280–282 (1995)
Raghunathan, R., Alok, D., Baliga, B.J.: High voltage 4H-SiC Schottky barrier diodes. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 16, 226–227 (1995)
Gao, G.B., Sterner, J., Morkoc, H.: High frequency performance of SiC heterojunction bipolar transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 41, 1092–1097 (1994)
Negoro, Y., Katsumoto, K., Kimoto, T., Matsunami, H.: Electronic behaviors of high-dose phosphorus-ion implanted 4H–SiC (0001). J. Appl. Phys. 96, 224–228 (2004)
Matsunami, H., Kimoto, T.: Step-controlled epitaxy of SiC: high-quality homoepitaxial growth. Diam. Relat. Mater. 7, 342–347 (1998)
Kanaya, M., Takahashi, J., Fujiwara, Y., Moritani, A.: Controlled sublimation growth of single crystalline 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC and identification of polytypes by x-ray diffraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 58, 56–58 (1991)
Levinshtein, M.E., Mnatsakanov, T.T., Agarwal, A.K., Palmour, J.W.: Analytical and numerical studies of p + -emitters in silicon carbide bipolar devices. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 26, 055024 (2011)
Lu, L., Zhang, H., Wu, X., Shi, J., Sun, Y.Y.: Atomic and electronic structures of p-type dopants in 4H-SiC. Chinese Phys. B 30, 096806 (2021)
Khanna, V.K.: Extreme-temperature and harsh-environment electronics, pp. 3–20. IOP Publishing Limited, Bristol (2017)
Contreras, S., Konczewicz, L., Arvinte, R., Peyre, H., Chassagne, T., Zielinski, M., Juillaguet, S.: Electrical transport properties of p-type 4H-SiC. Phys. Status Solidi A 214, 1600679 (2017)
Huang, Y., Wang, R., Zhang, Y., Yang, D., Pi, X.: Compensation of p-type doping in Al-doped 4H-SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 131, 185703 (2022)
Kondo, J.: Chem. Commun. 3, 357–358 (1998)
Kuo, C.H., Yang, Y.C., Gwo, S., Huang, M.H.: Facet-dependent and au nanocrystal-enhanced electrical and photocatalytic properties of Au-Cu2O core-shell heterostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 1052–1057 (2011)
Olsen, L.C., Bohara, R.C., Urie, M.W.: Explanation for low-efficiency Cu2O Schottky-barrier solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 34, 47–49 (1979)
Tan, C.S., Hsu, S.C., Ke, W.H., Chen, L.J., Huang, M.H.: Facet-dependent electrical conductivity properties of Cu2O crystals. Nano Lett. 15, 2155–2160 (2015)
Rakhshani, A.E., Varghese, J.: Galvanostatic deposition of thin films of cuprous oxide. Sol. Energy Mater. 15, 237–248 (1987)
Muñoz-Rojas, D., Jordan, M., Yeoh, C., Marin, A.T., Kursumovic, A., Dunlop, L.A., Iza, D.C., Chen, A., Wang, H., MacManus Driscoll, J.L.: Growth of ∼5 cm 2V−1s−1 mobility, p-type Copper(I) oxide (Cu2O) films by fast atmospheric atomic layer deposition (AALD) at 225°C and below. AIP Adv. 2, 042179 (2012)
Drobny, V.F., Pulfrey, L.: Properties of reactively-sputtered copper oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 61, 89–98 (1979)
Bergum, K., Riise, H.N., Gorantla, S., Lindberg, P.F., Jensen, I.J.T., Gunnæs, A.E., Galeckas, A., Diplas, S., Svensson, B.G., Monakhov, E.: Improving carrier transport in Cu2O thin films by rapid thermal annealing. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 30, 075702 (2018)
Minami, T., Nishi, Y., Miyata, T.: Impact of incorporating sodium into polycrystalline p-type Cu2O for heterojunction solar cell applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 212104 (2014)
Ishizuka, S., Kato, S., Okamoto, Y., Akimoto, K.: Control of hole carrier density of polycrystalline Cu2O thin films by Si doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 950–952 (2002)
Takiguchi, Y., Takei, Y., Nakada, K., Miyajima, S.: Fabrication and characterization of sputtered Cu2O: N/c-Si heterojunction diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 093501 (2017)
Diwald, O., Thompson, T.L., Zubkov, T., Goralski, E.G., Walck, S.D., Yates, J.T.: Photochemical activity of nitrogen-doped rutile TiO 2 (110) in visible light. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 6004–6008 (2004)
Li, J., Mei, Z., Liu, L., Liang, H., Azarov, A., Kuznetsov, A., Liu, Y., Ji, A., Meng, Q., Du, X.: Probing defects in nitrogen-doped Cu2O. Sci. Rep. 4, 7240 (2014)
Malerba, C., Azanza Ricardo, C.L.A., D’Incau, M., Biccari, F., Scardi, P., Mittiga, A.: Nitrogen doped Cu2O: a possible material for intermediate band solar cells? Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 105, 192–195 (2012)
Lee, Y.S., Heo, J., Winkler, M.T., Siah, S.C., Kim, S.B., Gordon, R.G., Buonassisi, T.: Nitrogen-doped cuprous oxide as a p-type hole-transporting layer in thin-film solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 15416–15422 (2013)
Liu, A., Liu, G., Zhu, H., Shin, B., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Shan, F.: Hole mobility modulation of solution-processed nickel oxide thin-film transistor based on high-k dielectric. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 233506 (2016)
Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhu, M.: NiO films consisting of vertically aligned cone-shaped NiO rods. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 033101 (2006)
Hwang, J.D., Ho, T.H.: Effects of oxygen content on the structural, optical, and electrical properties of NiO films fabricated by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 71, 396–400 (2017)
Manders, J.R., Tsang, S.W., Hartel, M.J., Lai, T.H., Chen, S., Amb, C.M., Reynolds, J.R., So, F.: Solution-processed nickel oxide hole transport layers in high efficiency polymer photovoltaic cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 2993–3001 (2013)
Jiang, J., Wang, X., Zhang, Q., Li, J., Zhang, X.X.: Thermal oxidation of Ni films for p-type thin-film transistors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 6875–6878 (2013)
Irwin, M.D., Buchholz, D.B., Hains, A.W., Chang, R.P.H., Marks, T.J.: p -Type semiconducting nickel oxide as an efficiency-enhancing anode interfacial layer in polymer bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 105, 2783–2787 (2008)
Hsu, C.C., Su, H.W., Hou, C.H., Shyue, J.J., Tsai, F.Y.: Atomic layer deposition of NiO hole-transporting layers for polymer solar cells. Nanotechnology 26, 385201 (2015)
Liu, S., Liu, R., Chen, Y., Ho, S., Kim, J.H., So, F.: Nickel oxide hole injection/transport layers for efficient solution-processed organic light-emitting diodes. Chem. Mater. 26, 4528–4534 (2014)
Jiang, F., Choy, W.C.H., Li, X., Zhang, D., Cheng, J.: Post-treatment-free solution-processed non-stoichiometric NiOx nanoparticles for efficient hole-transport layers of organic optoelectronic devices. Adv. Mater. 27, 2930–2937 (2015)
Seo, S., Park, I.J., Kim, M., Lee, S., Bae, C., Jung, H.S., Park, N.G., Kim, J.Y., Shin, H.: An ultra-thin, un-doped NiO hole transporting layer of highly efficient (16.4%) organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale 8, 11403–11412 (2016)
You, J., Meng, L., Song, T.B., Guo, T.F., Yang, Y.M., Chang, W.H., Hong, Z., Chen, H., Zhou, H., Chen, Q., Liu, Y., De Marco, N., Yang, Y.: Improved air stability of perovskite solar cells via solution-processed metal oxide transport layers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 75–81 (2016)
Yin, X., Chen, P., Que, M., Xing, Y., Que, W., Niu, C., Shao, J.: Highly efficient flexible perovskite solar cells using solution-derived NiOx hole contacts. ACS Nano 10, 3630–3636 (2016)
Lee, H., Huang, Y., Horn, M.W., Feng, S.P.: Engineered optical and electrical performance of rf–sputtered undoped nickel oxide thin films for inverted perovskite solar cells. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 5590 (2018)
Liu, G., Liu, A., Zhu, H., Shin, B., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Wang, Y., Shan, F.: Low-temperature, nontoxic water-induced metal-oxide thin films and their application in thin-film transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 2564–2572 (2015)
Socratous, J., Banger, K.K., Vaynzof, Y., Sadhanala, A., Brown, A.D., Sepe, A., Steiner, U., Sirringhaus, H.: Electronic structure of low-temperature solution-processed amorphous metal oxide semiconductors for thin-film transistor applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 1873–1885 (2015)
Liu, A., Liu, G.X., Zhu, H.H., Xu, F., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Shan, F.K.: Fully solution-processed low-voltage aqueous in 2o3 thin-film transistors using an ultrathin ZrO x dielectric. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 17364–17369 (2014)
Seo, S., Lee, M.J., Seo, D.H., Jeoung, E.J., Suh, D.-S., Joung, Y.S., Yoo, I.K., Hwang, I.R., Kim, S.H., Byun, I.S., Kim, J.-S., Choi, J.S., Park, B.H.: Reproducible resistance switching in polycrystalline NiO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5655–5657 (2004)
Jang, W.L., Lu, Y.M., Hwang, W.S., Hsiung, T.L., Wang, H.P.: Point defects in sputtered NiO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 062103 (2009)
Yang, J.L., Lai, Y.S., Chen, J.S.: Effect of heat treatment on the properties of non-stoichiometric p-type nickel oxide films deposited by reactive sputtering. Thin Solid Films 488, 242–246 (2005)
Shaikh, J.S., Pawar, R.C., Devan, R.S., Ma, Y.R., Salvi, P.P., Kolekar, S.S., Patil, P.S.: Synthesis and characterization of Ru doped CuO thin films for supercapacitor based on Bronsted acidic ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 56, 2127–2134 (2011)
Wang, Y., Lany, S., Ghanbaja, J., Fagot-Revurat, Y., Chen, Y.P., Soldera, F., Pierson, J.F.: Electronic structures of Cu2O, Cu4 O3, and CuO: a joint experimental and theoretical study. Phys. Rev. B 94, 245418 (2016)
Gong, H., Zhang, Y., Cao, Y., Luo, M., Feng, Z., Yang, W., Liu, K., Cao, H., Yan, H.: Pt@Cu2O/WO3 composite photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic water oxidation performance. Appl. Catal. B 237, 309–317 (2018)
Zhao, S., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Jiang, Y., Jiang, C., Yin, Z., Xiao, Y., Cao, S.: Silver nanoparticles confined in shell-in-shell hollow TiO2 manifesting efficiently photocatalytic activity and stability. Chem. Eng. J. 367, 249–259 (2019)
Yin, Z., Xiao, Y., Wan, X., Jiang, Y., Chen, G., Shi, Q., Cao, S.: High photocatalytic activity of Cu2O embedded in hierarchically hollow SiO2 for efficient chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes. J. Mater. Sci. 56, 3874–3886 (2021)
Osorio-Guillén, J., Lany, S., Zunger, A.: Nonstoichiometry and hole doping in NiO. AIP Conf. Proc. 1199, 128–129 (2010)
Wang, K.C., Shen, P.S., Li, M.H., Chen, S., Lin, M.W., Chen, P., Guo, T.F.: Low-temperature sputtered nickel oxide compact thin film as effective electron blocking layer for mesoscopic NiO/CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite heterojunction solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 11851–11858 (2014)
Kwon, U., Kim, B.G., Nguyen, D.C., Park, J.H., Ha, N.Y., Kim, S.J., Ko, S.H., Lee, S., Lee, D., Park, H.J.: Solution-processible crystalline NiO nanoparticles for high-performance planar perovskite photovoltaic cells. Sci. Rep. 6, 30759 (2016)
Salunkhe, P., Av, M.A., Kekuda, D.: Structural, spectroscopic and electrical properties of dc magnetron sputtered NiO thin films and an insight into different defect states. Appl. Phys. A 127, 390 (2021)
Roberts, M.W., Smart, R.S.C.: The defect structure of nickel oxide surfaces as revealed by photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1(80), 2957–2968 (1984)
Usha, K.S., Sivakumar, R., Sanjeeviraja, C., Sathe, V., Ganesan, V., Wang, T.Y.: Improved electrochromic performance of a radio frequency magnetron sputtered NiO thin film with high optical switching speed. RSC Adv. 6, 79668–79680 (2016)
Sawicka-Chudy, P., Sibiński, M., Rybak-Wilusz, E., Cholewa, M., Wisz, G., Yavorskyi, R.: Review of the development of copper oxides with titanium dioxide thin-film solar cells. AIP Adv. 10, 11 (2020)
Lam, N.D.: Modelling and numerical analysis of ZnO/CuO/Cu 2 O heterojunction solar cell using SCAPS. Eng. Res. Express 2, 025033 (2020)
Acknowledgements
Support from the Fostering Global Talents for Innovative Growth Program of the KIAT (P0017308), the Next-Generation Power Semiconductor Development of the KEIT (RS-2022-00154720), and a research grant provided by Kwangwoon University in 2023, made this work possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H-JL: Conceptualization; investigation; writing–original draft; visualization. S-YM: Formal analysis; data curation. K-YL: Writing–review & editing; supervision. S-MK: Writing–review & editing; supervision; project administration; funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HJ., Moon, SY., Lee, KY. et al. Impact of Post-Deposition Annealing on Electrical Properties of RF-Sputtered Cu2O/4H-SiC and NiO/4H-SiC PiN Diodes. Electron. Mater. Lett. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-024-00484-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-024-00484-1