Abstract
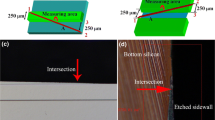
Metal-assisted chemical etching (MACE) has been used as a promising alternative method to fabricate micro/nano-structures on silicon substrates inexpensively. In this paper, profiles of deep trenches on silicon substrates, with different doping levels, fabricated by MACE were studied. A layer of interconnected gold islands was first deposited onto the silicon substrate as catalyst. Electrochemical etching was then performed in a hydrofluoric acid (HF) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) mixture solution with different HF-to-H2O2 ratio ρ (ρ = [HF]/([HF] + [H2O2])). Vertical deep trenches were fabricated successfully by using this method. It was observed that even under identical experimental condition, sidewalls with various tilting angles and different morphology could still form on silicon substrates with different resistivity. This possibly because with different resistivity silicon substrate, the gradient of holes in it greatly changed, and so did the final morphology. As a result, the tilting angle of etched trench sidewall can be tuned from 6° to 96° using silicon substrates with different resistivity and etchants with different ρ. By applying the angle-tuning technique revealed in this study, high aspect ratio patterns with vertical sidewalls could be fabricated and three-dimensional complex structures could be designed and realized in the future.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Hernandez, D. Lange, T. Trifonov, M. Garín, M. García, A. Rodríguez, and R. Alcubilla, Microelectron. Eng. 87, 1458 (2010).
M. D. Kelzenberg, S. W. Boettcher, J. A. Petykiewicz, D. B. Turner-Evans, M. C. Putnam, E. L. Warren, J. M. Spurgeon, R. M. Briggs, N. S. Lewis, and H. A. Atwater, Nat. Mater. 9, 239 (2010).
K. Q. Peng, X. Wang, L. Li, X. L. Wu, and S. T. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 6872 (2010).
Y. Cui, Q. Wei, H. Park, and C. M. Lieber, Science 293, 1289 (2001).
B. R. Murthy, J. K. K. Ng, E. S. Selamat, N. Balasubramanian, and W. T. Liu, Biosens. Bioelectron. 24, 723 (2008).
K. Peng, J. Jie, W. Zhang, and S.-T. Lee, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 033105 (2008).
A. I. Hochbaum, R. Chen, R. D. Delgado, W. Liang, E. C. Garnett, M. Najarian, A. Majumdar, and P. Yang, Nature 451, 163 (2008).
A. Snigirev, I. Snigireva, M. Grigoriev, V. Yunkin, M. D. Michiel, G. Vaughan, V. Kohn, and S. Kuznetsov, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 186, 012072 (2009).
J. Bondur, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 13, 1023 (1976).
M. Ahn, R. K. Heilmann, and M. L. Schattenburg, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 25, 2593 (2007).
V. Lehmann and H. Föll, J. Electrochem. Soc. 137, 653 (1990).
V. Lehmann and U. Grüning, Thin Solid Films 297, 13 (1997).
H. Föll, M. Christophersen, J. Carstensen, and G. Hasse, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 39, 93 (2002).
P. Lianto, S. Yu, J. Wu, C. V. Thompson, and W. K. Choi, Nanoscale 4, 7532 (2012).
L. Li, Y. Liu, X. Zhao, Z. Lin, and C. P. Wong, ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 6, 575 (2013).
Z. Huang, N. Geyer, P. Werner, J. De Boor, and U. Gösele, Adv. Mater. 23, 285 (2011).
X. Li and P. W. Bohn, Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 2572 (2000).
M. L. Zhang, K. Q. Peng, X. Fan, J. S. Jie, R. Q. Zhang, S. T. Lee, and N. B. Wong, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 4444 (2008).
M. Lajvardi, H. Eshghi, M. Izadifard, M. E. Ghazi, and A. Goodarzi, Physica E 75, 136 (2016).
C. Y. Chen, Y. R. Liu, J. C. Tseng, and P. Y. Hsu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 333, 152 (2015).
S. Cruz, A. Hönig-d’Orville, and J. Müller, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, C418 (2005).
J. Huang, S. Y. Chiam, H. H. Tan, S. Wang, and W. K. Chim, Chem. Mater. 22, 4111 (2010).
Z. Huang, T. Shimizu, S. Senz, Z. Zhang, N. Geyer, and U. Gösele, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 10683 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Z., Huang, Q., Zhao, C. et al. Study on the impact of silicon doping level on the trench profile using metal-assisted chemical etching. Electron. Mater. Lett. 12, 742–746 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-016-6197-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-016-6197-8