Abstract
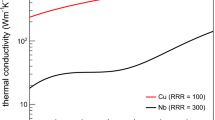
In this letter the evolution of the surface topography of a niobium superconducting radio frequency cavity caused by different plasma etching modes (isotropic and anisotropic) is studied by the three-dimensional level set method. The initial rough surface is generated starting from an experimental power spectral density. The time dependence of the rms roughness is analyzed and the growth exponential factors β are determined for two etching modes (isotropic and anisotropic) assuming that isotropic etching is a much more effective mechanism of smoothing. The obtained simulation results could be useful for optimizing the parameters of the etching processes needed to obtain high quality niobium surfaces for superconducting radio frequency cavities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Padamsee, RF Superconductivity: Science, Technology and Applications, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany (2009).
T. Hays, H. Padamsee, and D. Proch, Handbook of Accelerator Physics and Engineering, (eds., A. W. Chao and M. Tigner), World Scientific Publishing Co., Singapore (2002).
H. Tian, G. Ribeill, M. J. Kelley, and C. E. Reece, Proceedings of PAC09, p. 2132, Vancouver, BC, Canada (2009).
M. Rašković, L. Vušković, S. Popovic, L. Phillips, A.-M. Valente-Feliciano, S. B. Radovanov, and L. Godet, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 569, 663 (2006).
M. Rašković, J. Upadhyay, L. Vuškovic, S. Popovic, A.-M. Valente-Feliciano, and L. Phillips, Phys. Rev. Special Topics-Accelerators and Beams 13, 112001 (2010).
H. Tiana, G. Ribeill, C. Xu, C. E. Reece, and M. J. Kelley, Appl. Surface Sci. 257, 4781 (2011).
K. Uchida, J. Honda, and K.-Y. Yoon, J. Algorithms & Comput. Technol. 5, 259 (2011).
B. Radjenović and M. Radmilović-Radjenović, Mater. Lett. 86, 165 (2012).
B. Radjenović and M. Radmilović-Radjenović, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8, 491 (2012).
A. Duparré, J. Ferre-Borrull, S. Gilech, G. Notni, J. Steinert, and J. M. Bennett, Appl. Opt. 41, 154 (2002).
J. M. Elson and J. M. Bennett, Appl. Opt. 34, 201 (1995).
E. L. Church and H. C. Berry, Wear 83, 189 (1982).
J. Sethian, Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods: Evolving Interfaces in Computational Geometry, Fluid Mechanics, Computer Vision and Materials Sciences, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1998).
B. Radjenovic, J. K. Lee, and M. Radmilović-Radjenović, Comput. Phys.Commun. 174, 127 (2006).
F. Family and T. Viscek, J. Phys. A 18, L75 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radjenović, B., Radmilović-Radjenović, M. The effect of plasma etching on the surface topography of niobium superconducting radio frequency cavities. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 1039–1043 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-014-3362-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-014-3362-9