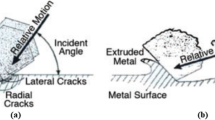
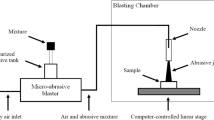
Abstract
Dental implants undergo a general surface treatment via micro-blasting, where solid particle erosion (SPE) occurs on their surfaces. Considering the high costs of SPE experiments, it is necessary to present a reliable computer simulation that can provide a correct understanding of the erosion rate, residual stress and the characteristics of the scar created. However, simulating the impacts of numerous erosive particles with different shapes is challenging. This article, using numerical and experimental approaches, focused on effects of particle velocity and angle of impact on the surface responses of Ti-6Al-4V. In the simulation, the real shapes of more than 1500 angular particles were reproduced through an image processing technique. Johnson-Cook/Zerilli-Armstrong constitutive model was established for analysis. The accuracy of finite element (FE) and smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) was compared with experiments at oblique and normal micro-blasting in three velocities. Erosion rate, residual stress and scar area were investigated. Higher velocities showed more accurate erosion rate results with SPH, whereas the FE model suited lower ones. SPH outperformed FE in predicting surface residual stress. For normal impacts, the SPH was more reliable in predicting the scar area, while the FE was more accurate for oblique impacts. SEM results indicated both penetration and cutting mechanisms at 35°, but only pure penetration was the main mechanism at 90°.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors guarantee that there is no data availability statement with other people or organizations in this article.
References
Khoddami, A.; Nasiri, M.A.; Mohammadi, B.: Experimental and numerical study on micro-blasting process of 3A dental implant titanium alloy: a comparison between finite element method and smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 132, 105269 (2022)
Nayak, S.K.; Satapathy, A.; Mantry, S.: Impact of process parameters on solid particle erosion behavior of waste marble dust-filled polyester composites. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 7197–7209 (2021)
Minhas, N.; Thakur, A.; Mehlwal, S.; Verma, R.; Sharma, V.S.; Sharma, V.: Multi-variable optimization of the shot blasting of additively manufactured alsi10mg plates for surface roughness using response surface methodology. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 11671–11685 (2021)
Joshi, S.; Franc, J.P.; Ghigliotti, G.; Fivel, M.: Bubble collapse induced cavitation erosion: plastic strain and energy dissipation investigations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 134, 103749 (2020)
Alroy, R.J.; Kamaraj, M.; Sivakumar, G.: HVAF vs oxygenated HVAF spraying: Fundamental understanding to optimize Cr3C2-NiCr coatings for elevated temperature erosion resistant applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 309, 117735 (2022)
Kedir, N.; Garcia, E.; Kirk, C.; Gao, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhai, X.; Sun, T.; Fezzaa, K.; Sampath, S.; Chen, W.W.: Impact damage of narrow silicon carbide (SiC) ceramics with and without environmental barrier coatings (EBCs) by various foreign object debris (FOD) simulants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 407, 126779 (2021)
Rajahram, S.S.: Erosion-corrosion mechanisms of stainless steel UNS S31603 (Doctoral dissertation, University of Southampton), (2010)
Kar, S.; Patowari, P.K.: An experimental investigation of the erosion phenomenon in µED-milling of titanium and its parametric optimization using desirability analysis. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47(7), 8847–8861 (2022)
Khoddami, A.; Mohammadi, B.: Finite element modeling of multiple solid particles erosion for Ti-6Al-4V based on Johnson-Cook plasticity and failure models. Modares Mech. Eng. 20(4), 877–887 (2020)
Kang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Yi, C.; He, J.; Li, D.: Custom design and biomechanical analysis of 3D-printed PEEK rib prostheses. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 17, 1083–1092 (2018)
Zhang, H.; Cai, Z.; Chi, J.; Sun, R.; Che, Z.; Lin, L.; Peng, P.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.: Gradient microstructure evolution in laser shock peened Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 437, 128378 (2022)
Vayron, R.; Nguyen, V.H.; Bosc, R.; Naili, S.; Haïat, G.: Finite element simulation of ultrasonic wave propagation in a dental implant for biomechanical stability assessment. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 14, 1021–1032 (2015)
Mohammadi, B.; Khoddami, A.: Representative volume element-based simulation of multiple solid particles erosion of a compressor blade considering temperature effect. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part J: J. Eng. Tribol. 234(8), 1173–1184 (2020)
Hu, Y.; Pan, J.; Dai, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.: Solid particle erosion-wear behaviour of SiC particle-reinforced Si matrix composite and neat Si—a comparison. Wear 496, 204286 (2022)
Saebi, D.; Khoddami, A.; Mohammadi, B.: Finite element investigation of multiple solid particle erosion of Al 7075–T6 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Aerosp. Mech. J. 16(4), 13–24 (2020)
Mohammadi, B.; Khoddami, A.; Pourhosseinshahi, M.: Numerical and experimental investigation of erosive wear of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Tribol. 141(10), 101603 (2019)
Nekahi, M.M.; Vazquez, E.V.; Papini, M.: Numerical simulation of solid particle erosion of alumina by overlapping irregular-shaped particle impacts. Tribol. Lett. 70(2), 50 (2022)
Parkash, O.; Kumar, A.; Sikarwar, B.S.: Computational erosion wear model validation of particulate flow through mitre pipe bend. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 12373–12390 (2021)
Parvandar Asadollahi, B.; Pour Panah, M.; Javdani, A.: Experimental investigation and molecular dynamics simulation of contributing variables on abrasive water jet on aluminum alloy 7075 reinforced with Al2O3, graphite and silicon carbide. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47(12), 15303–15321 (2022)
Hutchings, I.M.; Winter, R.E.; Field, J.E.: Solid particle erosion of metals: the removal of surface material by spherical projectiles. Proc. Royal Soc. London. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 348(1654), 379–392 (1976)
Dhar, S.; Krajac, T.; Ciampini, D.; Papini, M.: Erosion mechanisms due to impact of single angular particles. Wear 258(1–4), 567–579 (2005)
Hu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.: Characteristics of multiphase jet machining: a comparison with the absence of water. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 291, 117050 (2021)
Smeltzer, C.E.; Gulden, M.E.; Compton, W.A.: Mechanisms of metal removal by impacting dust particles. J. Basic Eng. 92(3), 639–652 (1970)
Tilly, G.P.: A two stage mechanism of ductile erosion. Wear 23(1), 87–96 (1973)
Winter, R.E.; Hutchings, I.M.: Solid particle erosion studies using single angular particles. Wear 29(2), 181–194 (1974)
Hutchings, I.M.: Deformation of metal surfaces by the oblique impact of square plates. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 19(1), 45–52 (1977)
Takaffoli, M.; Papini, M.: Numerical simulation of solid particle impacts on Al6061-T6 Part II: materials removal mechanisms for impact of multiple angular particles. Wear 296(1–2), 648–655 (2012)
Wang, Y.F.; Yang, Z.G.: A coupled finite element and meshfree analysis of erosive wear. Tribol. Int. 42(2), 373–377 (2009)
ElTobgy, M.S.; Ng, E.; Elbestawi, M.A.: Finite element modeling of erosive wear. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 45(11), 1337–1346 (2005)
Wang, Y.F.; Yang, Z.G.: Finite element model of erosive wear on ductile and brittle materials. Wear 265(5–6), 871–878 (2008)
Khoddami, A.; Nasiri, M.; Mohammadi, B.: Study on effect of particle velocity and impact angle on erosion of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Modares Mech. Eng. 22(8), 509–518 (2022)
Du, M.; Li, Z.; Dong, X.; Fan, C.; Che, J.; Zhang, Y.: Experiment and simulation of erosion behavior and deformation characteristics in Al6061-T6 beam due to rhomboid particle impacts. Tribol. Lett. 69, 1–25 (2021)
Liu, Z.G.; Wan, S.; Nguyen, V.B.; Zhang, Y.W.: A numerical study on the effect of particle shape on the erosion of ductile materials. Wear 313(1–2), 135–142 (2014)
Mohseni-Mofidi, S.; Drescher, E.; Kruggel-Emden, H.; Teschner, M.; Bierwisch, C.: Particle-based numerical simulation study of solid particle erosion of ductile materials leading to an erosion model, including the particle shape effect. Materials 15(1), 286 (2021)
Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Mao, Z.; Lin, T.: A development of a SPH model for simulating surface Erosion by impact (s) of irregularly shaped particles. Int. J. Comput. Methods 15(08), 1850074 (2018)
Khoddami, A.; Salimi-Majd, D.; Mohammadi, B.: Finite element and experimental investigation of multiple solid particle erosion on Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy coated by multilayer wear-resistant coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 372, 173–189 (2019)
Kumar, N.; Shukla, M.: Finite element analysis of multi-particle impact on erosion in abrasive water jet machining of titanium alloy. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 236(18), 4600–4610 (2012)
Hadavi, V.: Experimental analysis and numerical modeling of particle embedment and fracture in the solid particle erosion of ductile materials (Doctoral dissertation, Ryerson University) (2016)
Takaffoli, M: Experimental And numerical study of single and multiple imapcts of angular particles on ductile metals (Doctoral dissertation, Ryerson University), (2012)
Yerramareddy, S.; Bahadur, S.: Effect of operational variables, microstructure and mechanical properties on the erosion of Ti-6Al-4V. Wear 142(2), 253–263 (1991)
Avcu, E.; Fidan, S.; Yıldıran, Y.; Sınmazçelik, T.: Solid particle erosion behaviour of Ti6Al4V alloy. Tribol.-Mater., Surf. Interfaces 7(4), 201–210 (2013)
Naveed, M.; Schlag, H.; König, F.; Weiß, S.: Influence of the erodent shape on the erosion behavior of ductile and brittle materials. Tribol. Lett. 65(1), 18 (2017)
Atroshenko, S.A.; Evstifeev, A.D.; Kazarinov, N.A.; Petrov, Y.V.; Valiev, R.Z.: Behavior of the grade 5 titanium alloy in different structural states in conditions of high-speed erosion. Proced. Struct. Integr. 6, 190–195 (2017)
Kazarinov, N.A.; Evstifeev, A.D.; Petrov, Y.V.; Atroshenko, S.A.; Valiev, R.R.: The effect of grain refinement on solid particle erosion of grade 5 Ti alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27, 3054–3059 (2018)
Granato, R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Castellano, A.; Khan, R.; Jimbo, R.; Marin, C.; Morsi, S.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P.G.: Osteointegrative and microgeometric comparison between micro-blasted and alumina blasting/acid etching on grade II and V titanium alloys (Ti-6Al-4V). J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 97, 288–295 (2019)
Zboun, M.; Arısan, V.; Topcuoglu, N.; Kuruoglu, F.; Sener, L.T.; Sarcan, F.: In vitro comparison of titanium surface conditioning via boron-compounds and sand-blasting acid-etching. Surf. Interfaces 21, 100703 (2020)
Inokoshi, M.; Shimizubata, M.; Nozaki, K.; Takagaki, T.; Yoshihara, K.; Minakuchi, S.; Vleugels, J.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Zhang, F.: Impact of sandblasting on the flexural strength of highly translucent zirconia. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 115, 104268 (2021)
Ruff, A.W.; Ives, L.K.: Measurement of solid particle velocity in erosive wear. Wear 35(1), 195–199 (1975)
Bousser, E.: Solid particle erosion mechanisms of protective coatings for aerospace applications. Department of Engineering Physics, POLYTECHNIQUE MONTRÉAL'S INSTITUTIONAL (2013)
Khanouki, H.A: Development of erosion equations for solid particle and liquid droplet impact. PhD Thesis, The University of Tulsa (2015)
Standard, A.S.T.M.: G76, standard test method for conducting erosion tests by solid particle impingement using gas jets. ASTM International, West Conshohocken (2013)
Yang, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.E.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D.: Constitutive models for temperature-, strain rate-and time-dependent behaviors of ionomers in laminated glass. J. Mater. Sci. 58(8), 3608–3624 (2023)
Che, J.; Zhou, T.; Liang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.: An integrated Johnson-Cook and Zerilli-Armstrong model for material flow behavior of Ti–6Al–4V at high strain rate and elevated temperature. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40, 1–10 (2018)
Samantaray, D.; Mandal, S.; Borah, U.; Bhaduri, A.K.; Sivaprasad, P.V.: A thermo-viscoplastic constitutive model to predict elevated-temperature flow behaviour in a titanium-modified austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 526(1–2), 1–6 (2009)
Johnson, G.R: A constitutive model and date for metals subject to large strains, high strain rate and high temperatures. In: Proc. of 7th Int. Symp. on Ballistics, The Hague (1983)
Johnson, G.R.; Cook, W.H.: Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 21(1), 31–48 (1985)
Khan, A.S.; Suh, Y.S.; Kazmi, R.: Quasi-static and dynamic loading responses and constitutive modeling of titanium alloys. Int. J. Plast 20(12), 2233–2248 (2004)
Farrokh, B.; Khan, A.S.: Grain size, strain rate, and temperature dependence of flow stress in ultra-fine grained and nanocrystalline Cu and Al: synthesis, experiment, and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plast 25(5), 715–732 (2009)
Khan, A.S.; Zhang, H.; Takacs, L.: Mechanical response and modeling of fully compacted nanocrystalline iron and copper. Int. J. Plast 16(12), 1459–1476 (2000)
Barkoula, N.M.; Karger-Kocsis, J.: Solid particle erosion of unidirectional GF reinforced EP composites with different fiber/matrix adhesion. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 21(15), 1377–1388 (2002)
Ravindran, S.; Gandhi, V.; Lawlor, B.; Ravichandran, G.: Mesoscale shock structure in particulate composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 174, 105239 (2023)
Najafi, A.; Khoddami, A.; Akbarzadeh, S.: Numerical and experimental investigation of correlation between wear and temperature in dry sliding of polyethylene-zinc oxide nanocomposite. Modares Mech. Eng. 20(10), 2547–2558 (2020)
Chen, Q.; Li, D.Y.: Computer simulation of solid particle erosion. Wear 254(3–4), 203–210 (2003)
Desale, G.R.; Gandhi, B.K.; Jain, S.C.: Effect of erodent properties on erosion wear of ductile type materials. Wear 261(7–8), 914–921 (2006)
Feng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Du, M.; Fan, C.; Zhang, K.: Modeling method and experimental study on the random distribution of abrasive particles in the jet cutting process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 121(5–6), 3173–3191 (2022)
Ballout, Y.A.; Mathis, J.A.; Talia, J.E.: Effect of particle tangential velocity on erosion ripple formation. Wear 184(1), 17–21 (1995)
Wu, W.; Goretta, K.C.; Routbort, J.L.: Erosion of 2014 Al reinforced with SiC or Al2O3 particles. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 151(1), 85–95 (1992)
Chen, L.; Luo, G.; Liu, K.; Ma, J.; Yao, B.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.: Bonding of glass-based microfluidic chips at low-or room-temperature in routine laboratory. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 119(1), 335–344 (2006)
Bararpour, S.M.; Jamshidi Aval, H.; Jamaati, R.; Javidani, M.: Comparison of finite element and smoothed-particle hydrodynamics models in the simulation of hypereutectic Al-Si alloy friction surfacing: calibrations from experiments. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 23(4), 224 (2023)
Bitter, J.G.A.: A study of erosion phenomena part I. Wear 6(1), 5–21 (1963)
Bitter, J.G.A.: A study of erosion phenomena: part II. Wear 6(3), 169–190 (1963)
Wan, M.; Ye, X.Y.; Wen, D.Y.; Zhang, W.H.: Modeling of machining-induced residual stresses. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 1–35 (2019)
Alharbi, N.: Energy-efficient ultrasonic shot peening as post-treatment for SS316L fabricated by laser powder bed fusion. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47(7), 9119–9136 (2022)
Sahin, B.; Gov, I.; Kalak, M.; Koca, M.S.; Gov, K.: Surface treatment of AISI 304 stainless steel by GOV (Flow Peening) process. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 49(2), 1–27 (2023)
Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, R.: Compressive residual stress introduced by shot peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 73(1–3), 64–73 (1998)
Finnie, I.: Erosion of surfaces by solid particles. Wear 3(2), 87–103 (1960)
Neilson, J.H.; Gilchrist, A.: Erosion by a stream of solid particles. Wear 11(2), 111–122 (1968)
Hashish, M: An improved model of erosion by solid particle impact. In: Erosion by Liquid and Solid Impact, Seventh International Conference (p. 66), (1987)
Cao, Z.C.; Wang, M.; Yan, S.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H.: Surface integrity and material removal mechanism in fluid jet polishing of optical glass. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 311, 117798 (2023)
Funding
This study was funded by the authors. The authors guarantee that there is no grant by other people or organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK (first author) contributed to conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, data curation, writing—original draft, and formal analysis. BM (corresponding author) contributed to review & editing, supervision, and project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. They guarantee that there are no conflicts, financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) our work.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khoddami, A., Mohammadi, B. A Novel Simulation Model for Multiple Solid Particle Erosion in Micro-blasting Process of Ti-6Al-4V Dental Implant Alloy Considering Actual Geometry of Impacting Particles. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09058-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09058-7