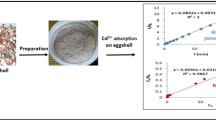
Abstract
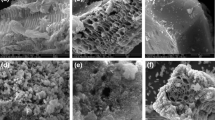
While emerging pollutants are being detected in water bodies globally, a significant amount of solid waste that could be used for effluent remediation is being discarded. This not only reduces the half-life of landfills but also contributes to environmental pollution. Of these, eggshells (ES) are one of the most discarded food waste items worldwide. This paper presents the development and characterization of ES-based adsorbent for the removal of oxytetracycline (OTC), an emerging pharmaceutical pollutant, from aqueous solutions. The sorption of OTC on ES and ES-derived materials has not been previously studied. The ES was modified by removing the organic layer and both materials were used to grow Fe oxides, which can impart magnetic response to allow indirect manipulation or the addition of new sorption sites. Two methodologies were employed to synthesize Fe oxides: alkaline oxidation in the presence of nitrate and impregnation–pyrolysis (IP), which have not been used previously for developing magnetic ES. The materials developed by IP exhibit the highest total specific surface area and display a magnetic response due to the presence of magnetite and maghemite. Moreover, they exhibit a negative zeta potential over a wide range of pH values. All materials were able to adsorb OTC at pH 3, 7, or 9, indicating that ES (the simplest material) and ESIP (composite with good enough magnetic response) are suitable for removing OTC from aqueous solution. ES is recommended when indirect manipulation is not necessary, whereas ESIP is recommended when it is required. In order to explore the potential for reuse of the composite-pollutant materials, their antibacterial capacity against E. coli and E. faecium was evaluated. The findings of the present work contribute to the development of a circular economy by reducing waste generation, minimizing the consumption of natural resources, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, while improving environmental protection.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Quina, M.J.; Soares, M.A.R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.: Applications of industrial eggshell as a valuable anthropogenic resource. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 123, 176–186 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.09.027
Peigneux, A.; Puentes-Pardo, J.D.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Hincke, M.T.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.: Development and characterization of magnetic eggshell membranes for lead removal from wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 192, 110307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110307
Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kang, Z.-W.; Gao, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, D.-P.: Waste eggshell membrane-assisted synthesis of magnetic CuFe2O4 nanomaterials with multifunctional properties (adsorptive, catalytic, antibacterial) for water remediation. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 612, 125874 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125874
Vijayaraghavan, K.; Joshi, U.M.: Chicken Eggshells Remove Pb(II) Ions from Synthetic Wastewater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 30, 67–73 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2012.0038
Baláž, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Baláž, P.; Zorkovská, A.; Danková, Z.; Briančin, J.: Adsorption of cadmium(II) on waste biomaterial. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 454, 121–133 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.03.046
Flores-Cano, J.V.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Mendoza-Barron, J.; Guerrero-Coronado, R.M.; Aragón-Piña, A.; Labrada-Delgado, G.J.: Sorption mechanism of Cd(II) from water solution onto chicken eggshell. Appl. Surf. Sci. 276, 682–690 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.03.153
Tizo, M.S.; Blanco, L.A.V.; Cagas, A.C.Q.; Dela Cruz, B.R.B.; Encoy, J.C.; Gunting, J.V.; Arazo, R.O.; Mabayo, V.I.F.: Efficiency of calcium carbonate from eggshells as an adsorbent for cadmium removal in aqueous solution. Sustain. Environ. Res. 28, 326–332 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2018.09.002
Ahmad, R.; Kumar, R.; Haseeb, S.: Adsorption of Cu2+ from aqueous solution onto iron oxide coated eggshell powder: Evaluation of equilibrium, isotherms, kinetics, and regeneration capacity. Arab. J. Chem. 5, 353–359 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.09.003
Chojnacka, K.: Biosorption of Cr(III) ions by eggshells. J. Hazard. Mater. 121, 167–173 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.02.004
Yeddou Mezenner, N.; Bensmaili, A.: Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of iron adsorption by eggshells in a batch system: effect of temperature. Desalination 206, 127–134 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.04.052
Yeddou Mezenner, N.Y.; Bensmaili, A.: Kinetics and thermodynamic study of phosphate adsorption on iron hydroxide-eggshell waste. Chem. Eng. J. 147, 87–96 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.06.024
Bhaumik, R.; Mondal, N.; Das, B.; Roy, P.; Pal, K.; Das, C.; Banerjee, A.; Datta, J.: Eggshell powder as an adsorbent for removal of fluoride from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Chem. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/790401
Moosavi, A.; Amooey, A.A.; Mir, A.A.; Marzbali, M.H.: Extraordinary adsorption of acidic fuchsine and malachite green onto cheap nano-adsorbent derived from eggshell. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 28, 1591–1602 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.02.031
Chowdhury, S.; Das, P.: Utilization of a domestic waste-Eggshells for removal of hazardous Malachite Green from aqueous solutions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 31, 415–425 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10564
Ehrampoush, M.H.; Ghanizadeh, G.; Ghaneian, M.T.: Equilibrium and kinetics study of reactive red 123 dye removal from aqueous solution by adsorption on eggshell. Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng. 8(2), 101–108 (2011)
Zulfikar, M.A.; Mariske, E.D.; Djajanti, S.D.: Adsorption of lignosulfonate compounds using powdered eggshell, Songklanakarin. J. Sci. Technol. 34, 309–316 (2012)
Tsai, W.-T.; Hsien, K.-J.; Hsu, H.-C.; Lin, C.-M.; Lin, K.-Y.; Chiu, C.-H.: Utilization of ground eggshell waste as an adsorbent for the removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 1623–1629 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.010
Köse, T.E.; Kıvanç, B.: Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solutions using calcined waste eggshell. Chem. Eng. J. 178, 34–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.09.129
Eletta, O.A.A.; Ajayi, O.A.; Ogunleye, O.O.; Akpan, I.C.: Adsorption of cyanide from aqueous solution using calcinated eggshells: Equilibrium and optimisation studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 1367–1375 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.01.020
Elkady, M.F.; Ibrahim, A.M.; El-Latif, M.M.A.: Assessment of the adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic for the potential removal of reactive red dye using eggshell biocomposite beads. Desalination 278, 412–423 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.05.063
Barraqué, F., Montes, M.L., Fernandéz, M.A., Mercader, R.C., Candal, R., Torre Sánchez, R. maría: Synthesis of high-saturation magnetization composites by montmorillonite loading with hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium ions and magnetite nucleation for improved effluent sludge handling and dye removal. Appl. Phys. A.. 736 (2020)
Montes, M.L.; Barraqué, F.; Bursztyn Fuentes, A.L.; Taylor, M.A.; Mercader, R.C.; Miehé-Brendlé, J.; Torres Sánchez, R.M.: Effect of synthetic beidellite structural characteristics on the properties of beidellite/Fe oxides magnetic composites as Sr and Cs adsorbent materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 245, 122760 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122760
Mudhoo, A.; Sillanpää, M.: Magnetic nanoadsorbents for micropollutant removal in real water treatment: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 4393–4413 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01289-6
He, C.; Fang, K.; Gong, H.; Liu, J.; Song, X.; Liang, R.; He, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, K.: Advanced organic recovery from municipal wastewater with an enhanced magnetic separation (EMS) system: Pilot-scale verification. Water Res. 217, 118449 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118449
Nithya, R.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.; Sathya, A.B.; Sivashankar, R.: Magnetic materials and magnetic separation of dyes from aqueous solutions: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 1275–1294 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01149-9
Urruchua, F.C.; Fernández, M.A.; Jaworski, M.; Mendoza Zelis, P.; Olivelli, M.S.; Montes, M.L.: Yerba mate waste: transformation to magnetic composites for the adsorption of chemically diverse pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 110824 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110824
Barraqué, F.; Montes, M.L.; Fernández, M.A.; Candal, R.; Torres Sánchez, R.M.; Marco-Brown, J.L.: Arsenate removal from aqueous solution by montmorillonite and organo-montmorillonite magnetic materials. Environ. Res. 192, 110247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110247
Zelaya Soulé, M.E.; Barraqué, F.; Morantes, C.F.; Flores, F.M.; Fernández, M.A.; Sánchez, R.M.T.; Montes, M.L.: Magnetic nanocomposite based on montmorillonite, Fe oxides, and hydrothermal carbon: Synthesis, characterization and pollutants adsorption tests. Materialia 15, 100973 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100973
Barraqué, F.; Montes, M.L.; Fernández, M.A.; Mercader, R.C.; Candal, R.J.; Torres Sánchez, R.M.: Synthesis and characterization of magnetic-montmorillonite and magnetic-organo-montmorillonite: Surface sites involved on cobalt sorption. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 376–384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.07.052
Rocha, L.S.; Pereira, D.; Sousa, É.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I.; Calisto, V.: Recent advances on the development and application of magnetic activated carbon and char for the removal of pharmaceutical compounds from waters: a review. Sci. Total. Environ. 718, 137272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137272
Gao, F.; Xu, Z.; Dai, Y.: Removal of tetracycline from wastewater using magnetic biochar: a comparative study of performance based on the preparation method. Environ. Technol. Innov. 24, 101916 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101916
Rodrigo, P.M.; Navarathna, C.; Pham, M.T.H.; McClain, S.J.; Stokes, S.; Zhang, X.; Perez, F.; Gunatilake, S.R.; Karunanayake, A.G.; Anderson, R.; Thirumalai, R.V.K.G.; Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T.E.: Batch and fixed bed sorption of low to moderate concentrations of aqueous per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on Douglas fir biochar and its Fe3O4 hybrids. Chemosphere 308, 136155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136155
Elanchezhiyan, S.S.D.; Karthikeyan, P.; Rathinam, K.; Hasmath-Farzana, M.; Park, C.M.: Magnetic kaolinite immobilized chitosan beads for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from an aqueous environment. Carbohydr. Polym. 261, 117892 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117892
Ren, J.; Bopape, M.; Setshedi, K.; Kitinya, J.; Onyango, M.: Sorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) by low-cost magnetic eggshells-Fe3O4 powder. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 18, 221–231 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2298/CICEQ110919063R
Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Hatamifard, A.: Waste chicken eggshell as a natural valuable resource and environmentally benign support for biosynthesis of catalytically active Cu/eggshell, Fe3O4/eggshell and Cu/Fe3O4/eggshell nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 191, 209–227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.042
Ravi, T.; Sundararaman, S.: Synthesis and characterization of chicken eggshell powder coated magnetic nano adsorbent by an ultrasonic bath assisted co-precipitation for Cr(VI) removal from its aqueous mixture. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 103877 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103877
Prabowo, B.; Khairunnisa, T.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D.: Economic perspective in the production of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles by co-precipitation method. World Chem. Eng. J. 2, 1–4 (2018)
Fuentes, O.P.; Trujillo, D.M.; Sánchez, M.E.; Abrego-Perez, A.L.; Osma, J.F.; Cruz, J.C.: Embracing sustainability in the industry: a study of environmental, economic, and exergetic performances in large-scale production of magnetite nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 12, 760–772 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c05000
Tang, S.; Xia, D.; Yao, Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, J.; Yin, Y.; Shen, W.; Peng, Y.: Dye adsorption by self-recoverable, adjustable amphiphilic graphene aerogel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 554, 682–691 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.07.041
Mastrángelo, M.M.; Valdés, M.E.; Eissa, B.; Ossana, N.A.; Barceló, D.; Sabater, S.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Giorgi, A.D.N.: Occurrence and accumulation of pharmaceutical products in water and biota of urban lowland rivers. Sci. Total. Environ. 828, 154303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154303
Li, Z.; Qi, W.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ebrahim, S.; Long, J.: Degradation mechanisms of oxytetracycline in the environment. J. Integr. Agric. 18, 1953–1960 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62121-5
Jin, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z.: Enhanced removal of oxytetracycline from wastewater using bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles combined with ZIF-8 nanocomposites. J. Environ. Manage. 318, 115526 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115526
Martínez-Olivas, A.; Torres-Pérez, J.; Balderas-Hernández, P.; Reyes-López, S.Y.: Oxytetracycline sorption onto synthetized materials from hydroxyapatite and aluminosilicates. Water Air Soil Pollut. 231, 264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04638-3
Ramanayaka, S.; Sarkar, B.; Cooray, A.T.; Ok, Y.S.; Vithanage, M.: Halloysite nanoclay supported adsorptive removal of oxytetracycline antibiotic from aqueous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 384, 121301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121301
Bracco, E.B.; Marco-Brown, J.L.; Butler, M.; Candal, R.J.: Degradation of oxytetracycline and characterization of byproducts generated by Fenton or photo-Fenton like processes after adsorption on natural and iron(III)-modified montmorillonite clays. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 19, 100778 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2023.100778
Yuan, L.; Yan, M.; Huang, Z.; He, K.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; Hu, L.; Li, H.; Peng, M.; Huang, T.; Chen, G.: Influences of pH and metal ions on the interactions of oxytetracycline onto nano-hydroxyapatite and their co-adsorption behavior in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 541, 101–113 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.078
Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, R.; Wei, W.: Enhanced tetracycline adsorption onto hydroxyapatite by Fe(III) incorporation. J. Mol. Liq. 247, 171–181 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.09.110
Lach, J.; Ociepa-Kubicka, A.; Mrowiec, M.: Oxytetracycline adsorption from aqueous solutions on commercial and high-temperature modified activated carbons. Energies 14, 3481 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123481
Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hu, J.; Zhao, J.: Performance and mechanism of sycamore flock based biochar in removing oxytetracycline hydrochloride. Bioresour. Technol. 350, 126884 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.126884
Liang, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Qin, T.; Xie, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.: Efficient removal of oxytetracycline from aqueous solution using magnetic montmorillonite-biochar composite prepared by one step pyrolysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 695, 133800 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133800
Weerasooriyagedara, M.; Ashiq, A.; Gunatilake, S.R.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Vithanage, M.: Surface interactions of oxytetracycline on municipal solid waste-derived biochar–montmorillonite composite. Sustain. Environ. 8, 2046324 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/27658511.2022.2046324
Bartonkova, H.; Mashlan, M.; Medrik, I.; Jancik, D.; Zboril, R.: Magnetically modified bentonite as a possible contrast agent in MRI of gastrointestinal tract. Chem. Pap. 61, 413–416 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-007-0057-9
Lagarec, K., Rancourt, D.: Recoil-Mössbauer Spectral Analysis Software for Windows (1998)
Nakamoto, K.: Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds: Part A: Theory and Applications in Inorganic Chemistry (2008)
Sócrates, G.: Infrared Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts (2004)
Cui, H.; Ren, W.; Lin, P.; Liu, Y.: Structure control synthesis of iron oxide polymorph nanoparticles through an epoxide precipitation route. J. Exp. Nanosci. 8, 869–875 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2011.616541
Vandenberghe, R.E.; De Grave, E.: Application of Mössbauer spectroscopy in earth sciences. In: Yoshida, Y.; Langouche, G. (Eds.) Mössbauer Spectroscopy: Tutorial Book, pp. 91–185. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Graf, D.L.: Crystallographic tables for the rhombohedral carbonates. Am. Mineral. 46, 1283–1316 (1961)
Wechsler, B.A.; Lindsley, D.H.; Prewitt, C.T.: Crystal structure and cation distribution in titanomagnetites (Fe3−xTixO4). Am. Mineral. 69, 754–770 (1984)
Dunlop, D.J.: Superparamagnetic and single-domain threshold sizes in magnetite. J. Geophys. Res. 1896–1977(78), 1780–1793 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1029/JB078i011p01780
Mooney, R.W.; Keenan, A.G.; Wood, L.A.: Adsorption of water vapor by montmorillonite. I. Heat of desorption and application of BET theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 1367–1371 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01126a001
Torres Sánchez, R.M.: Mechanochemical effects on physicochemical parameters of homoionic smectite. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 127, 135–140 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(97)00105-2
Wan, J.; Simon, S.; Deluchat, V.; Dictor, M.-C.; Dagot, C.: Adsorption of As III, As V and dimethylarsinic acid onto synthesized lepidocrocite. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A. 48, 1272–1279 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2013.776916
Zhong, D.; Feng, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Du, X.; He, F.: Goethite and lepidocrocite catalyzing different double-oxidant systems to degrade chlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 72764–72776 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20855-1
Nurdin, I.: Ridwan, satriananda: the effect of pH and time on the stability of superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticle suspensions. MATEC Web Conf. 39, 01001 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20163901001
Kulshrestha, P.; Giese, R.F.; Aga, D.S.: Investigating the molecular interactions of oxytetracycline in clay and organic matter: insights on factors affecting its mobility in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4097–4105 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/es034856q
Nguyen, D.T.C.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Nguyen, C.N.Q.; Pham, L.H.A.; Le, H.T.N.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Tran, T.V.: Box-Behnken design, kinetic, and isotherm models for oxytetracycline adsorption onto Co-based ZIF-67. Appl. Nanosci. 11, 2347–2359 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01954-w
Xie, H.; Pan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Zou, G.; Du, L.; Guo, X.: Micro- and nano-plastics play different roles in oxytetracycline adsorption on natural zeolite: additional adsorbent and competitive adsorbate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 109648 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109648
Acknowledgements
OL, HEC, and FCU acknowledge CONICET’s doctoral scholarship; all the authors acknowledge CONICET, CETMIC, and IFLP who provided the infrastructure for the study. Authors acknowledge the financial support from the Argentine Ministry of Science (ANPCyT—PICT 2018-01536), Exactas Sciences Faculty, UNLP (EX002), and CONICET (PUE 066, PIBBA 0043).
Funding
This study was financially supported by the projects from the Argentine Ministry of Science (ANPCyT—PICT 2018-01536), Exactas Sciences Faculty, UNLP (EX002), and CONICET (PUE 066, PIBBA 0043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by OL, MAF, and MLM. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez, O., Fernández, M.A., Horue, M. et al. Fe Oxides–Eggshell Composites: Development, Characterization, and Oxytetracycline Adsorption Test. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08815-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08815-y