Abstract
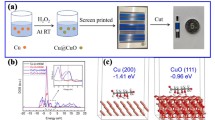
In this paper, the Cu/Cu2O and Cu/Cu2O/CuO electrodes were successfully fabricated from the copper layer of a printed circuit board using an electrical oxidation method. The physical properties of these samples were verified through X-Ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) measurements. The Cu/Cu2O and Cu/CuO/Cu2O electrodes were employed as non-enzyme sensors for the detection of glucose in the alkaline solution. The properties of electrodes were investigated using cyclic voltammetry and amperometry measurements with glucose solution. The results show that both types of electrodes can detect and quantify glucose concentrations. The Cu/Cu2O/CuO composite electrode demonstrated superior performance compared to the Cu/Cu2O electrode. The proposed sensor demonstrated a limit of detection of approximately 63.08 nM. Additionally, the proposed sensor was also investigated with various interfering substances, including ascorbic acid, urea, and table salt. The results revealed that the current intensity remained nearly unchanged for these substances, while it significantly increased from 0.3 to 2.5 mA/cm2 for glucose. With these achieved results, the developed system shows promise for application in glucose testing systems, benefiting diabetic patients in the future.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, H.C.; Lee, A.R.: Recent developments in blood glucose sensors. J. Food Drug Anal. 23(2), 191–200 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFDA.2014.12.001
Wu, P.; Shao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jin, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.: Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase assembled on graphene and application to glucose detection. Electrochim. Acta 55(28), 8606–8614 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ELECTACTA.2010.07.079
Yoshida, H.; Sakai, G.; Mori, K.; Kojima, K.; Kamitori, S.; Sode, K.: Structural analysis of fungus-derived FAD glucose dehydrogenase. Nat. Publ. Gr. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13498
Yoo, S.; Min, K.; Tae, G.; Han, M.S.: A long-term stable paper-based glucose sensor using a glucose oxidase-loaded, Mn2BPMP-conjugated nanocarrier with a smartphone readout. Nanoscale 13(8), 4467–4474 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR06348G
Jeon, W.Y.; Kim, H.H.; Choi, Y.B.: Development of a glucose sensor based on glucose dehydrogenase using polydopamine-functionalized nanotubes. Membranes (Basel). 11(6), 384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/MEMBRANES11060384/S1
Jeon, W.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jang, H.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, U.S.; Kim, H.H.; Choi, Y.B.A.: Stable glucose sensor with direct electron transfer, based on glucose dehydrogenase and chitosan hydro bonded multi-walled carbon nanortubes. Biochem. Eng. J. 187, 108589 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BEJ.2022.108589
Hwang, D.W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D.: Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors – A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 1033, 1–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2018.05.051
Wei, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, J.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Shi, X.; Lu, W.; Sun, X.: Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: recent progress and perspectives. Chem. Commun. 56(93), 14553–14569 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC05650B
Lakshmy, S.; Santhosh, S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Rout, C.S.; Chakraborthy, B.: A review of electrochemical glucose sensing based on transition metal phosphides. J. Appl. Phys. 133(7), 70702 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0111591/2876617
Niu, X.; Li, X.; Pan, J.; He, Y.; Qiu, F.; Yan, Y.: Recent advances in non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on non-precious transition metal materials: opportunities and challenges. RSC Adv. 6(88), 84893–84905 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA12506A
Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X.: Advances in non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on metal oxides. J. Mater. Chem. B 4(46), 7333–7349 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB02037B
Dong, Q.; Ryu, H.; Lei, Y.: Metal oxide based non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors for glucose detection. Electrochim. Acta 370, 137744 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ELECTACTA.2021.137744
Harper, A.; Anderson, M.R.: Electrochemical glucose sensors—developments using electrostatic assembly and carbon nanotubes for biosensor construction. Sensors 10(9), 8248–8274 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3390/S100908248
Wei, H.; Xu, Q.; Li, A.; Wan, T.; Huang, Y.; Cui, D.; Pan, D.; Dong, B.; Wei, R.; Naik, N.; Guo, Z.: Dendritic core-shell copper-nickel alloy@metal oxide for efficient non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 337, 129687 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2021.129687
Khayyat, S.A.; Ansari, S.G.; Umar, A.: Glucose Sensor Based on Copper Oxide Nanostructures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14(5), 3569–3574 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1166/JNN.2014.7918
Cheng, C.E.; Tangsuwanjinda, S.; Cheng, H.M.; Lee, P.H.: Copper oxide decorated zinc oxide nanostructures for the production of a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Coatings 11(8), 936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/COATINGS11080936
Waqas, M.; Wu, L.; Tang, H.; Liu, C.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J.; Chen, W.: Cu2O microspheres supported on sulfur-doped carbon nanotubes for glucose sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3(5), 4788–4798 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSANM.0C00847/SUPPL_FILE/AN0C00847_SI_001.PDF
Mamleyev, E.R.; Weidler, P.G.; Nefedov, A.; Szabó, D.V.; Islam, M.; Mager, D.; Korvink, J.G.: Nano- and microstructured copper/copper oxide composites on laser-induced carbon for enzyme-free glucose sensors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4(12), 13747–13760 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSANM.1C03149/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/AN1C03149_0007.JPEG
Zhong, Y.; Shi, T.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Huang, Y.; Tao, X.; Liao, G.; Tang, Z.: Ultrasensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on different copper oxide nanostructures by in-situ growth. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 236, 326–333 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2016.06.020
Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.: One-dimensional copper oxide nanotube arrays: biosensors for glucose detection. RSC Adv. 4(3), 1449–1455 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA45598J
Inyang, A.; Kibambo, G.; Palmer, M.; Cummings, F.; Masikini, M.; Sunday, C.; Chowdhury, M.: One step copper oxide (CuO) thin film deposition for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose detection. Thin Solid Films 709, 138244 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TSF.2020.138244
Sridara, T.; Upan, J.; Saianand, G.; Tuantranont, A.; Karuwan, C.; Jakmunee, J.: Non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor based on carbon nanodots and copper oxide nanocomposites electrode. Sensors 20(3), 808 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/S20030808
Gao, Z.; Liu, J.; Chang, J.; Wu, D.; He, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, F.; Jiang, K.: Mesocrystalline Cu2O hollow nanocubes: synthesis and application in non-enzymatic amperometric detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. CrystEngComm 14(20), 6639–6646 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CE25498K
Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Du, G.; He, X.; Xi, Y.: Synthesis of CuO nanostructures and their application for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 144(1), 220–225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2009.09.067
Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.: Hydrothermal synthesis of Cu2O/CuO/hierarchical porous N-doped activated carbon with exceptional electrochemical performance. J. Energy Storage 60, 106600 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EST.2022.106600
Kim, A.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Cho, K.; Woo, J.Y.; Lee, Y.; Han, S.H.; Byun, D.; Choi, W.; Lee, J.K.: One-step catalytic synthesis of CuO/Cu2O in a graphitized porous C matrix derived from the cu-based metal-organic framework for Li- and Na-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(30), 19514–19523 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSAMI.6B05973/SUPPL_FILE/AM6B05973_SI_001.PDF
Wang, L.H.; Gao, S.; Ren, L.L.; Zhou, E.L.; Qin, Y.F.: The synergetic effect induced high electrochemical performance of CuO/Cu2O/Cu nanocomposites as lithium-ion battery anodes. Front. Chem. 9, 1035 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2021.790659/BIBTEX
Siddiqui, H.; Parra, M.R.; Haque, F.Z.: Optimization of process parameters and its effect on structure and morphology of CuO nanoparticle synthesized via the sol−gel technique. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 87(1), 125–135 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-018-4663-5/FIGURES/7
Ujjain, S.K.; Roy, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Singha, S.; Khare, K.: Uniting superhydrophobic, superoleophobic and lubricant infused slippery behavior on copper oxide nano-structured substrates. Sci. Reports 6(1), 1–10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35524
Lu, C.; Li, Z.; Ren, L.; Su, N.; Lu, D.; Liu, Z.: In situ oxidation of Cu2O crystal for electrochemical detection of glucose. Sensors 19(13), 2926 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/S19132926
Ye, J.S.; Liu, Z.T.; Lai, C.C.; Lo, C.T.; Lee, C.L.: Diameter effect of electrospun carbon fiber support for the catalysis of Pt nanoparticles in glucose oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 283, 304–312 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2015.07.071
Shi, L.; Zhu, X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, H.; Lan, M.: Encapsulating Cu nanoparticles into metal-organic frameworks for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 227, 583–590 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2015.12.092
Huo, K.; Fu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Gao, B.; Mooni, S.; Li, Y.; Fu, J.: Phase separation induced rhizobia-like Ni nanoparticles and TiO2 nanowires composite arrays for enzyme-free glucose sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 244, 38–46 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2016.12.088
Mu, Y.; Jia, D.; He, Y.; Miao, Y.; Wu, H.L.: Nano nickel oxide modified non-enzymatic glucose sensors with enhanced sensitivity through an electrochemical process strategy at high potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26(6), 2948–2952 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOS.2010.11.042
Huo, H.; Guo, C.; Li, G.; Han, X.; Xu, C.: Reticular-vein-like Cu@Cu2O/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. RSC Adv. 4(39), 20459–20465 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA02390K
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Vietnam Ministry of Science and Technology under Grant NĐT.101.TW/21. Chi Tran Nhu was funded by the Master, PhD Scholarship Programme of Vingroup Innovation Foundation (VINIF), code VINIF.2023.TS.016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tran Nhu, C., Bui Thanh, T., Chu Duc, T. et al. Development of a Non-Enzyme Sensor to Detect Glucose Based on the Modification of Copper Electrode. Arab J Sci Eng (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08594-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08594-y