Abstract
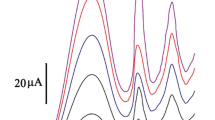
Sensitive and selective detection of hydroxylamine (HX) in environmental samples, particularly in the presence of phenol, is of significant importance. Herein, we present an electrochemical sensor based on a carbon paste electrode (CPE) modified with magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles (NPs) and 3,4-dihydroxy benzaldehyde, 2-(Phenyl) hydrazine (DHP), for the simultaneous determination of hydroxylamine and phenol. Employing voltammetric techniques, we investigated the electrocatalytic oxidation of hydroxylamine using the DHP/MgO NPs/CPE electrode. Under optimized conditions (pH = 7), the sensor exhibited a low detection limit of 1.7 μM and a wide linear range of 5.0–650.0 μM for hydroxylamine. The results revealed that the modified electrode significantly enhanced the oxidation activity of HX, resulting in a notable increase in current response compared to the bare electrode. The altered electrode demonstrated satisfactory stability, selectivity, and sensitivity for the detection of hydroxylamine. Furthermore, the developed electrode was successfully utilized for the determination of hydroxylamine in real drinking water samples. The satisfactory recoveries for HX (98.0–102.2%) indicated the high performance and reliable of the proposed method for the assessment of hydroxylamine in water samples. Distinct anodic peaks were observed in the differential pulse voltammetry responses of hydroxylamine and phenol at the surface of the proposed electrode, indicating the feasibility of simultaneous determination of these two compounds. In conclusion, the electrochemical sensor, using MgO NPs and DHP modification, detects hydroxylamine with precision and enables environmental monitoring and water quality assessment.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data and material are available and can be presented in the case of needed.
References
Sadeghi, R.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Beitollahi, H.; Ranjbarha, Z.; Zanousi, M.B.P.: A new strategy for determination of hydroxylamine and phenol in water and waste water samples using modified nanosensor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20(9), 6584–6593 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1733-7
Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Ma, S.: Fabrication of highly sensitive and stable hydroxylamine electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles and metal–metalloporphyrin framework modified electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(28), 18173–18181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b04819
Afkhami, A.; Madrakian, T.; Maleki, A.: Spectrophotometric determination of hydroxylamine and nitrite in mixture in water and biological samples after micelle-mediated extraction. Anal. Biochem. 347(1), 162–164 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2005.09.018
Deepa, B.; Balasubramanian, N.; Nagaraja, K.S.: Spectrophotometric determination of hydroxylamine and its derivatives in pharmaceuticals. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 52(12), 1473–1475 (2004)
Frear, D.S.; Burrell, R.C.: Spectrophotometric method for determining hydroxylamine reductase activity in higher plants. Anal. Chem. 27(10), 1664–1665 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60106a054
Hu, B.; Tian, X.L.; Shi, W.N.; Zhao, J.Q.; Wu, P.; Mei, S.T.: Spectrophotometric determination of hydroxylamine in biological wastewater treatment processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15(2), 323–332 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1387-y
Seike, Y.; Fukumori, R.; Senga, Y.; Oka, H.; Fujinaga, K.; Okumura, M.: A simple and sensitive method for the determination of hydroxylamine in fresh-water samples using hypochlorite followed by gas chromatography. Anal. Sci. 20(1), 139–142 (2004)
Korte, W.D.: Determination of hydroxylamine in aqueous solutions of pyridinium aldoximes by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV and fluorometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 603(1–2), 145–150 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(92)85355-W
Christova, R.; Ivanova, M.; Novkirishka, M.: Indirect potentiometric determination of arsenite, sulphite, ascorbic acid, hydrazine and hydroxylamine with an iodide-selective electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 85(2), 301–307 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)84695-X
Canterford, D.R.: Polarographic determination of hydroxylamines: application to analysis of photographic processing solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 98(2), 205–214 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)84047-2
Banaei, M.; Benvidi, A.; Abbasi, Z.; Tezerjani, M.D.; Akbari, A.: Electocatalytic oxidation of hydroxylamine at an imidazole derivative-TiO2 nanoparticle carbon sensor: determination of hydroxylamine and phenol as pollutant agents. Analyt. Bioanalyt. Electrochem. 11(6), 757–773 (2019)
Benvidi, A.; Jahanbani, S.; Akbari, A.; Zare, H.R.: Simultaneous determination of hydrazine and hydroxylamine on a magnetic bar carbon paste electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanoparticles and a heterogeneous mediator. J. Electroanal. Chem. 758, 68–77 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.03.010
Foroughi, M.M.; Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Hamzavi, M.; Parvan, H.: Hydroxylamine electrochemical sensor based on a modified carbon nanotube paste electrode: application to determination of hydroxylamine in water samples. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 9(6), 2955–2965 (2014)
Hajisafari, M.; Nasirizadeh, N.: An electrochemical nanosensor for simultaneous determination of hydroxylamine and nitrite using oxadiazole self-assembled on silver nanoparticle-modified glassy carbon electrode. Ionics 23(6), 1541–1551 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1962-0
Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.: Sensitive detection of hydroxylamine at a simple baicalin carbon nanotubes modified electrode. Talanta 93, 67–71 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.01.037
Ensafi, A.A.; Heydari-Bafrooei, E.; Rezaei, B.: Simultaneous detection of hydroxylamine and phenol using p-aminophenol-modified carbon nanotube paste electrode. Chin. J. Catal. 34(9), 1768–1775 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60652-4
Moghaddam, H.M.; Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Malakootian, M.; Maleh, H.K.: Simultaneous determination of hydroxylamine and phenol using a nanostructure-based electrochemical sensor. Environ. Monit. Assess. 186(11), 7431–7441 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3938-8
Nagal, V.; Khan, M.; Masrat, S.; Alam, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Ahmad, R.: Hexagonal cobalt oxide nanosheet-based enzymeless electrochemical uric acid sensor with improved sensitivity. New J. Chem. 47(9), 4206–4212 (2023)
Revenga-Parra, M.; Lorenzo, E.; Pariente, F.: Synthesis and electrocatalytic activity towards oxidation of hydrazine of a new family of hydroquinone salophen derivatives: application to the construction of hydrazine sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 107(2), 678–687 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.11.053
Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Cepria, G.: Electrocatalytic modified electrode for remote monitoring of hydrazines. Talanta 43(8), 1387–1391 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(96)01908-X
Li, M.; Guo, W.; Li, H.; Dai, W.; Yang, B.: Electrochemical biosensor based on one-dimensional MgO nanostructures for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Sens. Actuators B 204, 629 (2014)
Gupta, V.K.; Shamsadin-Azad, Z.; Cheraghi, S.; Agarwai, S.; Taher, M.A.; Karimi, F.: Electrocatalytic determination of L-cysteine in the presence of tryptophan using carbon paste electrode modified with MgO nanoparticles and acetylferrocene. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 4309–4318 (2018)
Le, Q.H.; Sajadi, S.M.; Karooby, E.; Ghahderijani, M.J.; Koochaki, A.; Shahgholi, M.; Inc, M.: Molecular dynamics method for numerical study of thermal performance of hexacosane PCM in a Cu-nanochannel. Eng. Anal. Boundary Elem. 151, 457–463 (2023)
Eskandari, V.; Sahbafar, H.; Karooby, E.; Heris, M.H.; Mehmandoust, S.; Razmjoue, D.; Hadi, A.: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) filter paper substrates decorated with silver nanoparticles for the detection of molecular vibrations of Acyclovir drug. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 298, 122762 (2023)
Krishnamoorthy, K.; Moon, J.Y.; Hyun, H.B.; Cho, S.K.; Kim, S.J.: Mechanistic investigation on the toxicity of MgO nanoparticles toward cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. 22(47), 24610–24617 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM35087D
Karooby, E.; Granpayeh, N.: Potential applications of nanoshell bow-tie antennas for biological imaging and hyperthermia therapy. Opt. Eng. 58(6), 065102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.OE.58.6.065102
Farasati Far, B.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Jahanbakhshi, M.; Mohammed, H.T.; Altimari, U.S.; Ansari, J.: Poly (3-thienylboronic acid) coated magnetic nanoparticles as a magnetic solid-phase adsorbent for extraction of methamphetamine from urine samples. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2022.2124169
Sharp, M.; Petersson, M.; Edström, K.: Preliminary determinations of electron transfer kinetics involving ferrocene covalently attached to a platinum surface. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 95(1), 123–130 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(79)80227-2
Farahani, K.Z.; Benvidi, A.; Rezaeinasab, M.; Abbasi, S.; Abdollahi-Alibeik, M.; Rezaeipoor-Anari, A.; Zarchi, M.A.K.; Abadi, S.S.A.D.M.: Potentiality of PARAFAC approaches for simultaneous determination of N-acetylcysteine and acetaminophen based on the second-order data obtained from differential pulse voltammetry. Talanta 192, 439–447 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.092
Zheng, L.; Song, J.F.: Curcumin multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode and its electrocatalytic activity towards oxidation of hydrazine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 135(2), 650–655 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.09.035
Ghoreishi, S.M.; Behpour, M.; Golestaneh, M.: Selective voltammetric determination of tartrazine in the presence of red 10B by nanogold-modified carbon paste electrode. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 60(1), 120–126 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201200143
Mohammadi, S.Z.; Beitollahi, H.; Mousavi, M.: Determination of hydroxylamine using a carbon paste electrode modified with graphene oxide nano sheets. Russ. J. Electrochem. 53(4), 374–379 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193517040097
Ardakani, M.M.; Karimi, M.A.; Mirdehghan, S.M.; Zare, M.M.; Mazidi, R.: Electrocatalytic determination of hydroxylamine with alizarin red S as a homogenous mediator on the glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 132(1), 52–59 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.01.012
Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R.: Fundamentals and applications: electrochemical methods. Electrochem. Methods 2(482), 580–632 (2001)
Premlatha, S.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Bapu, G.R.: Preparation of cobalt-RuO2 nanocomposite modified electrode for highly sensitive and selective determination of hydroxylamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 252, 375–384 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.013
Zare, H.R.; Nasirizadeh, N.: Electrocatalytic characteristics of hydrazine and hydroxylamine oxidation at coumestan modified carbon paste electrode. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Aspects Electroanal. 18(5), 507–512 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200503408
Zare, H.R.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Ajamain, H.; Sahragard, A.: Preparation, electrochemical behavior and electrocatalytic activity of chlorogenic acid multi-wall carbon nanotubes as a hydroxylamine sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 31(5), 975–982 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2011.02.023
Zare, H.R.; Sobhani, Z.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M.: Electrocatalytic oxidation of hydroxylamine at a rutin multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode: Improvement of the catalytic activity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 126(2), 641–647 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2007.04.015
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Yazd University Research Council for financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB: Project administration; Conceptualization; Methodology. FN: Software, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing—original draft. KZF: Methodology; Writing—Review and Editing; Data Curation; Validation. BFF: Writing—Review and Editing. EK: Validation; Visualization. AA: Methodology; Writing—Review and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Benvidi, A., Naserpour, F., Zarnousheh Farahani, K. et al. Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor Modified by Hydroquinone Derivative and Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Determination of Hydroxylamine and Phenol. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08444-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08444-x