Abstract
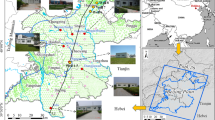
The dynamic variation of deep groundwater level and the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of land subsidence in Dezhou city were systematically analyzed based on a vast amount of monitoring data concerning groundwater level and land subsidence in this area. Taking the hydrogeological engineering characteristics in Dezhou city as the research background, a three-dimensional fluid–solid coupling model of land subsidence was established. The spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, transfer law, and essential reason of land subsidence in sand-clay interbed were analyzed and discussed by adopting the Biot’s poroelasticity theory, and the sensitivity analysis of soil parameters was carried out. The research results are as follows: (1) The soil shows different subsidence characteristics when pumping groundwater from different confined aquifers; (2) The land subsidence is smaller when pumping from the deeper and thicker confined aquifer, and the location of the maximum subsidence is not at the land surface; (3) The lower transfer rate of the additional stress in the aquifuge is the essential reason that the process of land subsidence has usually been lagged behind the pumping process; (4) The response degree and sensitivity of land subsidence to the main physical and mechanical parameters are different. The most sensitive parameter in aquifers is the permeability coefficient, followed by the elastic modulus, followed by the Biot–Willis coefficient and Poisson’s ratio. The most sensitive parameter in aquifuges is the elastic modulus, followed by the permeability coefficient, followed by the Biot–Willis coefficient and Poisson’s ratio.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ortega-Guerrero, A.; Rudolph, D.L.; Cherry, J.A.: Analysis of long-term land subsidence near Mexico City: field investigations and predictive modeling. Water Resour. Res. 35(11), 3327–3341 (1999)
Galloway, D.L.; Jones, D.R.; Ingebritsen, S.E.: Land subsidence in the united states. Center for Integrated Data Analytics Wisconsin Science Center, USGS circ 1182 (1999)
Booker, J.R.; Carter, J.P.: Long term subsidence due to fluid extraction from a saturated, anisotropic, elastic soil mass. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 39(1), 85–98 (1986)
Poland, J.F.: Guidebook to Studies of Land Subsidence Due to Ground-Water Withdrawal. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, London (1984)
Liu, C.H.; Pan, Y.W.; Liao, J.J.; Huang, C.T.; Ouyang, S.: Characterization of land subsidence in the Choshui River alluvial fan, Taiwan. Environ. Geol. 45(8), 1154–1166 (2004)
Holzer, T.L.; Johnson, A.I.: Land subsidence caused by groundwater withdrawal in urban areas. GeoJournal 11(3), 245–255 (1985)
Abidin, H.Z.; Andreas, H.; Gumilar, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Pohan, Y.E.; Deguchi, T.: Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its relation with urban development. Nat. Hazards 59(3), 1753–1771 (2011)
Phien-Wej, N.; Giao, P.H.; Nutalaya, P.: Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng. Geol. 82(4), 187–201 (2006)
Zhang, A.G.; Wei, Z.X.: Past present and future research on land subsidence in Shanghai City. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 29(05), 72–75 (2002). (in Chinese)
Duan, Y.H.: Research status on land subsidence and sustainable development in the 21st century of China. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 02, 3–7 (1998). (in Chinese)
Xue, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, S.J.; Li, Q.F.: Land subsidence in China and its problems. Quat. Sci. 23(6), 585–593 (2003). (in Chinese)
Yin, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.C.; Zhang, K.P.: Land subsidence and countermeasures for its prevention in China. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 16(02), 1–8 (2005). (in Chinese)
Cui, Z.D.; Tang, Y.Q.: Domestic and international recent situation and research of land subsidence disasters. China Earthq. Eng. J. 29(3), 275–278 (2007). (in Chinese)
Yuan, M.; Bai, J.W.; Qin, Y.K.: A review on land subsidence research. J. Suzhou Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 33(01), 1–5 (2016). (in Chinese)
Zhang, Y.W.: Formation Mechanism, Monitoring and Warning, Controlling Research of Subsidence of Dezhou in North China Plain. Shandong University, Jinan (2014). (in Chinese)
Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.W.; Han, J.M.; Xu, X.Q.: Susceptibility area regionalization of land subsidence based on extenics theory. Clust. Comput. 20(1), 53–66 (2017)
Jia, C.; Zhang, G.R.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.W.: Study on land subsidence induced by groundwater extraction and its engineering application: taking Dezhou area of Shandong as an example. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 37(04), 102–110 (2015). (in Chinese)
Cai, W.X.: Research on Relationship Between Deep Groundwater Exploitation and Land Subsidence in Dezhou. Jilin University, Jilin (2009). (in Chinese)
Zhao, Y.Q.: Research of the Ground Subsidence Disaster Caused by Groundwater Exploitation in Dezhou Regional. Jilin University, Jilin (2016). (in Chinese)
Shen, S.L.; Xu, Y.S.: Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 48(9), 1378–1392 (2011)
Shi, X.Q.; Xue, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.X.; Yu, J.: Characterization of regional land subsidence in Yangtze Delta, China: the example of Su-Xi-Chang area and the city of Shanghai. Hydrogeol. J. 16(3), 593–607 (2008)
Liu, Y.; Huang, H.J.: Characterization and mechanism of regional land subsidence in the Yellow River Delta, China. Nat Hazards 68(2), 687–709 (2013)
Yang, J.M.; Huo, W.W.: Linear s-lnr relation of land subsidence induced by group wells pumping distributed as line and area. Rock Soil Mech. 39(10), 3565–3572 (2018). (in Chinese)
Xing, Y.F.: Study on Influence Factors, Prediction and Evaluation of Land Subsidence in Cangzhou. China University Of Mining And Technology, Beijing (2017). (in Chinese)
Hu, J.P.: A Study on the Land Subsidence Effect After Prohibiting Extraction of Groundwater in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou Area. Nanjing University, Nanjing (2011). (in Chinese)
Wan, W.F.: Numerical Simulation of Land Subsidence Due to Groundwater Withdrawal in Xi’an and its Prevention Schemes. Chang’an University, Xi’an (2008). (in Chinese)
Ye, S.J.; Xue, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.F.; Wang, H.M.: Study on the deformation characteristics of soil layers in regional land subsidence model of Shanghai. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 27(02), 140–147 (2005). (in Chinese)
Ghazifard, A.; Moslehi, A.; Safaei, H.; Roostaei, M.: Effects of groundwater withdrawal on land subsidence in Kashan Plain, Iran. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 75(3), 1157–1168 (2016)
Jeanne, P.; Farr, T.G.; Rutqvist, J.; Vasco, D.W.: Role of agricultural activity on land subsidence in the San Joaquin Valley, California. J. Hydrol. 569, 462–469 (2019)
Smith, R.; Knight, R.: Modeling land subsidence using InSAR and Airborne Electromagnetic Data. Water Resour. Res. 55(4), 2801–2819 (2019)
Hutabarat, L.E.; Ilyas, T.: Mapping of land subsidence induced by groundwater extraction in Urban Areas as basic data for sustainability countermeasures. Int. J. Technol. 8(6), 1001–1011 (2017)
Rajabi, A.M.: A numerical study on land subsidence due to extensive overexploitation of groundwater in Aliabad plain, Qom-Iran. Nat. Hazards 93(2), 1085–1103 (2018)
Koster, K.; Erkens, G.; Zwanenburg, C.: A new soil mechanics approach to quantify and predict land subsidence by peat compression. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43(20), 10, 792–10,799 (2016)
Biot, M.A.: Mechanics of deformation and acoustic propagation in porous media. J. Appl. Phys. 33, 1482–1498 (1962)
Wen, H.C.; Wolfgang, K.: 3D Groundwater Modeling with PMWIN-A Simulation System for Modeling Groundwater Flow and Pollution. Springer, USA (2001)
Luo, Z.J.; Liu, J.B.; Li, L.: Three-dimensional full coupling numerical simulation of groundwater dewatering and land-subsidence in quaternary loose sediments. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 30(02), 193–198 (2008). (in Chinese)
Xu, S.; Miao, J.F.; Wei, J.H.; Xu, L.P.: Numerical simulation of dewatering of foundation pits and land subsidence based on 3D viscoelastic coupling model. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 30(S1), 41–45 (2008). (in Chinese)
Ye, S.J.; Xue, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Li, Q.F.: Land subsidence modeling based on the modified merchant model: a case study of Shanghai. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 47(03), 291–298 (2011). (in Chinese)
Wang, C.B.; Ding, W.Q.; Liu, W.J.; Qiao, Y.F.: Distribution law of soil settlement caused by unsteady dewatering of confined water. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 41(03), 361–367 (2013). (in Chinese)
Zheng, G.; Zeng, C.F.; Xue, X.L.: Settlement mechanism of soils induced by local pressure-relief of confined aquifer and parameter analysis. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 36(05), 802–817 (2014). (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, C., Di, S., Sun, X. et al. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Transfer Law of Land Subsidence in Sand-Clay Interbed Caused by Exploiting the Groundwater. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 5733–5753 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05149-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05149-3