Abstract
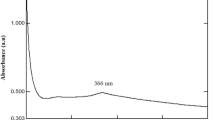
In the present study, the effect of in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxic properties was investigated in the biologically and chemically synthesized zinc oxide (ZnO)- and chitosan (CTS)-encapsulated ZnO (ZnO–CTS) nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were biologically synthesized using Phoenix loureiroi fruit and characterized using Fourier transform infrared, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, field emission scanning transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and ultra violet-diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. The biologically synthesized ZnO–CTS nanoparticles (B-ZnO–CTS) results revealed good chemical structure (H–N–H, O–H, C=O, Zn and O groups), crystalline size (18 nm), morphology (spherical), elemental composition (Zn = 61.10%; O = 25.86%; C = 13.04%) and optical properties (λ = 374 nm; Eg = 3.18 eV). The B-ZnO–CTS also exhibited higher DPPH· (IC50 = 419.32 µg/mL), ABTS·+ (45.61%), nitric oxide (21.28%), hydroxyl radical (77.10%) scavenging activities and superoxide anion radical production (27.89%). The cytotoxicity of B-ZnO–CTS revealed less hemolytic property (2.17%) and inhibited the Caco-2 cancerous cell viability (IC50 = 70.45 µg/mL). In conclusion, biological synthesis presents better prospects in pharmacotherapeutic applications in nano-herbal drug delivery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous.: The Wealth of India, Raw Materials, vol. 3, pp. 24. Council of Scientific and Industrial Publication and Information Directorate, New Delhi (1969)
Murugan, R.; Chandran, R.; Parimelazhagan, T.: Effect of in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion of Phoenix loureirii on polyphenolics, antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 74, 363–370 (2016)
Murugan, R.; Saravanan, S.; Parimelazhagan, T.: Study of intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of Phoenix loureiroi Kunth (Arecaceae) fruit. Biomed. Pharmacother. 93C, 156–164 (2017)
AbouZaid, O.A.R.; Sonbaty, S.M.E.; Sogheer, H.M.: Evaluation of protective and therapeutic role of zinc oxide nanoparticles and aloin on dextran sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Benha Vet. Med. J. 30, 208–218 (2016)
Wang, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, D.; Zhu, L.: Exploration of zinc oxide nanoparticles as a multitarget and multifunctional anticancer nanomedicine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 9, 39971–39984 (2017)
Schneider, J.C.: Can microparticles contribute to inflammatory bowel disease: innocuous or inflammatory? Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 232, 1–2 (2007)
Kang, T.; Guan, R.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, J.: In vitro toxicity of different sized ZnO nanoparticles in Caco-2 cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 1–8 (2013)
Song, Y.; Guana, R.; Lyub, F.; Kanga, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.: In vitro cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles to human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells. Mutat. Res. 769, 113–118 (2014)
Dutta, P.K.; Ravikumar, M.N.; Dutta, J.: Chitin and chitosan for versatile applications. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C. 42, 307–354 (2002)
Krishna Sailaja, A.; Amareshwar, P.; Chakravarty, P.: Chitosan nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 3, 474–484 (2010)
Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R.: Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2560–2566 (2011)
Prakash, T.; Jayaprakash, R.; Neri, G.; Kumar, S.: Synthesis of ZnO nanostructures by microwave irradiation using albumen as a template. J. Nanopart. Article ID 274894, 1–8 (2013)
Girigoswami, K.; Viswanathan, M.; Murugesan, R.; Girigoswami, A.: Studies on polymer-coated zinc oxide nanoparticles: UV-blocking efficacy and in vivo toxicity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 56, 501–510 (2015)
Parimelazhagan, T.: Pharmacological Assays of Plant Based Natural Products. Progress in Drug Research. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I.: Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 44, 276–287 (1971)
Rajavel, K.; Gomathi, R.; Manian, S.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T.: In vitro bacterial cytotoxicity of CNTs: reactive oxygen species mediate cell damage edges over direct physical puncturing. Langmuir 30, 592–601 (2014)
Das, D.; Nath, B.C.; Phukon, P.; Kalita, A.; Doluia, S.K.: Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and evaluation of antioxidant and cytotoxic activity. Colloid. Surf. B Biointerfaces 111, 556–560 (2013)
Mishra, A.; Chaudhary, N.: Study of povidone iodine loaded hydrogels as wound dressing material. Trend Biomater. Artif. Organ 23, 122–128 (2010)
Mosmann, T.: Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65, 55–63 (1983)
Yuvakkumar, R.; Suresh, J.; Saravanakumar, B.; Nathanaeld, A.J.; Honga, S.I.; Rajendran, V.: Rambutan peels promoted biomimetic synthesis of bioinspired zinc oxide nanochains for biomedical applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 137, 250–258 (2015)
Umar, H.; Kavaz, D.; Rizaner, N.: Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizia lebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 87–100 (2019)
Getie, S.; Belay, A.; Chandra Reddy, A.R.; Belay, Z.: Synthesis and characterizations of zinc oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. S8, 1–8 (2017)
Venu Gopal, V.R.; Susmita, K.: Effect of temperature on the morphology of ZnO nanoparticles: a comparative study. Appl. Nanosci. 7, 75–82 (2017)
Veena, R.; Srimathi, K.; Panigrahi, P.N.; Subramaniam, G.A.: Comparative approach for the synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles: green and chemical method. Int. J. Technol. Res. Appl. 38, 27–31 (2016)
Leceta, I.; Guerrero, P.; Ibarburu, I.; Duenasb, M.T.; De La Cabaa, K.: Characterization and antimicrobial analysis of chitosan based films. J. Food Eng. 116, 889–899 (2013)
Nagajyothi, P.C.; Cha, S.J.; Yang, I.J.; Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Kim, K.J.; Heung, M.S.: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Polygala tenuifolia root extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 146, 10–17 (2015)
Yan, E.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, D.: Synthesis and characterization of fluorescent chitosan-ZnO hybrid nanospheres. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 458–461 (2011)
Nagajyothi, P.C.; Sreekanth, T.V.M.; Tettey, C.O.; Jun, Y.I.; Mook, S.H.: Characterization, antibacterial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of ZnO nanoparticles using Coptidis Rhizoma. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 24, 4298–4303 (2014)
Shujahadeen, B.A.: Morphological and optical characteristics of chitosan(1-x):Cu°x (4 ≤ x≤12) based polymer nano-composites: optical dielectric loss as an alternative method for Tauc’s model. Nanomaterials 7, 1–15 (2017)
Qu, F.; Morais, P.C.: The pH dependence of the surface charge density in oxide-based semiconductor nanoparticles immersed in aqueous solution. IEEE Trans. Magn. 37, 2654–2656 (2001)
Kumar, B.; Smita, K.; Cumbal, L.; Debut, A.: Green approach for fabrication and applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 523869, 1–7 (2014)
Ranjith, K.S.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T.: Surfactant free, simple, morphological and defect engineered ZnO nanocatalyst: effective study on sunlight driven and reusable photocatalytic properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 329, 35–45 (2016)
Ranjith, K.S.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T.: Regeneration of an efficient, solar active hierarchial ZnO flower photocatalyst for repeatable usage: controlled desorption of poisoned species from active catalytic sites. RSC Adv. 7, 4983–4992 (2017)
Noudeh, G.D.; Sharififar, F.; Khatib, M.; Behravan, E.; Afzadi, M.A.: Study of aqueous extract of three medicinal plants on cell membrane-permeabilizing and their surface properties. Afric. J. Biotech. 9, 110–116 (2012)
Zohra, M.; Fawzia, A.: Hemolytic activity of different herbal extracts used in Algeria. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 5, 495–500 (2014)
Singhal, J.P.; Ray, A.R.: Synthesis of blood compatible polyamide block copolymers. Biomaterial 23, 1139–1145 (2002)
Fogh, J.; Fogh, J.M.; Orfeo, T.: One hundred and twenty seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 59, 221–226 (1977)
Oonsivilai, R.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Ninganond, S.: Antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity of Rang Chuet (Thunbergia laurifolia Lindl.) extracts. Asian J. Food Agro-Ind. 1, 116–128 (2008)
Elavarasan, N.; Kokila, K.; Inbasekar, G.; Sujatha, V.: Evaluation of photocatalytic activity, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles by Sechium edule leaf extract. Res. Chem. Intermed. 43, 3361–3376 (2017)
Liewhiran, C.; Seraphin, S.; Phanichphant, S.: Synthesis of nano-sized ZnO powders by thermal decomposition of zinc acetate using Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) Vent pulp as a dispersant. Curr. Appl. Phys. 6, 499–502 (2006)
Ong, C.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.: A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 536–551 (2018)
Song, Y.; Guana, R.; Lyub, F.; Kanga, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.: In vitro cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles to human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells. Mutat. Res. 769, 113–118 (2014)
Gunjan, K.; Hemali, P.; Pooja, M.; Sumitra, C.: Peltophorum pterocarpum flower-mediated synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of zno nanoparticles. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 3393–3401 (2018)
Stan, M.; Popa, A.; Toloman, D.; Silipas, T.; Cristian, D.: Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using extracts of Allium sativum, Rosmarinus officinalis and Ocimum basilicum. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 29, 228–236 (2016)
Lingaraju, K.; Raja, N.H.; Manjunath, K.; Basavaraj, R.B.; Nagabhushana, H.; Nagaraju, G.; Suresh, D.: Biogenic synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruta graveolens (L.) and their antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Appl. Nanosci. 6, 703–710 (2016)
Sathyabama, S.; Sankaranarayanan, S.: An in vitro biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using rich flavonoid extract from the petals of Delonix regia and evaluation of their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 7, 1112–1119 (2015)
Pavan Kumar, M.A.; Suresh, D.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S.C.: Beta vulgaris aided green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their luminescence, photocatalytic and antioxidant properties. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 130, 109 (2015)
Mahendiran, D.; Subash, G.; Arumai Selvan, D.; Rehana, D.; Senthil Kumar, R.; Kalilur Rahiman, A.: Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts of Aloe vera and Hibiscus sabdariffa: phytochemical, antibacterial, antioxidant and anti-proliferative studies. BioNanoScience 7, 530–545 (2017)
Rajakumar, G.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Mydhili, G.; Gomathi, T.; Chung, I.: Green approach for synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Andrographis paniculata leaf extract and evaluation of their antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and anti-inflammatory activities. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 41, 21–30 (2018)
Venkateasan, A.; Prabakaran, R.; Sujatha, V.: Phytoextract-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous leaves extract of Ipomoea pes-caprae (L).R.Br revealing its biological properties and photocatalytic activities. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2, 1–15 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The author (Murugan Rajan) acknowledges the support of Programa Nacional de Pós-doutorado (PNPD/CAPES-086/2013), Brazil, for postdoctoral fellowship. The authors also acknowledge Defence Research and Development Organization Centre for Life Sciences, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India, to carry out the characterization analysis.
Funding
Funding was provided by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (573781/2008-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajan, M., Anthuvan, A.J., Muniyandi, K. et al. Comparative Study of Biological (Phoenix loureiroi Fruit) and Chemical Synthesis of Chitosan-Encapsulated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and their Biological Properties. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 15–28 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04174-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04174-1