Abstract
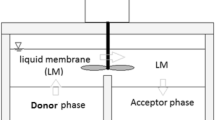
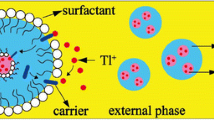
The extraction of cadmium from aqueous solution using kerosene as a bulk liquid membrane (BLM) with Tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) as a carrier was experimentally investigated under various operating conditions. The effects of feed and strip pH, feed initial concentration, TBP concentration, and strip to feed volume ratio on the cadmium ions transport efficiency were investigated. A stripping agent EDTA was used to enhance the transport efficiency of the cadmium ions. Flax and sesame oils were also considered as green liquid membrane alternatives to kerosene. They were evaluated in terms of extraction and separation efficiency. Cadmium extraction and stripping efficiencies of 89 and 94% were, respectively, obtained under specific conditions (100 ppm initial concentration of cadmium ions, 10% (v/v) TBP concentration, (1:2) strip to feed volume ratio, feed phase pH of 3, and strip phase pH of 11). The kinetics of \(\hbox {Cd}^{2+}\) transport across BLM was investigated using kinetic model derived from the kinetic law of two consecutive irreversible first-order model. Both flax and sesame oils were found less efficient than kerosene in cadmium extraction and stripping rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton, K.A.; Evans, L.J.: Cadmium adsorption capacity of selected Ontario soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 76(2), 183–189 (1996)
Tsezos, M.: Biosorption of metals: the experience accumulated and the outlook for technology development. Hydrometallurgy 59(2–3), 241–243 (2011)
Peany, H.S.; Rowe, D.R.; Techobangalos, G.: Environmental Engineering. McGraw Hill, New York (1985)
Orhan, Y.; Buyukgungor, H.: The removal of heavy metals by using agricultural waste. Water Sci. Technol. 28(2), 247–255 (1993)
Mirbagheri, S.A.; Hosseini, S.N.: Pilot plant investigation on petrochemical wastewater treatment for the removal of copper and chromium with the objective of reuse. Desalination 171(1), 85–93 (2005)
Larous, S.; Meniai, A.H.; Lehocine, M.B.: Experimental study of the removal of copper from aqueous solutions by adsorption using sawdust. Desalination 185(1–3), 483–490 (2005)
Sulaymon, A.H.; Mohammed, A.A.; Al-Musawi, T.J.: Competitive biosorption of lead, cadmium, copper, and arsenic ions using algae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20(5), 3011–3023 (2013)
Rao, K.S.; Mohapatra, M.; Ananad, S.; Venkateswarlu, P.: Review on cadmium removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2(7), 81–103 (2010)
Mohammed, A.A.; Ebrahim, S.E.; Alwared, A.I.: Flotation and sorptive flotation methods for removal of lead from wastewater using SDS as surfactant and barley husk as biosorbent. J. Chem. (2013)
Zouboulis, A.I.; Matis, K.A.: Biosorptive flotation for metal ions removal: the influence of surface tension. Desalination 248(1–3), 740–752 (2009)
Chaabane, T.; Taha, S.; Ahmed, M.T.; Maachi, R.; Dorange, G.: Removal of copper from industrial effluent using a spiral wound module: film theory and hydrodynamic approach. Desalination 200, 403–405 (2006)
Hatfield, T.L.; Kleven, T.L.; Pierce, D.T.: Electro chemical remediation of metal-bearing wastewaters, part I: copper removal from simulated mine drainage waters. J. Appl. Electrochem. 26(6), 567–574 (1996)
Escobar, C.; Soto-Salazar, C.; Toral, M.I.: Optimization of the electrocoagulation process for the removal of copper, lead and cadmium in natural waters and simulated wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 81(4), 384–391 (2006)
Ahluwalia, S.S.; Goyal, D.: Removal of heavy metals from waste tea leaves from aqueous solution. Eng. Life Sci. 5(2), 158–162 (2005)
Dimitrov, K.; Gancel, F.; Montastruca, L.; Nikov, I.: Liquid membrane extraction of bio-active amphiphilic substances: recovery of surfactin. Biochem. Eng. J. 42(3), 248–253 (2008)
Minhas, F.T.; Memon, S.; Bhanger, M.I.: Transport of Hg through bulk liquid membrane containing calix[4] arene thioalkyl derivative as a carrier. Desalination 262(1–3), 215–220 (2010)
Candela, A.M.; Benatti, V.; Palet, C.: Pre-concentration of uranium (VI) using bulk liquid and supported liquid membrane systems optimized containing bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid as carrier in low concentrations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 120, 172–179 (2013)
Malijevsk’y, A.: Physical Chemistry in Brief. Institute of Chemical Technology, Prague (2005)
Szpakowska, M.; Nagy, O.B.: Membrane material effect on copper coupled transport through liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 64(1–2), 129–143 (1991)
He, D.; Ma, M.; Zaho, Z.: Transport of cadmium ions through a liquid membrane containing amine extractants as carriers. J. Membr. Sci. 196(1), 53–59 (2000)
Aydan, Y.; Ahmet, K.; Korkomaz, H.; Mustafa, E.; Mustafa, Y.: Kinetic analysis of chromium ions transport through a bulk liquid membrane containing p-tert-butylcalix[4] arene dioxaoctylamid derivative. Sep. Purif. Technol. 59(1), 1–8 (2008)
Dalali, N.; Yavarizadeh, H.; Agrawal, Y.K.: Separation of zinc and cadmium from nickel and cobalt by facilitated transport through bulk liquid membrane using trioctyl methyl ammonium chloride as carrier. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 18(3), 1001–1005 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, A.A., Hussein, M.A. & Albdiri, A.D.Z. Application of Bulk Liquid Membrane Technique for Cadmium Extraction from Aqueous Solution. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 5851–5858 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-3039-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-3039-4