Abstract
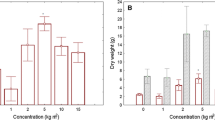
This study investigates the impact of sewage sludge application on nutrient uptake and growth parameters of larch seedlings (Larix decidua). Heavy metals and minerals distribution were also addressed. Sludge was applied at three loading rates (0, 30, and 60 Mg DW ha−1), and harvesting was done after 6 weeks. The results demonstrated that nitrogen and phosphorus contents increased significantly in top soil of pots receiving sludge, while no modification appeared in bottom soils. Similar results were obtained only at higher dose for Cu and Zn concentrations. However, no such difference was observed for total soil micronutrients. Despite a significant increase in plant nitrogen concentration, the use of sewage sludge did not affect larch seedling growth at this stage. Nitrate reductase activity decreased significantly with increasing sludge application rates. For all heavy metals, sludge application did not lead to an increase in plant concentrations, but the superoxide dismutase activity measured in needles and lateral roots increased significantly. It was concluded that sewage application brought about notable benefits to soil fertility, but Cu and Zn accumulation needs to be monitored.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy, M.; Couillard, D.: Use of municipal sewage sludge for the fertilization of forests. Mobility of metals and the risk of surface- and ground-water contamination. Revue des Sci. de l’eau 4, 507–525 (1997)
Singh, R.P.; Agrawal, M.: Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 28, 347–358 (2008)
Ahmed, H.K.; Fawy, H.A.; Abdel-Hady, E.S.: Study of sewage sludge use in agriculture and its effect on plant and soil. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. (2010). doi:10.5251/abjna.2010.1.5.1044.1049
Scheifler, R.; BenBrahim, M.; Gomot de Vaufleury, A.; Carnus, J.M.; Badot, P.M.: A field method using microcosms to evaluate transfer of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from sewage sludge amended forest soils to Helix aspersa snails. Environ. Pollut. 122, 343–350 (2003)
Bastian, R.K.: Seeing the future through the eyes of the past. In: Henry, C.L.; Harrison, R.B.; Bastian, R.K. (eds.) The Forest Alternative for Treatment and Utilisation of Municipal and Industrial Wastes. University of Washington Press, Seattle (2000)
Thomas, A.-L.; Carnus, J.-M.; Denaix, L.; Gautry, J.-Y.; Bailly, A.; Thiberville, F.: Le réseau “ERESFOR”: Epandage de Produits Résiduaires sur Parcelles Forestières. https://www.bordeaux.inra.fr/eresfor/biblio/collademe2004.pdf (2004). Accessed 26 Nov 2012
Henry, C.L.; Cole, D.W.: Use of biosolids in the forest: technology, economics and regulations. Biomass Bioenerg. 13, 269–277(1997)
Mosquera-Losada, M.R.; Lopez-Diaz, L.; Rigueiro-Rodriguez, A.: Sewage sludge fertilisation of a silvopastoral system with pines in northwestern Spain. Agrofor. Syst. 53, 1–10 (2001)
Ferrier, R.C.; Edward, A.C.; Dutch, J.; Wolstenholme, R.; Mitchell, D.S.: Sewage sludge as a fertilizer of pole stage forests: short-term hydrochemical fluxes and foliar response. Soil Use Manag. 12, 1–7 (1996)
Bramryd, T.: Effects of liquid and dewatered sewage sludge applied to a Scots pine stand (Pinus sylvestris L.) in Central Sweden. For. Ecol. Manag. 147, 197–216 (2001)
Fuentes, D.; Valdecantos, A.; Cortina, J.; Vallejo, V.R.: Seedling performance in sewage sludge-amended degraded mediterranean woodlands. Ecol. Eng. 31, 281–291 (2007)
Garcia-Delgado, M.; Rodriguez-Cruz, M.S.; Lorenzo, L.F.; Arienzo, M.; Sanchez-Martin, M.J.: Seasonal and time variability of heavy metal content and of its chemical forms in sewage sludges from different wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 382, 82–92 (2007)
Billard, J.-P.; Langlois, J.: Détermination in vivo de l’activité nitrate réductase des feuilles de haricot. Biopedagos 1, 42–50 (1986)
Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I.: Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 44, 276–287 (1971)
Oberley, L.W.; Spitz, D.R.: Nitroblue tetrazolium. In: Greenwald, R.A. (ed.) CRC andbook of Methods for Oxygen Radical Research, pp. 217–220. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1985)
Bradford, N.M.: A rapid and a sensitive method for the quantification of microgram of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976)
Mañas, P.; Castro, E.; Vila, P.; de las Heras, J.: Use of waste materials as nursery growing media for Pinus halepensis production. Eur. J. For. Rehabil. 129, 521–530 (2010)
Egiarte, G.; Camps Arbestain, M.; Alonso, A.; Ruiz-Romera, E.; Pinto, M.: Effect of repeated applications of sewage sludge on the fate of N in soils under Monterey pine stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 216, 257–269 (2005)
Nieminen, J.K.; Räisänen, M.: Effects of sewage sludge addition to Norway spruce seedlings on nitrogen availability and soil fauna in clear-cut areas. Environ. Pollut. 178, 306–311 (2013)
Rentsch, D.; Schmidt, S.; Tegeder, M.: Transporters for uptake and allocation of organic nitrogen compounds in plants. FEBS Lett. 581, 2281–2289 (2007)
Aarnes, H.; Eriksen, A.B.; Petersen, D.; Rise, F.: Accumulation of ammonium in Norway spruce (Picea abies) seedlings measured by in vivo 14N-NMR. J. Exp. Bot. 58, 929–934 (2007)
Orebamjo, T.O.; Stewart, G.R.: Ammonium inactivation of nitrate reductase in Lemna minor L. Planta 122, 37–44 (1975)
Smith, M.T.E.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Tibbett, M.: Soil phosphorus dynamics and phytoavailability from sewage sludge at different stages in a treatment stream. Biol. Fertil. Soils 42, 186–197 (2006)
Bonneau, M.: Le diagnostique foliaire. http://documents.irevues.inist.fr/bitstream/handle/2042/25930/RFF_1988_S_19.pdf (1988). Accessed 26 Nov 2012
Cogliatti, D.H.; Santa Maria, G.E.: Influx and efflux of phosphorus in roots of wheat plants in non-growth-Limiting concentrations of phosphorus. J. Exp. Bot. 41, 601–607 (1990)
Topa, M.A.; Sisak, C.L.: Characterization of phosphorus uptake in slow-and fast-growing southern pine seedlings grown in solution culture. Plant Soil 190, 317–329 (1997)
Miah, M.Y.; Chiu, C.Y.; Hayashi, H.; Chino, M.: Barley growth in response to potassium fertilization of soil with long-term application of sewage sludge. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 45, 499–504 (1999)
Marschner, H.: Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego (1995)
Wang, P.; Zhou, D.M.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Lian-Zhen, Li, L.Z.; Weng, N.: Evaluating mechanisms for plant-ion (Ca2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ or Ni2+) interactions and their effectiveness on rhizotoxicity. Plant Soil 334, 277–288 (2010)
Baize, D.: Teneurs totales en “métaux lourds” dans les sols français. Premiers résultats du programme ASPITET. Le Courr. de l’environnement de l’INRA 22, 37–46 (1994)
Pezeshki, S.R.: Wetland plant responses to soil flooding. Environ. Exp. Bot. 46, 299–312 (2001)
Kabata-Pendias, A.; Pendias, H.: Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1992)
Yoon, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, Q.L.: Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci. Total Environ. 368, 456–464 (2006)
Lozano-Rodriguez, E.; Hernandez, L.E.; Bonay, P.; Carpena-Ruiz, R.O.: Distribution of cadmium in shoot and root tissues of maize and pea plants: physiological disturbances. J. Exp. Bot. 48, 123–128 (1997)
Grant, C.A.; Clarke, J.M.; Duguid, S.; Chaney, R.L.: Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 390, 301–310 (2008)
Staszewski, T.; Lukasik, W.; Kubiesa, P.: Contamination of Polish national parks with heavy metals. Environ. Monit. Assess. 184, 4597–4608 (2012)
Arduini, I.; Godbold, D.L.; Onnis, A.: Influence of copper on root growth and morphology of Pinus pinea L. and Pinus pinaster Ait. seedlings. Tree Physiol. 15, 411–415 (1995)
Liao, M.T.; Hedley, M.J.; Woolley, D.J.; Brooks, R.R.; Nichols, M.A.: Copper uptake and translocation in chicory (Cichorium intybus L. cv. Grasslands Puna) and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv. Rondy) plants grown in NFT system. I. Copper uptake and distribution in plants. Plant Soil 221, 135–142 (2000)
Drazkiewicz, M.; Skorzynska-Polit, E.; Krupa, Z.: The redox state and activity of superoxide dismutase classes in Arabidopsis thaliana under cadmium or copper stress. Chemosphere 67, 188–193 (2007)
Song, H.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, C.C.; Wu, M.L.; Peng, Y.L.; Deng, C.; Li, Q.P.: Effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure on antioxidant system activities and proline content in Kandelia candel. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 40, 9–18 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bourioug, M., Alaoui-Sossé, L., Laffray, X. et al. Evaluation of Sewage Sludge Effects on Soil Properties, Plant Growth, Mineral Nutrition State, and Heavy Metal Distribution in European Larch Seedlings (Larix decidua). Arab J Sci Eng 39, 5325–5335 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1100-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1100-0