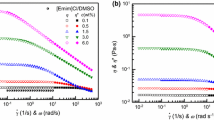
Abstract
Many researches have studied the viscoelasticity of cellulose/ionic liquid solutions through the conventional scaling rules which assume the monodisperse polymer. However, they are not suitable for cellulose since natural polymers such as cellulose have molecular weight distribution. In this paper, dynamic rheological behaviors of 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium acetate solutions dissolving three kinds of celluloses were measured in a large range of concentrations from the dilute regime to the entangled semidilute regime at 25°C. We compared the viscosity-fitting scaling (Chen et al., 2011) and the phenomenological scaling to replace the conventional scaling. Two scaling methods were applied to the linear viscoelasticity of the cellulose solutions with different molecular weights and molecular weight distributions. The results of each scaling were compared by the superposition of master curves obtained from each scaling. The effects of molecular weight distribution were observed by the dependence of the scaling factors on concentration and molecular weight of cellulose.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, J.-E. and K.S. Cho, 2016, A systematic approximation of discrete relaxation time spectrum from the continuous spectrum. J. Non-Newton. Fluid 235, 64–75.
Chen, X., Y. Zhang, H. Wang, S.-W. Wang, S. Liang, and R.H. Colby, 2011, Solution rheology of cellulose in 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride. J. Rheol. 55, 485–494.
Chen, X., Y. Zhang, L. Cheng, and H. Wang, 2009, Rheology of concentrated cellulose solutions in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. J. Polym. Environ. 17, 273–279.
Cho, K.S., 2016, Viscoelasticity of Polymers: Theory and Numerical Algorithms, Springer, New York.
Cho, K.S., J.W. Kim, J.-E. Bae, J.H. Youk, H.J. Jeon, and K.-W. Song, 2015, Effect of temporary network structure on linear and nonlinear viscoelasticity of polymer solutions. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 27, 151–161.
Colby, R.H., 2010, Structure and linear viscoelasticity of flexible polymer solutions: Comparison of polyelectrolyte and neutral polymer solutions. Rheol. Acta 49, 425–442.
Colby, R.H., L.J. Fetters, W.G. Funk, and W.W. Graessley, 1991, Effect of concentration and thermodynamic interaction on the viscoelastic properties of polymer solutions. Macromolecules 24, 3873–3882.
Collier, J.R., J.L. Watson, B.J. Collier, and S. Petrovan, 2008, Rheology of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride cellulose solutions. II. Solution character and preparation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 111, 1019–1027.
Dealy, J.M. and R.G. Larson, 2006, Structure and Rheology of Molten Polymers: From Structure to Flow Behavior and Back Again, Hanser Verlag, München.
Fuchs, K., C. Friedrich, and J. Weese, 1996, Viscoelastic properties of narrow-distribution poly(methyl methacrylates). Macromolecules 29, 5893–5901.
Gericke, M., K. Schlufter, T. Lieber, T. Heinze, and T. Budtova, 2009, Rheological properties of cellulose/ionic liquid solutions: from dilute to concentrated states. Biomacromolecules 10, 1188–1194.
Haward, S.J., V. Sharma, C.P. Butts, G.H. McKinley, S.S. Rahatekar, 2012, Shear and extensional rheology of celllose/ionic liquid solutions. Biomacromolecules 13, 1688–1699.
Kim, S., J. Lee, S. Kim, and K.S. Cho, 2018, Applications of Monte Carlo method to nonlinear regression of rheological data. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 30, 21–28.
Kosan, B., C. Michels, and F. Meister, 2008, Dissolution and forming of cellulose with ionic liquids. Cellulose 15, 59–66.
Kosan, B., K. Schwikal, and F. Meister, 2010, Solution states of cellulose in selected direct dissolution agents. Cellulose 17, 495–506.
Kuang, Q.L., J.-C. Zhao, Y.-H. Niu, J. Zhang, and Z.-G. Wang, 2008, Cellulose in an ionic liquid: The rheological properties of the solutions spanning the dilute and semidilute regimes. J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 10234–10240.
Lee, Y.J., M.K. Kwon, S.J. Lee, S.W. Jeong, H.C. Kim, T.H. Oh, and S.G. Lee, 2016, Influence of water on phase transition and rheological behavior of cellulose/ionic liquid/water ternary systems, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 134, 44658.
Lu, F., B. Cheng, J. Song, and Y. Liang, 2011, Rheological characterization of concentrated cellulose solutions in 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 124, 3419–3425.
Lu, F., J. Song, B.-W. Cheng, X.-J. Ji, and L.-J. Wang, 2013, Viscoelasticity and rheology in the regimes from dilute to concentrated in cellulose 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate solutions. Cellulose 20, 1343–1352.
Lv, Y., J. Wu, J. Zhang, Y. Niu, C. Y. Liu, J. He, and J. Zhang, 2012, Rheological properties of cellulose/ionic liquid/dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) solutions. Polymer 53, 2524–2531.
Maeda, A., T. Inoue, and T. Sato, 2013, Dynamic segment size of the cellulose chain in an ionic liquid. Macromolecules 46, 7118–7124.
Malkin, A.Y. and I. Masalova, 2001, From dynamic modulus via different relaxation spectra to relaxation and creep functions. Rheol. Acta 40, 261–271.
Morse, D.C., 1997, Viscoelasticity of tightly entangled solutions of semiflexible polymer. Phys. Rev. E 58, R1237–R1240.
Regalado E.J., J. Selb, and F. Candau, 1999, Viscoelastic behavior of semidilute solutions of multi sticker polymer chains. Macromolecules 32, 8501–8588.
Rubinstein, M. and R.H. Colby, 2003, Polymer Physics, Oxford University Press, New York.
Sammons, R.J., R. Collier, T.G. Rials, and S. Petrovan, 2008, Rheology of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride cellulose solutions. I. Shear rheology. J. Appl. Polym, Sci. 110, 1175–1181.
Seddon, K., 1996, Ionic liquids for clean technology. J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol. 68, 351–356.
Sescousse, R., K.A. Le, M.E. Ries, and T. Budtova, 2010, Viscosity of cellulose-imidazolium-based ionic liquid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 7222–7228.
Song, H., J. Zhang, Y. Niu, and Z. Wang, 2010, Phase transition and rheological behaviors of concentrated cellulose/ionic liquid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 6006–6013.
Swatloski, R.P., S.K. Spear, J.D. Holbrey, and R.D. Rogers, 2002, Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 4974–4975.
Tsenoglou, C., 1991, Molecular weight polydispersity effects on the viscoelasticity of entangled linear polymers. Macromolecules 24, 1762–1767.
Wang, L., L. Gao, B. Cheng, X. Ji, J. Song, and F. Lu, 2014, Rheological behaviors of cellulose in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride/dimethylsulfoxide. Carbohyd. Polym. 110, 292–297.
Watanabe, H., 1999, Viscoelasticity and dynamics of entangled polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 24, 1253–1403.
Xia, X., Y. Yao, M. Gong, H. Wang, and Y. Zhang, 2014, Rheological behaviors of cellulose/[BMIM]Cl solutions varied with the dissolving process, J. Polym. Res. 21, 512.
Zhang, H., J. Wu, J. Zhang, and J. He, 2005, 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature ionic liquid: A new and powerful nonderivatizing solvent for cellulose. Macromolecules 38, 8272–8277.
Zhu, S., Y. Wu, Q. Chen, Z. Yu, C. Wang, S. Jin, Y. Ding, and G. Wu, 2006, Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: A mini-review. Green Chem. 8, 325–327.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Mid-Career Researcher Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2017R1A2B1005506). This work was also supported by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT (18-ET-02) of the Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, M.K., Lee, J., Cho, K.S. et al. Scaling analysis on the linear viscoelasticity of cellulose 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium acetate solutions. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 31, 123–139 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-019-0014-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-019-0014-5