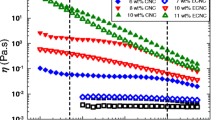
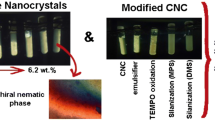
Abstract
The change in ionic strength of cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) suspensions is shown to contribute to a respective change in colloidal behavior, such as stiffness and fractal gelation. In this study, dynamic colloidal behavior and stability of aqueous CNC suspensions and their correlation with nonlinear viscoelastic properties of the CNC gel structures in the presence of different concentrations of sodium chloride (NaCl) salt were investigated. The microstructure of CNC/salt suspensions/gels were investigated with a wide range of characterization technique. To obtain further insight into the network structure of CNC/salt systems, for the first time, nonlinear rheology of the suspensions/gels was analyzed to correlate macro-mechanical viscoelastic response of the CNC/salt aqueous systems to structural changes as a response to strain. The intra-cycle viscoelasticity, explained utilizing qualitative Lissajous–Bowditch plots and quantitative nonlinear parameters, demonstrates a strong dependence of the nonlinear response of the samples to salt concentration, CNC concentration, and frequency of deformation. Higher intra-cycle nonlinearity was observed upon increasing the salt loading.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliabadian E, Sadeghi S, Kamkar M, Chen Z, Sundararaj U (2018) Rheology of fumed silica nanoparticles/partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide aqueous solutions under small and large amplitude oscillatory shear deformations. J Rheol 62:1197–1216
Aliabadian E, Kamkar M, Chen Z, Sundararaj U (2019) Prevention of network destruction of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM): Effects of salt, temperature, and fumed silica nanoparticles. Phys Fluids 31:013104
Araki J (2013) Electrostatic or steric preparations and characterizations of well dispersed systems containing rod-like nanowhiskers of crystalline polysaccharides. Soft Matter 9:4125–4141
Beck-Candanedo S, Roman M, Gray DG (2005) Effect of reaction conditions on the properties and behavior of wood cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Biomacromol 6:1048–1054
Benavides EEU (2011) Cellulose nanocrystals properties and applications in renewable nanocomposites. Clemson University, Clemson
Boluk Y, Lahiji R, Zhao L, McDermott MT (2011) Suspension viscosities and shape parameter of cellulose nanocrystals (CNC). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 377:297–303
Chau M et al (2015) Ion-mediated gelation of aqueous suspensions of cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromol 16:2455–2462
Chaudhuri O et al (2016) Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nat Mater 15:326
Chen Y, Xu C, Huang J, Wu D, Lv Q (2017) Rheological properties of nanocrystalline cellulose suspensions. Carbohydr Polym 157:303–310
Cherhal F, Cousin F, Capron I (2015) Influence of charge density and ionic strength on the aggregation process of cellulose nanocrystals in aqueous suspension, as revealed by small-angle neutron scattering. Langmuir 31:5596–5602
Cho KS, Hyun K, Ahn KH, Lee SJ (2005) A geometrical interpretation of large amplitude oscillatory shear response. J Rheol 49:747–758
Conti M, Meerson B, Sasorov PV (1998) Breakdown of scale invariance in the phase ordering of fractal clusters. Phys Rev Lett 80:4693
Cowin SC (2001) Bone mechanics handbook. CRC Press, Boca Raton
de Souza Lima MM, Borsali R (2002) Static and dynamic light scattering from polyelectrolyte microcrystal cellulose. Langmuir 18:992–996
Dong XM, Revol J-F, Gray DG (1998) Effect of microcrystallite preparation conditions on the formation of colloid crystals of cellulose. Cellulose 5:19–32
Elazzouzi-Hafraoui S, Putaux J-L, Heux L (2009) Self-assembling and chiral nematic properties of organophilic cellulose nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 113:11069–11075
Ewoldt RH, Hosoi A, McKinley GH (2008) New measures for characterizing nonlinear viscoelasticity in large amplitude oscillatory shear. J Rheol 52:1427–1458
Ewoldt RH, Winter P, Maxey J, McKinley GH (2010) Large amplitude oscillatory shear of pseudoplastic and elastoviscoplastic materials. Rheol Acta 49:191–212
Giacomin AJ, Dealy JM (1993) Large-amplitude oscillatory shear. In: Collyer AA (ed) Techniques in rheological measurement. Springer, Berlin, pp 99–121
Goudoulas TB, Germann N (2019a) Nonlinear rheological behavior of gelatin gels: In situ gels and individual gel layers filled with hard particles. J Colloid Interf Sci 556:1–11
Goudoulas TB, Germann N (2019b) Nonlinear rheological behavior of gelatin gels: In situ gels and individual layers. J Colloid Interf Sci 553:746–757
Groenewold J, Zhang T, Kegel WK (2011) Electrophoresis in charge-stabilized colloidal cluster phases. J Phys Chem B 115:7264–7267
Hyun K, Kim W (2011) A new non-linear parameter Q from FT-Rheology under nonlinear dynamic oscillatory shear for polymer melts system. Korea-Australia Rheol J 23:227–235
Hyun K et al (2011) A review of nonlinear oscillatory shear tests: analysis and application of large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS). Prog Polym Sci 36:1697–1753
Israelachvili J (2011) Intermolecular and surface forces, 3rd edn. Academic, Burlington
Kamkar M (2020) Large amplitude oscillatory shear flow: microstructural assessment of polymer nanocomposites, hydrogels, and interfaces. http://hdl.handle.net/1880/111737
Kamkar M, Aliabadian E, Shayesteh Zeraati A, Sundararaj U (2018) Application of nonlinear rheology to assess the effect of secondary nanofiller on network structure of hybrid polymer nanocomposites. Phys Fluids 30:023102
Kamkar M, Sadeghi S, Arjmand M, Sundararaj U (2019) Structural Characterization of CVD Custom-Synthesized Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Nanocomposites in Large-Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (LAOS) Mode: Effect of Dispersion Characteristics in Confined Geometries Macromolecules
Kamkar M et al (2020) The key role of processing in tuning nonlinear viscoelastic properties and microwave absorption in CNT-based polymer nanocomposites. Mater Today Commun 24:101010
Laurati M, Egelhaaf S, Petekidis G (2011) Nonlinear rheology of colloidal gels with intermediate volume fraction. J Rheol 55:673–706
Lenfant G, Heuzey M-C, van de Ven TG, Carreau PJ (2017) A comparative study of ECNC and CNC suspensions: effect of salt on rheological properties. Rheol Acta 56:51–62
Lewis L, Derakhshandeh M, Hatzikiriakos SG, Hamad WY, MacLachlan MJ (2016) Hydrothermal gelation of aqueous cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Biomacromol 17:2747–2754
Lv H, Li L, Sun M, Zhang Y, Chen L, Rong Y, Li Y (2015) Mechanism of regulation of stem cell differentiation by matrix stiffness. Stem Cell Res Therapy 6:103
Mariano M, El Kissi N, Dufresne A (2014) Cellulose nanocrystals and related nanocomposites: review of some properties and challenges. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 52:791–806
Moud AA, Arjmand M, Yan N, Nezhad AS, Hejazi SH (2018) Colloidal behavior of cellulose nanocrystals in presence of sodium chloride. Chem Select 3:4969–4978
Moud AA, Arjmand M, Liu J, Yang Y, Sanati-Nezhad A, Hejazi SH (2019) Cellulose nanocrystal structure in the presence of salts. Cellulose 26(18):9387–9401
Oguzlu H, Danumah C, Boluk Y (2017) Colloidal behavior of aqueous cellulose nanocrystal suspensions Current opinion in colloid & interface. Science 29:46–56
Peddireddy KR, Capron I, Nicolai T, Benyahia L (2016) Gelation kinetics and network structure of cellulose nanocrystals in aqueous solution. Biomacromol 17:3298–3304
Revol J-F (1982) On the cross-sectional shape of cellulose crystallites in Valonia ventricosa. Carbohydr Polym 2:123–134
Rogers SA, Erwin BM, Vlassopoulos D, Cloitre M (2011) A sequence of physical processes determined and quantified in LAOS: Application to a yield stress fluid. J Rheol 55:435–458
Saengow C, Giacomin AJ (2019) Review of nonlinear oscillatory shear flow notations and presentations: Polymeric liquids Current opinion in colloid & interface science
Salehiyan R, Yoo Y, Choi WJ, Hyun K (2014) Characterization of morphologies of compatibilized polypropylene/polystyrene blends with nanoparticles via nonlinear rheological properties from FT-rheology. Macromolecules 47:4066–4076
Salehiyan R, Song HY, Choi WJ, Hyun K (2015) Characterization of effects of silica nanoparticles on (80/20) PP/PS blends via nonlinear rheological properties from Fourier transform rheology. Macromolecules 48:4669–4679
Shafiei-Sabet S, Hamad W, Hatzikiriakos S (2014) Ionic strength effects on the microstructure and shear rheology of cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Cellulose 21:3347–3359
Shih W-H, Shih WY, Kim S-I, Liu J, Aksay IA (1990) Scaling behavior of the elastic properties of colloidal gels. Phys Rev A 42:4772
Vedadghavami A, Minooei F, Mohammadi MH, Khetani S, Kolahchi AR, Mashayekhan S, Sanati-Nezhad A (2017) Manufacturing of hydrogel biomaterials with controlled mechanical properties for tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater 62:42–63
Wågberg L, Decher G, Norgren M, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Axnäs K (2008) The build-up of polyelectrolyte multilayers of microfibrillated cellulose and cationic polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 24:784–795
Wen JH et al (2014) Interplay of matrix stiffness and protein tethering in stem cell differentiation. Nat Mater 13:979
Wilhelm M, Reinheimer P, Ortseifer M (1999) High sensitivity Fourier-transform rheology. Rheol Acta 38:349–356
Wu H, Morbidelli M (2001) A model relating structure of colloidal gels to their elastic properties. Langmuir 17:1030–1036
Zaccone A, Wu H, Del Gado E (2009) Elasticity of arrested short-ranged attractive colloids: Homogeneous and heterogeneous glasses. Phys Rev Lett 103:208301
Zhong L, Fu S, Peng X, Zhan H, Sun R (2012) Colloidal stability of negatively charged cellulose nanocrystalline in aqueous systems. Carbohydr Polym 90:644–649
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial assistance from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Discovery Grant 05503-2015, Alberta Innovates BioSolution’s CNC Challenge II and III, University of Calgary Global Research Initiative in Unconventional Hydrocarbon Resources-Beijing Site, Kerui-MITACS Accelerate Research Fund Application Ref. IT09328. The authors also gratefully acknowledge infrastructure funding from Canadian Foundation for Innovation (CFI) CFI LOF Project# 30100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi Moud, A., Kamkar, M., Sanati-Nezhad, A. et al. Nonlinear viscoelastic characterization of charged cellulose nanocrystal network structure in the presence of salt in aqueous media. Cellulose 27, 5729–5743 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03166-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03166-x