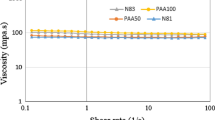
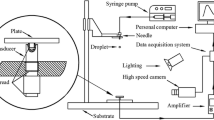
Abstract
In this paper, the impact dynamics of Boger drops on dry solid surfaces is investigated experimentally. The effects of viscosity, surface wettability, and impact velocity on the spreading and receding behavior of the Newtonian and viscoelastic drops are studied in detail. They are impinged upon Plexiglas and glass substrates, which have hydrophilic properties, at the impact velocities 4.03 m/s and 4.22 m/s. The polyacrylamide drops spread out more widely and recede more rapidly than the glycerin drops. The impact velocity and the liquid viscosity have more influence on the spreading phase. However, the surface wettability shows only a minute effect on the spreading phase but a very significant effect on the receding phase. On the receding stage, the effect of impact velocity was only observed on the behavior of the low-viscosity drops. Therefore, when the low-viscosity drops impact on a hydrophilic substrate, the higher impact velocity, the receding velocity is increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, S.M. and S.Y. Lee, 2009, Examination of spread-recoil behavior of a shear-thinning liquid drop on a dry wall, J. ILASS-Korea 14(3), 131–138.
An, S.M. and S.Y. Lee, 2012a, Observation of the spreading and receding behavior of a shear-thinning liquid drop impacting on dry solid surfaces, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 37, 37–45.
An, S.M. and S.Y. Lee, 2012b, Maximum spreading of a shearthinning liquid drop impacting on dry solid surfaces, Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 38, 140–148.
Bartolo, D., A. Boudaoud, G. Narcy, and D. Bonn, 2007, Dynamics of non-Newtonian droplets, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 174502.
Bergeron, V., D. Bonn, J.Y. Martin, and L. Vovelle, 2000, Controlling droplet deposition with polymer additives, Nature 405, 772–775.
Bertola, V., 2004, Drop impact on a hot surface. Effect of a polymer additive, Exp. Fluids 37, 653–664.
Bertola, V., 2009, An experimental study of bouncing Leidenfrost drops: Comparison between Newtonian and viscoelastic liquids, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 52, 1786–1793.
Bertola, V., 2010, Effect of polymer additives on the apparent dynamic contact angle of impacting drops, Colloid Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 363, 135–140.
Biolè, D. and V. Bertola, 2015, A goniometric mask to measure contact angles from digital images of liquid drops, Colloid Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 467, 149–156.
Chandra, S. and C.T. Avedisian, 1992, Observations of droplet impingement on a ceramic porous surface, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 35, 2377–2388.
Copper-White, J.J., R. Crooks, and D.V. Boger, 2002a, A drop impact study of worm-like viscoelastic surfactant solutions, Colloid Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 210, 105–123.
Copper-White, J.J., R. Crooks, K. Chockalingam, and D.V. Boger, 2002b, Dynamics of polymer surfactant complexes: elongational properties and drop impact behavior, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 41, 6443–6459.
Crooks, R. and D.V. Boger, 2000, Influence of fluid elasticity on drops impacting on dry surfaces, J. Rheol. 44, 973–996.
Crooks, R., J. Copper-White, and D.V. Boger, 2001, The role of dynamic surface tension and elasticity on the dynamics of drop impact, Chem. Eng. Sci. 56, 5575–5592.
Dong, H., W.W. Carr, and J.F. Morris, 2006, Visualization of drop-on-demand inkjet: Drop formation and deposition, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 085101.
Edgerton, H.E. and J.R. Killian, 1954, Flash!: Seeing the Unseen by Ultra High-Speed Photography, 2nd Ed., CT Branford Co., Boston.
German, G. and V. Bertola, 2009, Impact of shear-thinning and yield-stress drops on solid substrates, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 21, 375111.
Han, J. and C. Kim, 2013, Spreading of Boger fluid on horizontal surface, J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 202, 120–130.
Huang, H., 2005, Non-Newtonian effects on inkjet droplets formation,” Nieuw Archief voor Wiskunde 5(6), 63–68.
Huang, X., P. Chen, M. Lan, X. Wang, and G. Liao, 2013, Experimental study of water drops with additive impact on wood surfaces, Procedia Eng. 62, 852–858.
Jung, S., 2011, Fluid Characterisation And Drop Impact In Inkjet Printing For Organic Semiconductor Devices, Ph.D Thesis, University of Cambridge.
Jung, S. and I.M. Hutchings, 2012, The impact and spreading of a small liquid drop on a non-porous substrate over an extended time scale, Soft Matter 8, 2686–2696.
Jung, S., S.D. Hoath, and I.M. Hutchings, 2013, The role of viscoelasticity in drop impact and spreading for inkjet printing of polymer solution on a wettable surface, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 14, 163–169.
Luu, L.H. and Y. Forterre, 2009, Drop impact of yield-stress fluids, J. Fluid Mech. 632, 301–327.
Moon, J.H., J.B. Lee, and S.H. Lee, 2013, Dynamic behavior of non-Newtonian droplets impinging on solid surfaces, Mater. Trans. 54, 260–265.
Nigen, S., 2005, Experimental investigation of the impact of an (apparent) yield-stress material, Atom. Sprays 15, 103–118.
Rafai, S., D. Bonn, and A. Boudaoud, 2004, Spreading of non-Newtonian fluids on hydrophilic surfaces, J. Fluid Mech. 513, 77–85.
Rioboo, R., M. Marengo, and C. Tropea, 2002, Time evolution of liquid drop impact onto solid, dry surfaces, Exp. Fluids 33, 112–124.
Roisman, I.V., 2009, Inertia dominated drop collisions. II. An analytical solution of the Navier-Stokes equations for a spreading viscous film, Phys. Fluids 21, 052104.
Roisman, I.V., R. Rioboo, and C. Tropea, 2002, Normal impact of a liquid drop on a dry surface: Model for spreading and receding, Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 458, 1411–1430.
Roux, D.C., J.J. Cooper-White, G.H. McKinley, and V. Tirtaatmadja, 2003, Drop impact of Newtonian and elastic fluids, Phys. Fluids 15, S12.
Saïdi, A, C. Martin, and A. Magnin, 2010, Influence of yield stress on the fluid drop impact control, J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 165, 596–606.
Scheller, B.L. and D.W. Bousfield, 1995, Newtonian drop impact with a solid surface, AIChE J. 41, 1357–1367.
Smith, M.I. and V. Bertola, 2010, Effect of polymer additives on the wetting of impacting droplets, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 154502.
Smith, M.I. and V. Bertola, 2011, Particle velocimetry inside Newtonian and non-Newtonian droplets impacting a hydrophobic surface, Exp. Fluids 50, 1385–1391.
Son, Y. and C. Kim, 2009, Spreading of inkjet droplet of non-Newtonian fluid on solid surface with controlled contact angle at low Weber and Reynolds numbers, J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 162, 78–87.
Son, Y., C. Kim, D.H. Yang, and D.J. Ahn, 2008, Spreading of an inkjet droplet on a solid surface with a controlled contact angle at low Weber and Reynolds numbers, Langmuir 24, 2900–2907.
Thoroddsen, S.T. and J. Sakakibara, 1998, Evolution of the fingering pattern of an impacting drop, Phys. Fluids 10, 1359–1374.
Thoroddsen, S.T., T.G. Etoh, and K. Takehara, 2008, High-speed imaging of drops and bubbles, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 40, 257–285.
Van Dam, D.B. and C.L. Clerc, 2004, Experimental study of the impact of an ink-jet printed droplet on a solid substrate, Phys. Fluids 16, 3403.
Versluis, M., 2013, High-speed imaging in fluids, Exp. Fluids 54, 1458.
Worthington, A.M., 1876, On the forms assumed by drops of liquids falling vertically on a horizontal plate, Proc. R. Soc. London 25, 261–272.
Worthington, A.M., 1908, A Study of Splashes, Longmans, Green, and Co., London.
Yang, X., V.H. Chhasatia, and Y. Sun, 2013, Oscillation and recoil of single and consecutively printed droplets, Langmuir 29, 2185–2192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandani, S., Norouzi, M. & Shahmardan, M.M. An experimental investigation on impact process of Boger drops onto solid surfaces. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 30, 99–108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-018-0011-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-018-0011-0