Abstract
Six hundred and one symptomatic potato samples were collected from nine provinces in Iran. Screening by double-antibody sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay using a potato virus X (PVX) together with a few potyviruses polyclonal antibodies, produced positive reactions in 4.3 % of samples against PVX. Based on symptoms on different test plant, the isolates were divided into two groups: the first groups causing blistering and malformation of leaves and the second showed mild mosaic and vein clearing in Nicotiana glutinosa. The almost complete nucleotide sequence of two isolates as a representative of severe and a mild isolates were determined. Genomes of two PVX Iranian isolates are identical to that of the most PVX isolates comprise 6435 nucleotides in length excluding 101 nucleotide in the 5′ end of the genome and shares 94.8–96.7 % identities with European and Asian, and 77–96.1 % with American isolates. Furthermore, the 3′-terminal sequences, including the coat protein coding region of other 13 Iranian isolates were determined and compared with the GenBank sequences. Phylogenetic analysis of the cp gene of 13 Iranian isolates together all those available in public databases indicated that the 13 Iranian isolates all belong to low diversity clade I.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beemster ABR, Rozendaal A. Potato viruses: properties and symptoms. In: De Borkz JA, editor. Viruses of potatoes and seed-potato production. Wageningen: Pubdoc; 1972. p. 115–43.
Clark MF, Adams AN. Characteristics of microplate method of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of plant viruses. J Gen Virol. 1977;34:475–83.
Cox BA, Jones RA. Genetic variability in the coat protein gene of Potato virus X and the current relationship between phylogenetic placement and resistance groupings. Arch Virol. 2010;155(8):1349–56.
Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(5):1792–7. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh340.
Esfandiari N, Kohi-Habibi M, Hohn T, Pooggin MM. Complete genome sequences of Potato virus X from the legume plant Pisum Sativum. Virus Genes. 2009;30:141–5.
Gilmer D, Bouzoubaa S, Hehn A, Guilley H, Richards K, Jonard G. Efficient cell-to-cell movement of beet necrotic yellow vein virus requires 3′ proximal genes located on RNA 2. Virology. 1992;189:40–7.
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol. 2010;59(3):307–21. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syq010.
Hagiwara K, Ichiki TU, Ogawa Y, Omura T, Tsuda S. A single amino acid substitution in 126-kDa protein of Pepper mild mottle virus associates with symptom attenuation in pepper; the complete nucleotide sequence of an attenuated strain, C-1421. Arch Virol. 2002;147:833–40.
Hahm Y, Slack SA, Slattery RJ. Reinfection of potato seed stocks with Potato virus S and Potato virus X in Wisconsin. Am Potato J. 1981;58(2):117–25.
Karpova O, Zayakina O, Arkhipenko M, Sheval E, Kiselyova O, Poljakov V, et al. Potato virus X RNA-mediated assembly of single-tailed ternary ‘coat protein–RNA–movement protein complexes. J Gen Virol. 2006;87(9):2731–40.
Khakvar R, Pourrahim R, Shamsbakhsh M. Study on six Potato viruses in Khuzestan Province. In: Proceeding of the 14th Iranian plant protection congress, Isfahan University of Technology, Iran 2000. p. 312.
Kobori T, Miyagawa M, Nishioka K, Ohki ST, Osaki T. Amino acid 129 of Cucumber mosaic virus coat protein determines local symptom expression and systemic movement in Tetragonia expansa, Momordica charantia and Physalis floridana. J Gen Plant Pathol. 2002;68:81–8.
Komatsu K, Kagiwada S, Takahashi S, Mori T, Yamaji Y, Hirata H, et al. Phylogenetic characteristics, genomic heterogenecity and symptomatic variation of five closely related Japanese strains of Potato virus X. Virus Genes. 2005;31:99–105.
Leshchiner A, Minina E, Rakitina D, Vishnichenko V, Solovyev A, Morozo S, et al. Oligomerization of the Potato virus X 25-kD movement protein. Biochem (Mosc). 2008;73:50–5.
Memelink J, van der Vlugt CI, Linthorst HJ, Derk AFL, Asjes C. Homologies between the genomes of a carlavirus (lily symptomless virus) and a potexvirus (lily virus X) from lily plants. J Gen Virol. 1990;71:917–24.
Morozov SY, Solovyev AG. Triple gene block: modular design of a multifunctional machine for plant virus movement. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:1351–66.
Morozov SY, Zakchariev VM, Chernow BK, Prasolov VS, Kozlov YV, Atabekov JG, et al. The analysis of the primary structure and localization of the coat protein gene on the genomic RNA of Potato virus X. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1983;271:211–5.
Muhire B, Martin DP, Brown JK, Navas-Castillo J, Moriones E, Zerbini FM, et al. A genome-wide pairwise-identity-based proposal for the classification of viruses in the genus Mastrevirus (family Geminiviridae). Arch Virol. 2013;158(6):1411–24. doi:10.1007/s00705-012-1601-7.
Posada D. Selection of models of DNA evolution with jModelTest. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;537:93–112. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-251-9_5.
Pourrahim R, Farzadfar SH, Golnaraghi AR, Ahoonmanesh A. Incidence and distribution of important viral pathogens in some Iranian potato fields. Plant Dis. 2007;91:609–15.
Santa Cruz S, Baulcombe D. Analysis of Potato virus X coat protein genes in relation to resistance conferred by the genes Nx, Nb and Rx1 of potato. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:2057–61.
Sharifi M, Massumi H, Heydarnejad J, Hosseini Pour A, Shaabanian M, Rahimian H. Analysis of biological and molecular variability of Watermelon mosaic virus isolates from Iran. Virus Genes. 2008;37:304–13.
Skryabin K, Morozov SY, Kraev AS, Rozanov MN, Chernov BK, Lukasheva LI, et al. Conserved and variable elements in RNA genomes of potexviruses. FEBS Lett. 1988;240:33–40.
Verchot-Lubicz J. A new cell-to-cell transport model for potexviruses. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005;18:283–90.
Yu XQ, Wang HY, Lan YF. Complete genome sequence of a Chinese isolate of Potato virus X and analysis of genetic diversity. J Phytopathol. 2008;156:346–51.
Yu X-Q, Jia JL, Zhang C, Li XD, Wang YJ. Phylogenetic analyses of an isolate obtained from potato in 1985 revealed Potato virus X was introduced to China via multiple events. Virus Genes. 2010;40:447–51.
Acknowledgment
This research work was supported by the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF; Grant No. 87041270).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
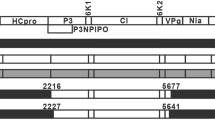
Supplementary Fig. 1
Schematic representative of Potato virus X genome and position of PCR primers used for sequencing of the full-length genome of the Iranian isolate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massumi, H., Poormohammadi, S., Pishyar, S. et al. Molecular characterization and field survey of Iranian potato virus X isolates. VirusDis. 25, 338–344 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-014-0222-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-014-0222-z