Abstract
Background
Vixotrigine is a voltage and use dependent sodium channel blocker currently under development for treatment of various neuropathic pain indications.
Objective
The objective of this work was to develop a population pharmacokinetic model and assess effects of various covariates on pharmacokinetic parameters of vixotrigine.
Method
Plasma concentration-time data from 12 Phase 1 or 2 studies were included in the analyses. The data were obtained following administration of single or multiple doses of vixotrigine in healthy volunteers and patients. One- and two-compartment pharmacokinetic models were evaluated as base structural pharmacokinetic models. The inclusion of selected covariates was assessed using a stepwise backward elimination approach (α = 0.001) once the base/full model was developed. The predictive ability of the model was evaluated using a visual predictive check (VPC). The final model was used to evaluate effect of covariates on exposure of vixotrigine.
Results
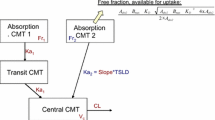
A total of 10,263 pharmacokinetic samples collected from 465 subjects were included in the analyses. The pharmacokinetics of vixotrigine was adequately described by a two-compartment model with two transit absorption compartments and first-order elimination. Predictability of the model was also established by VPC. The final model included covariates of age, weight and carbamazepine co-administration on clearance, weight on central volume of distribution, food on absorption rate constant and formulation and Japanese race on bioavailability. None of the covariates identified had a clinically relevant effect, as impact on area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) was within ± 25%.
Conclusion
The model characterizes the pharmacokinetics of vixotrigine well, and the exposure of vixotrigine was comparable between healthy subjects and patients. None of the covariates evaluated have a clinically relevant impact on the pharmacokinetics of vixotrigine.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cummins TR, Sheets PL, Waxman SG. The roles of sodium channels in nociception: implications for mechanisms of pain. Pain. 2007;131(3):243–57.
Challapalli V, Tremont-Lukats IW, McNicol ED, et al. Systemic administration of local anesthetic agents to relieve neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;4:CD03345.
Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. Efficacy of pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: an update and effect related to mechanism of drug action. Pain. 1999;83(3):389–400.
Zakrzewska JM, Linskey ME. Trigeminal neuralgia. BMJ. Clin Evid. 2009;2009:1207.
Kalso E. Sodium channel blockers in neuropathic pain. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(23):3005–11. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612054865028.
Hinckley C, Hinckley CA, Kuryshev Y, Sers A, Barre A, Buisson B, Naik H, Hajos M. Characterization of vixotrigine, a broad-spectrum voltage-gated sodium channel inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1124/molpharm.120.000079.
Tate S, Davis JB, Owen D, et al. CNV1014802 a novel potent state‐dependent sodium channel blocker with broad preclinical antihyperalgesic efficacy. Neuroscience Meeting Planner. Washington, DC: Society for Neuroscience; 2011: Program 275.206/LL272
Naik H, Steiner D, Versavel M, Palmer J, Fong R. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of single and repeat doses of vixotrigine in healthy Volunteers. J Transl Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12935.
Naik H, Versavel M, Zhao Y, Miao X, Dunbar J. Effect of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics of the Nav1.7-specific sodium channel blocker BIIB074 in healthy subjects [poster P081]. Presented at the American College of Clinical Pharmacology (ACCP) Annual Meeting; 17–19 September, 2017; San Diego (CA)).
Naik H, Versavel M, Dunbar J. Single and Multiple dose pharmacokinetics and safety of Vixotrigine in healthy Japanese and Caucasian volunteers [posterPII-079]. Presented at the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (ASCPT) 120th Annual Meeting; 13–16 March 2019; Washington DC.
Dunbar J, Versavel M, Zhao Y, Naik H. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetic interaction between the voltage- and use-dependent Nav1.7 channel blocker vixotrigine and carbamazepine in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2020;9(1):62–73.
Zakrzewska JM, Palmer J, Morisset V, et al. Safety and efficacy of a Nav1.7 selective sodium channel blocker in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised withdrawal phase 2a trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(4):291–300.
Naik H, Dunbar J, Layton G, Palmer J, Versavel M. Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and tolerability of BIIB074, a Nav1.7-selective sodium channel blocker in adult and elderly male and female volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018;103(S1):S46.
Fong R, Ballow CH, Naik H, Steiner D, Palmer J, White WB. Effects of a state- and use-dependent Nav1.7 channel blocker on ambulatory blood pressure: a randomized, controlled crossover study. J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;59(1):90–7.
Chassany O, Duracinsky M. Ethics and clinical trial. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1999;13(4):437–44.
Woodward C, Naik H, Versavel M, et al. Phase 1 study to evaluate the absorption, metabolism and excretion of the NAV1.7-selective sodium channel blocker BIIB074. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018;33(1):S74.
NONMEM Users Guide. Introduction to NONMEM 7. Ellicott City: ICON Development Solutions; 2010.
Ette EI, Williams PJ, Kim YH, Lane JR, Liu MJ, Capparelli EV. Model appropriateness and population pharmacokinetic modeling. J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;43:610–23.
Wählby U, Jonsson EN, Karlsson MO. Assessment of actual significance levels for covariate effects in NONMEM. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2001;28:231–52.
Gabrielsson J, Weiner D. Non-compartmental analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;929:377–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-050-2_16.
Mahmood I. Prediction of clearance and volume of distribution in the obese fron normal weight subjects: an allometric approach. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2012;51(8):527–42.
Acknowledgements
These analyses and the clinical studies involved were supported by Biogen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No specific funding was received for the preparation of this article.
Conflict of interest
H.N., Y.Z., S.C. (Cleall) and F.F. are employees and shareholders of Biogen. S.C. (Chapel) and H.B. are employees of Ann Arbor Pharmacometrics Group and performed the analyses funded by Biogen. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views or position of any of their employers.
Ethics approval
All the study protocol was approved by the local ethical committee.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient taking part to the study, in compliance with the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) Good Clinical Practice (GCP) Guideline.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed from various studies are not publicly available for confidentiality reasons.
Code availability
Custom NONMEM and R codes used for model building, simulations and computation/representation of VPC are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Author contributions
All authors were involved in planning, executing, data set generation, analysis interpretation and summarization of the analyses.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, H., Zhao, Y., Forrestal, F. et al. Population Pharmacokinetics of Vixotrigine in Healthy Volunteers and Subjects with Trigeminal Neuralgia, Painful Lumbosacral Radiculopathy and Erythromelalgia. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 46, 395–404 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-021-00678-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-021-00678-0