Abstract
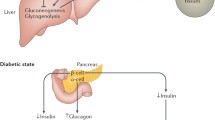
Diabetes mellitus is becoming an increasingly prevalent disease that concerns patients and healthcare professionals worldwide. Among many anti-diabetic agents in clinical uses, numerous reports are available on their altered pharmacokinetics because of changes in the expression of drug transporters and metabolic enzymes under diabetic states. These changes may affect the safety and efficacy of therapeutic agents and/or drug–drug interaction with co-administered agents. Therefore, the changes in transporter expression should be identified, and the underlying mechanisms should be clarified. This review summarizes the progress of recent studies on the alterations in important uptake and efflux transporters in liver of diabetic animals and their regulatory pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
More VR, Wen X, Thomas PE, Aleksunes LM, Slitt AL. Severe diabetes and leptin resistance cause differential hepatic and renal transporter expression in mice. Comp Hepatol. 2012;11(1):1. doi:10.1186/1476-5926-11-1.
Cheng Q, Aleksunes LM, Manautou JE, Cherrington NJ, Scheffer GL, Yamasaki H, et al. Drug-metabolizing enzyme and transporter expression in a mouse model of diabetes and obesity. Mol Pharm. 2008;5(1):77–91. doi:10.1021/mp700114j.
Nowicki MT, Aleksunes LM, Sawant SP, Dnyanmote AV, Mehendale HM, Manautou JE. Renal and hepatic transporter expression in type 2 diabetic rats. Drug Metab Lett. 2008;2(1):11–7.
Li L, Sham YY, Bikadi Z, Elmquist WF. pH-Dependent transport of pemetrexed by breast cancer resistance protein. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(9):1478–85. doi:10.1124/dmd.111.039370.
Vague P, Coste TC, Jannot MF, Raccah D, Tsimaratos M. C-peptide, Na + , K(+)-ATPase, and diabetes. Experim Diabesity Res. 2004;5(1):37–50. doi:10.1080/15438600490424514.
He L, Yang Y, Guo C, Yao D, Liu HH, Sheng JJ, et al. Opposite regulation of hepatic breast cancer resistance protein in type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;724:185–92. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.008.
Pan G, Elmquist WF. Mitoxantrone permeability in MDCKII cells is influenced by active influx transport. Mol Pharm. 2007;4:475–83.
Pan G, Winter TN, Roberts JC, Fairbanks CA, Elmquist WF. Organic cation uptake is enhanced in bcrp1-transfected MDCKII cells. Mol Pharm. 2010;7(1):138–45. doi:10.1021/mp900177r.
Anger GJ, Magomedova L, Piquette-Miller M. Impact of acute streptozotocin-induced diabetes on ABC transporter expression in rats. Chem Biodivers. 2009;6(11):1943–59. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200900053.
Liu L, Liu XD. Alterations in function and expression of ABC transporters at blood-brain barrier under diabetes and the clinical significances. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:273. doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00273.
Kobori T, Harada S, Nakamoto K, Tokuyama S. Functional alterations of intestinal P-glycoprotein under diabetic conditions. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(9):1381–90.
Anger GJ, Cressman AM, Piquette-Miller M. Expression of ABC Efflux transporters in placenta from women with insulin-managed diabetes. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(4):e35027. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035027.
Gandhi A, Ghose R. Altered drug metabolism and transport in pathophysiological conditions. Topics on Drug Metabolism 2012:111–36.
Carvalho TM, Cavalli Rde C, Cunha SP, de Baraldi CO, Marques MP, Antunes NJ, et al. Influence of gestational diabetes mellitus on the stereoselective kinetic disposition and metabolism of labetalol in hypertensive patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67(1):55–61. doi:10.1007/s00228-010-0896-0.
Dujic T, Zhou K, Donnelly LA, Tavendale R, Palmer CN, Pearson ER. Association of organic cation transporter 1 with intolerance to metformin in Type 2 diabetes: a GoDARTS study. Diabetes. 2015;64(5):1786–93. doi:10.2337/db14-1388.
Faber KN, Muller M, Jansen PL. Drug transport proteins in the liver. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55(1):107–24.
Kalliokoski A, Niemi M. Impact of OATP transporters on pharmacokinetics. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;158(3):693–705. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00430.x.
Niemi M. Role of OATP transporters in the disposition of drugs. Pharmacogenomics. 2007;8(7):787–802. doi:10.2217/14622416.8.7.787.
Ho RH, Kim RB. Transporters and drug therapy: implications for drug disposition and disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78(3):260–77. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.05.011.
Hasegawa Y, Kishimoto S, Shibatani N, Inotsume N, Takeuchi Y, Fukushima S. The disposition of pravastatin in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and organic anion transporting polypeptide 2 and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 expression in the liver. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(1):153–6.
More VR, Slitt AL. Alteration of hepatic but not renal transporter expression in diet-induced obese mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(6):992–9. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.037507.
Gorboulev V, Ulzheimer JC, Akhoundova A, Ulzheimer-Teuber I, Karbach U, Quester S, et al. Cloning and characterization of two human polyspecific organic cation transporters. DNA Cell Biol. 1997;16(7):871–81.
Motohashi H, Sakurai Y, Saito H, Masuda S, Urakami Y, Goto M, et al. Gene expression levels and immunolocalization of organic ion transporters in the human kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13(4):866–74.
Geier A, Dietrich CG, Grote T, Beuers U, Prufer T, Fraunberger P, et al. Characterization of organic anion transporter regulation, glutathione metabolism and bile formation in the obese Zucker rat. J Hepatol. 2005;43(6):1021–30. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2005.05.031.
Pizarro M, Balasubramaniyan N, Solis N, Solar A, Duarte I, Miquel JF, et al. Bile secretory function in the obese Zucker rat: evidence of cholestasis and altered canalicular transport function. Gut. 2004;53(12):1837–43. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.037689.
Kim MS, Wang S, Shen Z, Kochansky CJ, Strauss JR, Franklin RB, et al. Differences in the pharmacokinetics of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor agonists in genetically obese zucker and spraguedawley rats: implications of decreased glucuronidation in obese zucker rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004;32:909–14.
Nagel G, Volk C, Friedrich T, Ulzheimer JC, Bamberg E, Koepsell H. A reevaluation of substrate specificity of the rat cation transporter rOCT1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(51):31953–6.
Martel F, Vetter T, Russ H, Grundemann D, Azevedo I, Koepsell H, et al. Transport of small organic cations in the rat liver. The role of the organic cation transporter OCT1. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. 1996;354(3):320–6.
Grover B, Buckley D, Buckley AR, Cacini W. Reduced expression of organic cation transporters rOCT1 and rOCT2 in experimental diabetes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;308(3):949–56. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.058388.
Stieger B. The role of the sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) and of the bile salt export pump (BSEP) in physiology and pathophysiology of bile formation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2011;201:205–59. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-14541-4_5.
Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ. Sinusoidal (basolateral) bile salt uptake systems of hepatocytes. Semin Liver Dis. 1996;16(2):129–36. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1007226.
Guo C, He L, Yao D, Jiye A, Cao B, Ren J, et al. Alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate modulates hepatobiliary transporters in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett. 2014;224(1):93–100. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.09.019.
Koopen NR, Wolters H, Muller M, Schippers IJ, Havinga R, Roelofsen H, et al. Hepatic bile salt flux does not modulate level and activity of the sinusoidal Na + -taurocholate cotransporter (ntcp) in rats. J Hepatol. 1997;27(4):699–706.
Konig J, Nies AT, Cui Y, Leier I, Keppler D. Conjugate export pumps of the multidrug resistance protein (MRP) family: localization, substrate specificity, and MRP2-mediated drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1461(2):377–94.
van Waarde WM, Verkade HJ, Wolters H, Havinga R, Baller J, Bloks V, et al. Differential effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on expression of hepatic ABC-transporters in rats. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(7):1842–52.
Hasegawa Y, Kishimoto S, Shibatani N, Nomura H, Ishii Y, Onishi M, et al. The pharmacokinetics of morphine and its glucuronide conjugate in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and the expression of MRP2, MRP3 and UGT2B1 in the liver. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010;62(3):310–4. doi:10.1211/jpp.62.03.0004.
Lu SC, Kuhlenkamp J, Wu H, Sun WM, Stone L, Kaplowitz N. Progressive defect in biliary GSH secretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(2 Pt 1):G374–82.
Reisman SA, Csanaky IL, Aleksunes LM, Klaassen CD. Altered disposition of acetaminophen in Nrf2-null and Keap1-knockdown mice. Toxicol Sci. 2009;109(1):31–40. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp047.
Zamek-Gliszczynski MJ, Goldstein KM, Paulman A, Baker TK, Ryan TP. Minor compensatory changes in SAGE Mdr1a (P-gp), Bcrp, and Mrp2 knockout rats do not detract from their utility in the study of transporter-mediated pharmacokinetics. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(6):1174–8. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.051409.
Kubo K, Sekine S, Saito M. Compensatory Expression of MRP3 in the Livers of MRP2-Deficient EHBRs Is Promoted by DHA Intake. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;73(11):2432–8. doi:10.1271/bbb.90387.
Lam JL, Jiang Y, Zhang T, Zhang EY, Smith BJ. Expression and functional analysis of hepatic cytochromes P450, nuclear receptors, and membrane transporters in 10- and 25-week-old db/db Mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(12):2252–8. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.034223.
Anger GJ, Piquette-Miller M. Mechanisms of reduced maternal and fetal lopinavir exposure in a rat model of gestational diabetes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011;39(10):1850–9. doi:10.1124/dmd.111.040626.
Chen YN, Mickley LA, Schwartz AM, Acton EM, Hwang JL, Fojo AT. Characterization of adriamycin-resistant human breast cancer cells which display overexpression of a novel resistance-related membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(17):10073–80.
Nakagawa M, Schneider E, Dixon KH, Horton J, Kelley K, Morrow C, et al. Reduced intracellular drug accumulation in the absence of P-glycoprotein (mdr1) overexpression in mitoxantrone-resistant human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1992;52(22):6175–81.
Lee JS, Scala S, Matsumoto Y, Dickstein B, Robey R, Zhan Z, et al. Reduced drug accumulation and multidrug resistance in human breast cancer cells without associated P-glycoprotein or MRP overexpression. J Cell Biochem. 1997;65(4):513–26.
Maliepaard M, Scheffer GL, Faneyte IF, van Gastelen MA, Pijnenborg AC, Schinkel AH, et al. Subcellular localization and distribution of the breast cancer resistance protein transporter in normal human tissues. Cancer Res. 2001;61(8):3458–64.
Bloks VW, Bakker-Van Waarde WM, Verkade HJ, Kema IP, Wolters H, Vink E, et al. Down-regulation of hepatic and intestinal Abcg5 and Abcg8 expression associated with altered sterol fluxes in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia. 2004;47(1):104–12. doi:10.1007/s00125-003-1261-y.
Kullak-Ublick GA, Stieger B, Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ. Hepatic transport of bile salts. Semin Liver Dis. 2000;20(3):273–92. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9426.
Jin HE, Hong SS, Choi MK, Maeng HJ, Kim DD, Chung SJ, et al. Reduced antidiabetic effect of metformin and down-regulation of hepatic Oct1 in rats with ethynylestradiol-induced cholestasis. Pharm Res. 2009;26(3):549–59. doi:10.1007/s11095-008-9770-5.
Clarke JD, Dzierlenga AL, Nelson NR, Li H, Werts S, Goedken MJ, et al. Mechanism of altered metformin distribution in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes. 2015;64(9):3305–13. doi:10.2337/db14-1947.
Alkharfy KM. Influence of overt diabetes mellitus on cyclosporine pharmacokinetics in a canine model. Experim Diabetes Res. 2009;2009:363787. doi:10.1155/2009/363787.
Xu D, Li F, Zhang M, Zhang J, Liu C, Hu MY, et al. Decreased exposure of simvastatin and simvastatin acid in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014;35(9):1215–25. doi:10.1038/aps.2014.39.
Li J, Wang X, Liu H, Guo H, Zhang M, Mei D, et al. Impaired hepatic and intestinal ATP-binding cassette transporter G5/8 was associated with high exposure of beta-sitosterol and the potential risks to blood-brain barrier integrity in diabetic rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014;66(3):428–36. doi:10.1111/jphp.12178.
Mertens PR, Martin IV, Frye BC, Rauen T, Strauch S, Pabst M, et al. Rat Mrp2 gene expression is regulated by an interleukin-1beta-stimulated biphasic response with enhanced transcription and subcellular shuttling of YB-1. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012;91(6–7):533–41. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.12.002.
Kast HR, Goodwin B, Tarr PT, Jones SA, Anisfeld AM, Stoltz CM, et al. Regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (ABCC2) by the nuclear receptors pregnane X receptor, farnesoid X-activated receptor, and constitutive androstane receptor. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(4):2908–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109326200.
Teng S, Jekerle V, Piquette-Miller M. Induction of ABCC3 (MRP3) by pregnane X receptor activators. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003;31(11):1296–9. doi:10.1124/dmd.31.11.1296.
Jigorel E, Le Vee M, Boursier-Neyret C, Parmentier Y, Fardel O. Differential regulation of sinusoidal and canalicular hepatic drug transporter expression by xenobiotics activating drug-sensing receptors in primary human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006;34(10):1756–63. doi:10.1124/dmd.106.010033.
Assem M, Schuetz EG, Leggas M, Sun DX, Yasuda K, Reid G, et al. Interactions between hepatic Mrp4 and Sult2a as revealed by the constitutive androstane receptor and Mrp4 knockout mice. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(21):22250–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314111200.
Klaassen CD, Slitt AL. Regulation of hepatic transporters by xenobiotic receptors. Curr Drug Metab. 2005;6(4):309–28.
Moffit JS, Aleksunes LM, Maher JM, Scheffer GL, Klaassen CD, Manautou JE. Induction of hepatic transporters multidrug resistance-associated proteins (Mrp) 3 and 4 by clofibrate is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;317(2):537–45. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.093765.
Sinal CJ, Tohkin M, Miyata M, Ward JM, Lambert G, Gonzalez FJ. Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell. 2000;102(6):731–44.
Shih DQ, Bussen M, Sehayek E, Ananthanarayanan M, Shneider BL, Suchy FJ, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha is an essential regulator of bile acid and plasma cholesterol metabolism. Nat Genet. 2001;27(4):375–82. doi:10.1038/86871.
Jung D, Hagenbuch B, Gresh L, Pontoglio M, Meier PJ, Kullak-Ublick GA. Characterization of the human OATP-C (SLC21A6) gene promoter and regulation of liver-specific OATP genes by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(40):37206–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103988200.
Karpen SJ, Sun AQ, Kudish B, Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ, Ananthanarayanan M, et al. Multiple factors regulate the rat liver basolateral sodium-dependent bile acid cotransporter gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(25):15211–21.
Yacovino LL, Aleksunes LM. Renal efflux transporter expression in pregnant mice with Type I diabetes. Toxicol Lett. 2012;211(3):304–11. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.04.008.
Lam JL, Jiang Y, Zhang T, Zhang EY, Smith BJ. Expression and functional analysis of hepatic cytochromes P450, nuclear receptors, and membrane transporters in 10- and 25-week-old db/db mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(12):2252–8. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.034223.
Ananthanarayanan M, Balasubramanian N, Makishima M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Suchy FJ. Human bile salt export pump promoter is transactivated by the farnesoid X receptor/bile acid receptor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(31):28857–65. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011610200.
Ogasawara K, Terada T, Asaka J, Katsura T, Inui K. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4{alpha} regulates the human organic anion transporter 1 gene in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292(6):F1819–26. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00017.2007.
Saji T, Kikuchi R, Kusuhara H, Kim I, Gonzalez FJ, Sugiyama Y. Transcriptional regulation of human and mouse organic anion transporter 1 by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha/beta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324(2):784–90. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.128249.
Maher JM, Aleksunes LM, Dieter MZ, Tanaka Y, Peters JM, Manautou JE, et al. Nrf2- and PPAR alpha-mediated regulation of hepatic Mrp transporters after exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorodecanoic acid. Toxicol Sci. 2008;106(2):319–28. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn177.
Morohoshi M, Fujisawa K, Uchimura I, Numano F. Glucose-dependent interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor production by human peripheral blood monocytes in vitro. Diabetes. 1996;45(7):954–9.
Alexandraki KI, Piperi C, Ziakas PD, Apostolopoulos NV, Makrilakis K, Syriou V, et al. Cytokine secretion in long-standing diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: associations with low-grade systemic inflammation. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28(4):314–21. doi:10.1007/s10875-007-9164-1.
Moller DE. Potential role of TNF-α the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2. Diabetes. 2000;11:212–7.
Jhun H, Choi J, Hong J, Lee S, Kwak A, Kim E, et al. IL-32gamma overexpression accelerates streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 1 diabetes. Cytokine. 2014;69(1):1–5. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2014.05.002.
Le Vee M, Lecureur V, Stieger B, Fardel O. Regulation of drug transporter expression in human hepatocytes exposed to the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha or interleukin-6. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37(3):685–93. doi:10.1124/dmd.108.023630.
Petrovic V, Piquette-Miller M. Impact of polyinosinic/polycytidylic acid on placental and hepatobiliary drug transporters in pregnant rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38(10):1760–6. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.034470.
Vos TA, Hooiveld GJ, Koning H, Childs S, Meijer DK, Moshage H, et al. Up-regulation of the multidrug resistance genes, Mrp1 and Mdr1b, and down-regulation of the organic anion transporter, Mrp2, and the bile salt transporter, Spgp, in endotoxemic rat liver. Hepatology. 1998;28(6):1637–44. doi:10.1002/hep.510280625.
Tang W, Yi C, Kalitsky J, Piquette-Miller M. Endotoxin downregulates hepatic expression of P-glycoprotein and MRP2 in 2-acetylaminofluorene-treated rats. Mol Cell Biol Res Comm MCBRC. 2000;4(2):90–7. doi:10.1006/mcbr.2000.0264.
Cherrington NJ, Slitt AL, Li N, Klaassen CD. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated regulation of hepatic transporter mRNA levels in rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004;32(7):734–41.
Kameyama N, Arisawa S, Ueyama J, Kagota S, Shinozuka K, Hattori A, et al. Increase in P-glycoprotein accompanied by activation of protein kinase Calpha and NF-kappaB p65 in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1782(5):355–60. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.02.005.
Ghose R, Zimmerman TL, Thevananther S, Karpen SJ. Endotoxin leads to rapid subcellular re-localization of hepatic RXRalpha: a novel mechanism for reduced hepatic gene expression in inflammation. Nucl Recept. 2004;2(1):4. doi:10.1186/1478-1336-2-4.
Teng S, Piquette-Miller M. The involvement of the pregnane X receptor in hepatic gene regulation during inflammation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;312(2):841–8. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.076141.
Zimmerman TL, Thevananther S, Ghose R, Burns AR, Karpen SJ. Nuclear export of retinoid X receptor alpha in response to interleukin-1beta-mediated cell signaling: roles for JNK and SER260. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(22):15434–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M508277200.
Cressman AM, Petrovic V, Piquette-Miller M. Inflammation-mediated changes in drug transporter expression/activity: implications for therapeutic drug response. Exp Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2012;5(1):69–89. doi:10.1586/ecp.11.66.
Cheng J, Shah YM, Gonzalez FJ. Pregnane X receptor as a target for treatment of inflammatory bowel disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012;33(6):323–30. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2012.03.003.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81302836 and 81573499), Key Projects of National Science and Technology Program, China (Grant Nos. 2012ZX09301001-006, 2012ZX09302003 and 2012ZX09301001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Additional information
L. Ma, L. He and L. Wang are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., He, L., Wang, L. et al. Altered Expression of Transporters, its Potential Mechanisms and Influences in the Liver of Rodent Models Associated with Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 41, 199–210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-015-0306-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-015-0306-1