Abstract
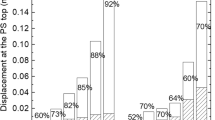
To study the seismic performances of steel frame structures in traditional-style buildings, the pseudo-dynamic test was carried out on a 1/2 ratio model built in the areas with a seismic design intensity of eight. The input earthquake waves included El Centro, Lanzhou and Wenchuan, and the maximum peak accelerations of these ground motions were 70, 200, 400 and 620 gal (0.7, 2, 4 and 6.2 m/s2). The seismic responses such as displacement, reaction force, acceleration were recorded. The hysteretic behavior, energy dissipation capacity, time-history curves of acceleration and displacement, bearing capacity and stiffness degradation were analyzed. The results show that the traditional-style steel frame structure stayed in the elastic stage subjected to no more than 400 gal (4 m/s2) PGA. There was no obvious pinch phenomenon in the hysteretic loops and the structural energy dissipation increased significantly with the increase of the seismic wave amplitude. When the 9-intensity seismic wave was applied, some unique members in traditional-style buildings yielded, and the spectral characteristic of the input seismic wave had a great influence on the seismic response of the structure. The modal analysis and time-history analyses were applied to the structure, the vertical deformation of the second and third modes of the steel frame was larger than that of the first modal shape, the reaction force value of finite element was a little larger than that of the test under the same loading condition. When the structure subjected to more severe earthquake, some unique members in traditional-style buildings acted as the first earthquake fortification line and dissipate most energy, and the structural most obvious reaction took place in advance or delayed a bit.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, G. L., Kang, L. G., Li, H. X., Li, X. W., & Zhao, C. L. (2011). Experimental study of the seismic performance of hybrid structure of SRC frame columns-RC disperse shear walls for large thermal power plants. China Civil Engineering Journal, 44(9), 20–26 (in Chinese).
Baker, S. J. F., & Charlton, T. M. (1958). A test on a two-storey single-bay portal structure. London: British Welding Research Association.
Fang, D. P., Iwasaki, S., Yu, M. H., Shen, Q. P., Miyamoto, Y., & Hikosaka, H. (2001). Ancient Chinese timber architecture. I: experimental study. Journal of Structural Engineering, 127(11), 1348–1357.
GB50011-2010. (2010). Code for seismic design of buildings. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press.
Jan, T. S., Liu, M. W., & Kao, Y. C. (2004). An upper-bound pushover analysis procedure for estimating the seismic demands of high-rise buildings. Engineering Structures, 26(1), 117–128.
Lauriola, M. P., & Sandhaas, C. (2006). Quasi-static and pseudo-dynamic tests on XLAM walls and buildings. COST E29 international workshop on earthquake engineering on timber structures, Coimbra, Portugal.
Ren, W. X., Zhao, T., & Harik, I. E. (2004). Experimental and analytical modal analysis of steel arch bridge. Journal of Structural Engineering, 130(7), 1022–1031.
Tian, Y. F. (2010). Chinese imitated ancient building explanation. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press (in Chinese).
Tremblay, R., Archambault, M.-H., & Filiatrault, A. (2003). Seismic response of concentrically braced steel frames made with rectangular hollow bracing members. Journal of Structural Engineering, 129(12), 1626–1636.
Tsai, K. C., Hsiao, P. C., Wang, K. J., Weng, Y. T., Lin, M. L., Lin, K. C., et al. (2008). Pseudo-dynamic tests of a full-scale CFT/BRB frame-Part I: specimen design, experiment and analysis. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 37(7), 1081–1098.
Wodzicki, T. (2001). Natural factors affecting wood structure. Wood Science and Technology, 35(1–2), 5–26.
Xue, J. Y., & Qi, L. J. (2016). Experimental studies on steel frame structures of traditional-style buildings. Steel and Composite Structures, 22(2), 235–255.
Xue, J. Y., Wu, Z. J., Sui, Y., Ge, H. P., & Wu, K. (2016). Experimental study and numerical analysis on aseismic performance of steel double-beams-column interior-joints in traditional style building. Engineering Mechanics, 33(5), 97–105 (in Chinese).
Xue, J. Y., Wu, Z. J., Sui, Y., & Liu, Z. Q. (2015). Experimental study on seismic performance of steel double-beams column exterior joints in antique style building. Journal of Building Structures, 36(3), 80–89 (in Chinese).
Yang, Y., Liu, R. Y., Xue, Y. C., & Li, H. (2017). Experimental study on seismic performance of reinforced concrete frames retrofitted with eccentric buckling-restrained braces (BRBs). Earthquakes and Structures, 12(1), 79–89.
Zhang, X. C., Xue, J. Y., Zhao, H. T., & Sui, Y. (2011). Experimental study on Chinese ancient timber-frame building by shaking table test. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 40(4), 453–469.
Zheng, S. S. (2000). Analogical ratio between scale models with less ballast and their prototypes under shaking table test. Industrial Construction, 30(3), 35–39 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51208411), the Technology Research Task of China State Construction Engineering Corporation (Grant No. CSCEC-2012-Z-16) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation of XAUAT (6040317006). Financial support from the China Scholarship Council for Liangjie Qi’s work at Virginia Tech, as a visiting scholar, is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, L., Xue, J. Pseudo Dynamic Test and Time-History Analyses of Traditional-Style Steel Frame Structures. Int J Steel Struct 18, 402–416 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-018-0007-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-018-0007-0