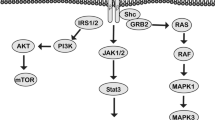
Abstract
Abnormal expression of insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression with largely unknown mechanisms. In this study, IGF-IR expression among different HCC cell lines and silencing its gene transcription on effects of HCC were investigated by short hairpin RNA (shRNA). Specific shRNA was successfully transfected into Bel-7404 or PLC/PRF/5 cells with 90 or 71 % efficiency. The inhibiting rate of IGF-IR at mRNA level were 54.9 % in Bel-7404 or 59.6 % in PLC/PRF/5 cells in accordance with its protein suppression, with the cell cycles at the G1 phase arrest and decreasing cyclinD1 via promoting apoptosis in vitro. With the xenograft models of PLC/PRF/5 cells inserted specific shRNA in vivo, the tumor-forming time (14.0 ± 1.1 days) or tumor volume (143 ± 24 mm3) in the shRNA group was significantly lengthened or smaller than those in the control group (7.2 ± 0.8 days or 372 ± 46 mm3, P < 0.001) or in the neg-shRNA group (7.5 ± 1.0 days or 350 ± 50 mm3, P < 0.001). Silencing the IGF-IR gene transcription inhibited cell proliferation or xenograft tumor growth of HCC, suggesting that IGF-IR might be a novel potential target for HCC gene therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFP:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein
- FQ-RT-PCR:
-
Fluorescence quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- IGF:
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- IGF-II:
-
Insulin-like growth factor II
- IGF-IR:
-
Insulin-like growth factor I receptor
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- PPP:
-
Picropodophyllin
References
Shiraha H, Yamamoto K, Namba M. Human hepatocyte carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 2013;42(4):1133–8.
Chi M, Mikhitarian K, Shi C, Goff LW. Management of combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma: a case report and literature review. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2012;5(6):199–202.
Cheng JW, Lv Y. New progress of non-surgical treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):381.
Hyodo T, Murakami T, Imai Y, Okada M, Hori M, Kagawa Y, et al. Hypovascular nodules in patients with chronic liver disease: risk factors for development of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2013;266(2):480–90.
Hu J, Gao DZ. Distinction immune genes of hepatitis-induced heptatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(24):3191–4.
Arzumanyan A, Reis HM, Feitelson MA. Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;13(2):123–35.
Kew MC. Hepatitis B virus x protein in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(S1):144–52.
Wang L, Yao M, Dong Z, Zhang Y, Yao D. Circulating specific biomarkers in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and its metastasis monitoring. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(1):9–20.
Zhu AX, Ancukiewicz M, Supko JG, Sahani DV, Blaszkowsky LS, Meyerhardt JA, et al. Efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics, and biomarkers of cediranib monotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II study. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(6):1557–66.
Hamed O, Kimchi ET, Sehmbey M, Gusani NJ, Kaifi JT, Staveley-O’Carroll K. Impact of genetic targets on cancer therapy: hepatocellular cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;779(1):67–90.
Maakaron JE, Cappellini MD, Graziadei G, Ayache JB, Taher AT. Hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis-negative patients with thalassemia intermedia: a closer look at the role of siderosis. Ann Hepatol. 2013;12(1):142–6.
Broderick JA, Zamore PD. MicroRNA therapeutics. Gene Ther. 2011;18(12):1104–10.
Xu C, Lee SA, Chen X. RNA interference as therapeutics for hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2011;6(1):106–15.
Gailhouste L, Ochiya T. Cancer-related microRNAs and their role as tumor suppressors and oncogenes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28(4):437–51.
EC, Li J, Shao D, Zhang D, Pan Y, Chen L, et al. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibitor picropodophyllin-induced selective apoptosis of hepato-cellular carcinoma cell through a caspase-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Oncol Res. 2014;21(2):103–10.
Hsu HH, Cheng LH, Ho TJ, Kuo WW, Lin YM, Chen MC, et al. Apicidin-resistant HA22T hepatocellular carcinoma cells massively promote pro-survival capability via IGF-IR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(1):303–13.
Dong ZZ, Yao M, Qian J, Yan XD, Chen J, Yan MJ, et al. Abnormal expression of insulin-like growth factor-II and intervening of its mRNA transcription in the promotion of HepG2 cell apoptosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;93(12):892–6 .Chinese
Qian J, Yao D, Dong Z, Wu W, Qiu L, Yao N, et al. Characteristics of hepatic igf-ii expression and monitored levels of circulating igf-ii mRNA in metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134(5):799–806.
Yao N, Yao D, Wang L, Dong Z, Wu W, Qiu L, et al. Inhibition of autocrine IGF-II on effect of human HepG2 cell proliferation and angiogenesis factor expression. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(5):1767–76.
Qiu LW, Yao DF, Zong L, Lu YY, Huang H, Wu W, et al. Abnormal expression of insulin-like growth factor-II and its dynamic quantitative analysis at different stages of hepatocellular carcinoma development. Hepatobiliary Pancreatol Dis Int. 2008;7(4):406–11.
Zhang HJ, Yao DF, Yao M, Huang H, Wang L, Yan MJ, et al. Annexin A2 silencing inhibits invasion, migration, and tumorigenic potential of hepatoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(24):3792–801.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379(9822):1245–55.
Yang JD, Roberts LR. Hepatocellular carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(8):449–58.
El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(6):1264–73.
Yang YH, Wen TF, Chen X. Resection margin in hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2012;59(117):1393–7.
Ubagai T, Kikuchi T, Fukusato T, Ono Y. Aflatoxin B1 modulates the insulin-like growth factor-2 dependent signaling axis. Toxicol in Vitro. 2010;24(3):783–9.
Chen YW, Boyartchuk V, Lewis BC. Differential roles of insulin-like growth factor receptor- and insulin receptor-mediated signaling in the phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Neoplasia. 2009;11(9):835–45.
Nussbaum T, Samarin J, Ehemann V, Bissinger M, Ryschich E, Khamidjanov A, et al. Autocrine insulin-like growth factor-II stimulation of tumor cell migration is a progression step in human hepato-carcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2008;48(1):146–56.
Okushin K, Asaoka Y, Fukuda I, Fujiwara N, Minami T, Sato M, et al. IGF-II producing hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib: metabolic complications and a foresight to molecular targeting therapy to the IGF signal. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2012;6(3):784–9.
Alexia C, Bras M, Fallot G, Vadrot N, Daniel F, Lasfer M, et al. Pleiotropic effects of PI-3′ kinase/Akt signaling in human hepatoma cell proliferation and drug- induced apoptosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1090(1):1–17.
El Tayebi HM, Salah W, El Sayed IH, Salam EM, Zekri AR, Zayed N, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II, matrix metalloproteinases, and their tissue inhibitors as predictive markers in the peripheral blood of HCC patients. Biomarkers. 2011;16(4):346–54.
Breuhahn K, Schirmacher P. Reactivation of the insulin-like growth factor-II signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(11):1690–8.
Aleem E, Nehrbass D, Klimek F, Mayer D, Bannasch P. Upregulation of the insulin receptor and type I insulin-like growth factor receptor are early events in hepatocarcinogenesis. Toxicol Pathol. 2011;39(3):524–43.
Weng CJ, Hsieh YH, Tsai CM, Chu YH, Ueng KC, Liu YF, et al. Relationship of insulin-like growth factors system gene polymorphisms with the susceptibility and pathological development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(7):1808–15.
Tomizawa M, Yokosuka O. Picropodophyllin suppresses the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma under serum starvation. Mol Med Rep. 2008;1(5):685–8.
Campbell CI, Moorehead RA. Mammary tumors that become independent of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor expressed elevated levels of platelet-derived growth factor receptors. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:480.
Lang SA, Hackl C, Moser C, Fichtner-Feigl S, Koehl GE, Schlitt HJ, et al. Implication of RICTOR in the mTOR inhibitor-mediated induction of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Her2) expression in gastrointestinal cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1803(4):435–42.
Cuevas EP, Escribano O, Monserrat J, Martínez-Botas J, Sánchez MG, Chiloeches A, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of insulin receptor substrate-4 enhances actinomycin D- and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death in hepato-carcinoma cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(6):1292–301.
Freise C, Ruehl M, Erben U, Neumann U, Seehofer D, Kim KY, et al. A hepatoprotective Lindera obtusiloba extract suppresses growth and attenuates insulin like growth factor-1 receptor signaling and NF-kappaB activity in human liver cancer cell lines. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011;11(1):39–46.
Alexia C, Fallot G, Lasfer M, Schweizer-Groyer G, Groyer A. An evaluation of the role of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and of type-I IGF receptor signalling in hepatocarcinogenesis and in the resistance of hepatocarcinoma cells against drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68(6):1003–15.
Tovar V, Alsinet C, Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, Chiang DY, Solé M, et al. IGF activation in a molecular subclass of hepatocellular carcinoma and pre-clinical efficacy of IGF-1R blockage. J Hepatol. 2010;52(4):550–9.
Zhao H, Desai V, Wang J, Epstein DM, Miglarese M, Buck E. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition predicts sensitivity to the dual IGF-1R/IR inhibitor OSI-906 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(2):503–13.
Cao H, Phan H, Yang LX. Improved chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(4):1379–86.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants-in-aid from the Projects of Nantong Society Development (HS2014078), the Jiangsu Health Projects (2014-YY-028 and 2013-WSN-011), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu (PADA), and the International S. & T. Cooperation Program of China (2013DFA32150). And we thank T. FitzGibbon, M.D., for comments on earlier drafts of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Min Yao, Li Wang, and Junling Yang contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, M., Wang, L., Yang, J. et al. IGF-I receptor as an emerging potential molecular-targeted for hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo . Tumor Biol. 37, 14677–14686 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5296-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5296-3