Abstract
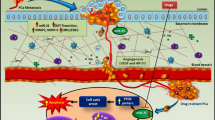
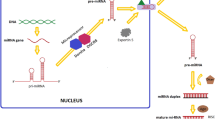
The expression of microRNAs (miRNAs), as novel biomarkers, is subject to change in many cancers. Therefore, the overall profile of miRNAs can be used for detection of cancer type, response to therapies, pathological variables, and other factors related to the disease. In this study, to evaluate miRNA expression associated with the tumor progression and response to treatment, 60 BALB/c mice received subcutaneous injections of 4T1 cells. The study includes ten groups: one group as control, six groups were euthanized at different time points to assess the role of miRNA expression in the tumor progression, and three groups received chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery to evaluate miRNA expression in response to treatment. MicroRNAs were extracted from the breast tumor and the plasma samples, and their relative expressions were quantified using qRT-PCR. MiR-155 expression was increased in the plasma in the early weeks after the cell injection but decreased in the plasma after surgery and radiotherapy and also in tumor samples after chemotherapy and radiotherapy. MiR-10b expression was increased in the late weeks both in the plasma and the tumor and was decreased in the plasma after radiotherapy and surgery and in the tumor after radiotherapy. MiR-21 expression was increased in the plasma and the tumor tissue during the disease progression at the third and the fourth weeks following tumor induction but was decreased in the plasma in all the therapy groups. Interestingly, miR-125a showed a significant decrease during the tumor progression, and its expression was increased after the treatment. Our results showed that the candidate miRNAs could be divided into two groups of oncomiRs and tumor suppressor miR based on their deregulation after tumor growth and treatments. It seems that the oncomiRs in the plasma can be an ideal noninvasive candidate biomarker for the early detection of breast cancer and also for following the response of the common therapies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–917.
Fritz S, Hackert T, Hinz U, Hartwig W, Büchler M, Werner J. Role of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen in distinguishing between benign and invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Br J Surg. 2011;98(1):104–10.
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DS, Pantel K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(6):426–37.
Si M, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F, Mo Y. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 2007;26(19):2799–803.
Zhu S, Si M-L, Wu H, Mo Y-Y. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14328–36.
Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP, Falconi M, Capelli P, Bersani S, et al. MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic features and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(29):4677–84.
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(2):1026–33.
Iorio MV, Casalini P, Tagliabue E, Ménard S, Croce CM. MicroRNA profiling as a tool to understand prognosis, therapy response and resistance in breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44(18):2753–9.
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Marcusson EG, et al. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):341–7.
Scott GK, Goga A, Bhaumik D, Berger CE, Sullivan CS, Benz CC. Coordinate suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3 by enforced expression of micro-RNA miR-125a or miR-125b. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(2):1479–86.
Jiang S, Zhang H-W, Lu M-H, He X-H, Li Y, Gu H, et al. MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. 2010;70(8):3119–27.
Isanejad A, Alizadeh AM, Shalamzari SA, Khodayari H, Khodayari S, Khori V, et al. MicroRNA-206, let-7a and microRNA-21 pathways involved in the anti-angiogenesis effects of the interval exercise training and hormone therapy in breast cancer. Life Sci. 2016;151:30–40.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu C-G, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(16):7065–70.
Alizadeh AM, Shiri S, Farsinejad S. Metastasis review: from bench to bedside. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(9):8483–523.
Sharbati-Tehrani S, Kutz-Lohroff B, Bergbauer R, Scholven J, Einspanier R. miR-Q: a novel quantitative RT-PCR approach for the expression profiling of small RNA molecules such as miRNAs in a complex sample. BMC Mol Biol. 2008;9(1):1–13.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105(30):10513–8.
Wang F, Hou J, Jin W, Li J, Yue Y, Jin H, et al. Increased circulating microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker for breast cancer screening: a meta-analysis. Molecules. 2014;19(5):6282–93.
Farhangi B, Alizadeh AM, Khodayari H, Khodayari S, Dehghan MJ, Khori V, et al. Protective effects of dendrosomal curcumin on an animal metastatic breast tumor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;758:188–96.
Alizadeh AM, Sadeghizadeh M, Najafi F, Ardestani SK, Erfani-Moghadam V, Khaniki M, et al. Encapsulation of curcumin in diblock copolymer micelles for cancer therapy. BioMed research international. 2015;2015:824746.
Wang W. Radiotherapy in the management of early breast cancer. Journal of medical radiation sciences. 2013;60(1):40–6.
Hemmati M, Abbaspour A, Alizadeh A, Khaniki M, Amanzadeh A, Mohagheghi M, et al. Rat xenograft chondrosarcoma development by human tissue fragment. Exp Oncol. 2011;33(1):52–4.
Mohsenikia M, Alizadeh AM, Khodayari S, Khodayari H, Karimi A, Zamani M, et al. The protective and therapeutic effects of alpha-solanine on mice breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;718(1):1–9.
Khori V, Shalamzari SA, Isanejad A, Alizadeh AM, Alizadeh S, Khodayari S, et al. Effects of exercise training together with tamoxifen in reducing mammary tumor burden in mice: possible underlying pathway of miR-21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;765:179–87.
Costinean S, Zanesi N, Pekarsky Y, Tili E, Volinia S, Heerema N, et al. Pre-B cell proliferation and lymphoblastic leukemia/high-grade lymphoma in Eμ-miR155 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(18):7024–9.
Sun Y, Wang M, Lin G, Sun S, Li X, Qi J, et al. Serum microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track disease in breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47003.
O’Connell RM, Kahn D, Gibson WS, Round JL, Scholz RL, Chaudhuri AA, et al. MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing inflammatory T cell development. Immunity. 2010;33(4):607–19.
Haque I, Banerjee S, Mehta S, De A, Majumder M, Mayo MS, et al. Cysteine-rich 61-connective tissue growth factor-nephroblastoma-overexpressed 5 (CCN5)/Wnt-1-induced signaling protein-2 (WISP-2) regulates microRNA-10b via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-TWIST signaling networks in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(50):43475–85.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449(7163):682–8.
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S, Itzykson RA, Come C, et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 2004;117(7):927–39.
Ibrahim SA, Yip GW, Stock C, Pan JW, Neubauer C, Poeter M, et al. Targeting of syndecan-1 by microRNA miR-10b promotes breast cancer cell motility and invasiveness via a Rho-GTPase- and E-cadherin-dependent mechanism. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(6):E884–96.
Anastasov N, Höfig I, Vasconcellos IG, Rappl K, Braselmann H, Ludyga N, et al. Radiation resistance due to high expression of miR-21 and G2/M checkpoint arrest in breast cancer cells. Radiat Oncol. 2012;7(1):1.
Fujita S, Ito T, Mizutani T, Minoguchi S, Yamamichi N, Sakurai K, et al. miR-21 gene expression triggered by AP-1 is sustained through a double-negative feedback mechanism. J Mol Biol. 2008;378(3):492–504.
Yan L-X, Huang X-F, Shao Q, Huang M-Y, Deng L, Wu Q-L, et al. MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008;14(11):2348–60.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu C-G, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(7):2257–61.
Asangani I, Rasheed S, Nikolova D, Leupold J, Colburn N, Post S, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27(15):2128–36.
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65(14):6029–33.
Hu HY, Li KP, Wang XJ, Liu Y, Lu ZG, Dong RH, et al. Set9, NF-κB, and microRNA-21 mediate berberine-induced apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(1):157–66.
Hu N, Wang C, Han X-Y, He L-J, Tang Z-Z, Giffen C, et al. Evaluation of BRCA2 in the genetic susceptibility of familial esophageal cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23(3):852–8.
Gao J, Zhang Q, Xu J, Guo L, Li X. Clinical significance of serum miR-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013;25(6):743–8.
Zhao D, Tu Y, Wan L, Bu L, Huang T, Sun X, et al. In vivo monitoring of angiogenesis inhibition via down-regulation of mir-21 in a VEGFR2-luc murine breast cancer model using bioluminescent imaging. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e71472.
Chaudhry MA, Sachdeva H, Omaruddin RA. Radiation-induced micro-RNA modulation in glioblastoma cells differing in DNA-repair pathways. DNA Cell Biol. 2010;29(9):553–61.
Chaudhry MA. Real-time PCR analysis of micro-RNA expression in ionizing radiation-treated cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009;24(1):49–56.
García-Becerra R, Santos N, Diaz L, Camacho J. Mechanisms of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: focus on signaling pathways, mirnas and genetically based resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(1):108–45.
Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, et al. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(12):849–59.
Sun Y-M, Lin K-Y, Chen Y-Q. Diverse functions of miR-125 family in different cell contexts. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6(6).
Bi Q, Tang S, Xia L, Du R, Fan R, Gao L, et al. Ectopic expression of MiR-125a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40169.
Wagner-Ecker M, Schwager C, Wirkner U, Abdollahi A, Huber PE. MicroRNA expression after ionizing radiation in human endothelial cells. Radiation Oncology. 2010; 5(25).
Zhao B-S, Liu S-G, Wang T-Y, Ji Y-H, Qi B, Tao Y-P, et al. Screening of microRNA in patients with esophageal cancer at same tumor node metastasis stage with different prognoses. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(1):139–43.
Kardeh S, Ashkani-Esfahani S, Alizadeh AM. Paradoxical action of reactive oxygen species in creation and therapy of cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;735:150–68.
Farsinejad S, Gheisary Z, Samani SE, Alizadeh AM. Mitochondrial targeted peptides for cancer therapy. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(8):5715–25.
Simone NL, Soule BP, Ly D, Saleh AD, Savage JE, DeGraff W, et al. Ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression. PLoS One. 2009;4(7):e6377.
Zhao L, Bode AM, Cao Y, Dong Z. Regulatory mechanisms and clinical perspectives of miRNA in tumor radiosensitivity. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33(11):2220–7.
Wang L, Yuan C, Lv K, Xie S, Fu P, Liu X, et al. Lin28 mediates radiation resistance of breast cancer cells via regulation of caspase, H2A.X and Let-7 signaling. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67373.
Marvaso G, Barone A, Amodio N. Emerging role of microRNAs in breast cancer radiotherapy. RNA & DISEASE. 2015;2(4):e786.
Cellini F, Morganti AG, Genovesi D, Silvestris N, Valentini V. Role of microRNA in response to ionizing radiations: evidences and potential impact on clinical practice for radiotherapy. Molecules. 2014;19(4):5379–401.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number 23797).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farsinejad, S., Rahaie, M., Alizadeh, A.M. et al. Expression of the circulating and the tissue microRNAs after surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy in mice mammary tumor. Tumor Biol. 37, 14225–14234 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5292-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5292-7