Abstract
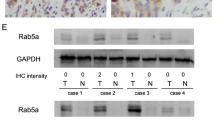
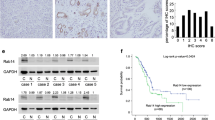
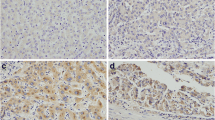
The Rab family GTPases regulate many major biological processes during tumor progression such as cell proliferation, cytoskeleton organization, cell movement, and invasion. The present study aims to examine the clinical significance, biological roles, and molecular mechanism of Rab11a in pancreatic cancer progression. We examined expression pattern of Rab11a in 96 cases of pancreatic cancer specimens using immunohistochemistry and found Rab11a overexpression correlated with tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (p = 0.0111). We depleted Rab11a in Bxpc3 cells using small interfering RNA (siRNA) and overexpressed Rab11a in Capan2 cells. Knockdown of Rab11a inhibited cell growth, invasion, and cell cycle progression while its overexpression facilitated cell growth, invasion, and cell cycle progression. In addition, Rab11a overexpression increased gemcitabine resistance and inhibited gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in Capan2 cells while its depletion reduced drug resistance. We investigated the role of Rab11a in the regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and we demonstrated that Rab11a overexpression upregulated GSK3β phosphorylation and nuclear β-catenin accumulation. Rab11a depletion inhibited while its overexpression enhanced β-catenin/T-cell factor (TCF) transcriptional activity with corresponding change of Wnt target genes including cyclin D1, cyclin E, MMP7, and c-myc. Wnt inhibitor (FH535) partly attenuated the effects of Rab11a on cell proliferation and Wnt target genes. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that Rab11a promotes aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer through GSK3β/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29.
Kessler D, Gruen GC, Heider D, Morgner J, Reis H, Schmid KW, et al. The action of small GTPases Rab11 and Rab25 in vesicle trafficking during cell migration. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;29(5–6):647–56.
Ramel D, Wang X, Laflamme C, Montell DJ, Emery G. Rab11 regulates cell-cell communication during collective cell movements. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(3):317–24.
Hehnly H, Doxsey S. Rab11 endosomes contribute to mitotic spindle organization and orientation. Dev Cell. 2014;28(5):497–507.
Kelly EE, Horgan CP, McCaffrey MW. Rab11 proteins in health and disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012;40(6):1360–7.
Desclozeaux M, Venturato J, Wylie FG, Kay JG, Joseph SR, Le HT, et al. Active Rab11 and functional recycling endosome are required for E-cadherin trafficking and lumen formation during epithelial morphogenesis. Am J Phys Cell Physiol. 2008;295(2):C545–56.
Palmieri D, Bouadis A, Ronchetti R, Merino MJ, Steeg PS. Rab11a differentially modulates epidermal growth factor-induced proliferation and motility in immortal breast cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;100(2):127–37.
Kazemi-Noureini S, Colonna-Romano S, Ziaee AA, Malboobi MA, Yazdanbod M, Setayeshgar P, et al. Differential gene expression between squamous cell carcinoma of esophageus and its normal epithelium; altered pattern of mal, akr1c2, and rab11a expression. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(12):1716–21.
Chung YC, Wei WC, Huang SH, Shih CM, Hsu CP, Chang KJ, et al. Rab11 regulates E-cadherin expression and induces cell transformation in colorectal carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:587.
Kornmann M, Ishiwata T, Itakura J, Tangvoranuntakul P, Beger HG, Korc M. Increased cyclin D1 in human pancreatic cancer is associated with decreased postoperative survival. Oncology. 1998;55(4):363–9.
Kornmann M, Arber N, Korc M. Inhibition of basal and mitogen-stimulated pancreatic cancer cell growth by cyclin D1 antisense is associated with loss of tumorigenicity and potentiation of cytotoxicity to cisplatinum. J Clin Invest. 1998;101(2):344–52.
Lin CJ, Malina A, Pelletier J. c-Myc and eIF4F constitute a feedforward loop that regulates cell growth: implications for anticancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2009;69(19):7491–4.
Shukla SK, Gunda V, Abrego J, Haridas D, Mishra A, Souchek J, et al. MUC16-mediated activation of mTOR and c-Myc reprograms pancreatic cancer metabolism. Oncotarget. 2015;6(22):19118–31.
Koenig A, Linhart T, Schlengemann K, Reutlinger K, Wegele J, Adler G, et al. NFAT-induced histone acetylation relay switch promotes c-Myc-dependent growth in pancreatic cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(3):1189–99 .e1-2
Kumar K, Raza SS, Knab LM, Chow CR, Kwok B, Bentrem DJ, et al. GLI2-dependent c-MYC upregulation mediates resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9489.
Kim DY, Kim MJ, Kim HB, Lee JW, Bae JH, Kim DW, et al. Suppression of multidrug resistance by treatment with TRAIL in human ovarian and breast cancer cells with high level of c-Myc. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1812(7):796–805.
McNeil CM, Sergio CM, Anderson LR, Inman CK, Eggleton SA, Murphy NC, et al. c-Myc overexpression and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006;102(1–5):147–55.
Wang L, Heidt DG, Lee CJ, Yang H, Logsdon CD, Zhang L, et al. Oncogenic function of ATDC in pancreatic cancer through Wnt pathway activation and beta-catenin stabilization. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(3):207–19.
Pilarsky C, Ammerpohl O, Sipos B, Dahl E, Hartmann A, Wellmann A, et al. Activation of Wnt signalling in stroma from pancreatic cancer identified by gene expression profiling. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(6B):2823–35.
Zhou W, Li Y, Gou S, Xiong J, Wu H, Wang C, et al. MiR-744 increases tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer by activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(35):37557–69.
Wang B, Zou Q, Sun M, Chen J, Wang T, Bai Y, et al. Reversion of trichostatin A resistance via inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(5):2015–22.
Cui J, Jiang W, Wang S, Wang L, Xie K. Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in drug resistance of pancreatic cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(17):2464–71.
Benelli R, Monteghirfo S, Vene R, Tosetti F, Ferrari N. The chemopreventive retinoid 4HPR impairs prostate cancer cell migration and invasion by interfering with FAK/AKT/GSK3beta pathway and beta-catenin stability. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:142.
Luo J. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2009;273(2):194–200.
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim NH, et al. A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(12):1398–406.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by China NSFC project (no. 31371177) and Health and Family Planning Commission of Liaoning project Province (LNCCC-D31-2015).We thank Dr. Yang Wang and Dr. Yang Liu for IHC evaluation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Li, X., Li, H. et al. Rab11a sustains GSK3β/Wnt/β-catenin signaling to enhance cancer progression in pancreatic cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 13821–13829 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5172-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5172-1