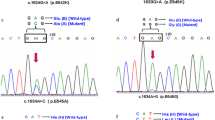
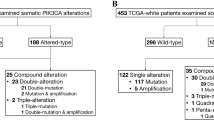
Abstract
Breast cancer (BCa) is the most common cancer and the second cause of death among women. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway has a crucial role in the cellular processes such as cell survival, growth, division, and motility. Moreover, oncogenic mutations in the PI3K pathway generally involve the activation phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase-catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) mutation which has been identified in numerous BCa subtypes. In this review, correlations between PIK3CA mutations and their clinicopathological parameters on BCa will be described. It is reported that PIK3CA mutations which have been localized mostly on exon 9 and 20 hot spots are detected 25–40 % in BCa. This relatively high frequency can offer an advantage for choosing the best treatment options for BCa. PIK3CA mutations may be used as biomarkers and have been major focus of drug development in cancer with the first clinical trials of PI3K pathway inhibitors currently in progress. Screening of PIK3CA gene mutations might be useful genetic tests for targeted therapeutics or diagnosis. Increasing data about PIK3CA mutations and its clinical correlations with BCa will help to introduce new clinical applications in the near future.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolfson B, Eades G, Zhou Q. Adipocyte activation of cancer stem cell signaling in breast cancer. World J Biol Chem. 2015;6(2):39–47.
Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:606–19.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2015. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2015. Available online: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@editorial/documents/document/acspc-044552.pdf. Accessed 23 Feb 2015.
Shi L. Racial differences in breast cancer patterns. Science. 2010;329:5987.
Sarkar S, Mahitosh Mandal. Breast cancer: classification based on molecular etiology influencing prognosis and prediction. Medicine » oncology » breast cancer - focusing tumor microenvironment, stem cells and metastasis (book). 978-953-307-766-6.
Kufe DW, Frei E, Hollander JF, Weichselbaum RR, Pollock RE, Bast RC, et al. Holland-Frei cancer medicine. 6th ed. Hamilton: B.C. Decker; 2003.
Bedard PL, Hansen AR, Ratain MJ, Siu LL. Tumour heterogeneity in the clinic. Nature. 2013;501:355–64.
Mayer EL. Understanding targeted therapy. Cancer.Net editorial board. 2015. http://www.cancer.net/navigating-cancer-care/how-cancer-treated/personalized-and-targeted-therapies/understandingtargeted-therapy. Accessed 21 Jan 2015.
Weinberg RA. Oncogenes and antioncogenes, and the molecular basis of multistep carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1989;49:3713–21.
Weinstein IB. The origins of human cancer: molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis and their implications for cancer prevention and treatment twenty-seventh G.H.A. Clowes Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res. 1988;48:4135–43.
Bozzone D. Causes of cancer (Biology of cancer). 1st ed. Broomall: Chelsea House Publishers; 2006.
Cohen SM, Ellwein LB. Cell proliferation in carcinogenesis. Science. 1990;249(4972):1007–11.
Saha Roy S, Vadlamudi RK. Role of estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer metastasis. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012;654–98.
Weber GF. Molecular mechanisms of cancer. Copyright: 2007.
Whitman M, Kaplan DR, Schaffhausen B, Cantley L, Roberts TM. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985;315(6016):239–42.
Sugimoto Y, Whitman M, Cantley LC, Erikson RL. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81:2117–21.
Gadina M, Sudarshan C, Visconti R, Zhou YJ, Gu H, Neel BG, et al. The docking molecule gab2 is induced by lymphocyte activation and is involved in signaling by interleukin-2 and interleukin-15 but not other common gamma chainusing cytokines. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:26959–66.
Okkenhaug K. Signaling by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase family in immune cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:675–704.
Karakas B, Bachman K, Park B. Mutation of the PIK3CA oncogene in human cancers. Br J Cancer. 2006;94:455–9.
Ligresti G, Militello L, Steelman L, Cavallaro A, Basile F, Nicoletti F, et al. PIK3CA mutations in human solid tumors. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:1352–8.
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Siliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304:554.
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:627–44.
Engelman JA. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(8):550–62.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Guillermet-Guibert J, Graupera M, Bilanges B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:329–41.
Andrews S, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT. PI3K class IB pathway in neutrophils. Sci STKE. 2007;cm3. doi:10.1126/stke.4072007cm3.
Bader AG, Kang S, Zhao L, Vogt PK. Oncogenic PI3K deregulates transcription and translation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:921–9.
Philp AJ, Campbell IG, Leet C, Vincan E, Rockman SP, Whitehead RH, et al. The phosphatidylinositol 3'‐kinase p85alpha gene is an oncogene in human ovarian and colon tumours. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7426–9.
Gallia GL, Rand V, Siu IM, Eberhart CG, James CD, Marie SK, et al. PIK3CA gene mutations in pediatric and adult glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer Res. 2006;4:709–14.
Carson JD, Van Aller G, Lehr R, Sinnamon RH, Kirkpatrick RB, Auger KR, et al. Effects of oncogenic p110alpha subunit mutations on the lipid kinase activity of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Biochem J. 2008;409:519–24.
Murugan AK, Hong NT, Fukui Y, Munirajan AK, Tsuchida N. Oncogenic mutations of the PIK3CA gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:101–11.
Riener MO, Bawohl M, Clavien PA, Jochum W. Rare PIK3CA hotspot mutations in carcinomas of the biliary tract. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2008;47:363–7.
COSMIC Database. 2015. http://www.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic. Accessed 28 July 2015.
Bowles DW, Jimeno A. New phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011;20(4):507–18.
Garcia-Dios DA, Lambrechts D, Coenegrachts L, Vandenput I, Capoen A, Webb PM, et al. High-throughput interrogation of PIK3CA, PTEN, KRAS, FBXW7 and TP53 mutations in primary endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;128(2):327–34.
Sun X, Huang J, Homma T, Kita D, Klocker H, Schafer G, et al. Genetic alterations in the PI3K pathway in prostate cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29(5):1739–43.
Liu CX, Li XY, Li CF, Chen YZ, Cui XB, Hu JM, et al. Compound HRAS/PIK3CA mutations in Chinese patients with alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(4):1771–4.
Tong L, Yang XX, Liu MF, Yao GY, Dong JY, Ye CS, et al. Mutational analysis of key EGFR pathway genes in Chinese breast cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13(11):5599–603.
Klarenbeek S, van Miltenburg MH, Jonkers J. Genetically engineered mouse models of PI3K signaling in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2013;7(2):146–64.
Levine DA, Bogomolniy F, Yee CJ, Lash A, Barakat RR, Borgen PI, et al. Frequent mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2875–8.
Saal LH, Holm K, Maurer M, Memeo L, Su T, Wang X, et al. PIK3CA mutations correlate with hormone receptors, node metastasis, and ERBB2, and are mutually exclusive with PTEN loss in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2554–9.
Miled N, Yan Y, Hon WC, Perisic O, Zvelebil M, Inbar Y, et al. Mechanism of two classes of cancer mutations in the phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit. Science. 2007;317:239–42.
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Ferrer-Lozano J, Stemke-Hale K, Sahin A, Liu S, Barrera JA, et al. PI3K pathway mutations and PTEN levels in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(6):1093–101.
Stemke-Hale K, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Neve RM, Kuo WL, Davies M, et al. An integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of PIK3CA, PTEN, and AKT mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68(15):6084–91.
Guo RX, Wei LH, Wang JL, Sun PM, Sun XL. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B (PI3K-PKB) induced by 17beta-estradiol in endometrial carcinoma cell (Ishikawa). Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2004;39(7):469–73.
Schuur ER, Loktev AV, Sharma M, Sun Z, Roth RA, Weigel RJ. Ligand-dependent interaction of estrogen receptoralpha with members of the forkhead transcription factor family. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(36):33554–60.
Generali D, Fox SB, Brizzi MP, Allevi G, Bonardi S, Aguggini S, et al. Down-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/AKT/molecular target of rapamycin metabolic pathway by primary letrozole-based therapy in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(9):2673–80.
Campbell M, Allen WE, Sawyer C, Vanhaesebroeck B, Trimble ER. Glucose-potentiated chemotaxis in human vascular smooth muscle is dependent on cross-talk between the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways. Circ Res. 2004;95(4):380–8.
Maruyama N, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Monden M, Noguchi S. Clinicopathologic analysis of breast cancer with PIK3CA mutations in Japanese women. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:408–14.
Kalinsky K, Jacks LM, Heguy A, et al. PIK3CA mutation associates with improved outcome in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5049–59.
Perez-Tenorio G, Alkhori L, Olsson B, Waltersson MA, Nordenskjöld B, Rutqvist LE, et al. PIK3CA mutations and PTEN loss correlate with similar prognostic factors and are not mutually exclusive in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(12):3577–84.
Cancer Genom Atlas Network. http://cancergenome.nih.gov. Accessed 13 Sep 2012.
Wright KL, Adams JR, Liu JC, Loch AJ, Wong RG, Jo CE, et al. Ras signaling is a key determinant for metastatic dissemination and poor survival of luminal breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2015;75(22):4960–72.
Stachler MD, Rinehart EM, Garcia E, Lindeman NI. PIK3CA Mutations are common in many tumor types and are often associated with other driver mutations. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2015 Jun 5. doi:10.1097/PAI.0000000000000195.
Pogue-Geile KL, Song N, Jeong JH, Gavin PG, Kim SR, Blackmon NL, et al. Intrinsic subtypes, PIK3CA mutation, and the degree of benefit from adjuvant trastuzumab in the NSABP B-31 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(12):1340–7.
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Schafer JM, Pendleton CS, Tang L, Johnson KC, et al. PIK3CA mutations in androgen receptor-positive triple negative breast cancer confer sensitivity to the combination of PI3K and androgen receptor inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(4):406.
Sakr RA, Weigelt B, Chandarlapaty S, Andrade VP, Guerini-Rocco E, Giri D, et al. King TA.PI3K pathway activation in high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ—implications for progression to invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(9):2326–37.
Arsenic R, Lehmann A, Budczies J, Koch I, Prinzler J, Kleine-Tebbe A, et al. Analysis of PIK3CA mutations in breast cancer subtypes. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2014;22(1):50–6.
Christgen M, Noskowicz M, Schipper E, Christgen H, Heil C, Krech T, et al. Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations in lobular breast cancer progression. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2013;52(1):69–80.
Dirican E, Kaya Z, Gullu G, Peker I, Ozmen T, Gulluoglu BM, et al. Detection of PIK3CA gene mutations with HRM analysis and association with IGFBP-5 expression levels in breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(21):9327–33.
Hanusch C, Schneeweiss A, Loibl S, Untch M, Paepke S, Kümmel S, et al. Dual blockade with AFatinib and trastuzumab as NEoadjuvant treatment for patients with locally advanced or operable breast cancer receiving taxaneanthracycline containing chemotherapy-DAFNE (GBG-70). Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(13):2924–31.
Druker BJ. Imatinib: a viewpoint by Brian J. Druker Drugs. 2001;61(12):1775–6.
Arteaga CL, Moulder SL, Yakes FM. HER (erbB) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2002;3(11):4–10.
Wakeling AE. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2002;2(4):382–7.
Motawi TM, Sadik NA, Fahim SA, Shouman SA. Combination of imatinib and clotrimazole enhances cell growth inhibition in T47D breast cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2015;233:147–56.
Zardavas D, Phillips WA, Loi S. PIK3CA mutations in breast cancer: reconciling findings from preclinical and clinical data. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(1):201.
Roulin D, Waselle L, Dormond-Meuwly A, Dufour M, Demartines N, Dormond O. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with NVP-BEZ235, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, in combination with sorafenib. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:90. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-90.
Hu Y, Guo R, Wei J, Zhou Y, Ji W, Liu J, et al. Effects of PI3K inhibitor NVP-BKM120 on overcoming drug resistance and eliminating cancer stem cells in human breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6, e2020. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.363.
Blackwell K, Burris H, Gomez P, Lynn Henry N, Isakoff S, Campana F, et al. Phase I/II dose-escalation study of PI3K inhibitors pilaralisib or voxtalisib in combination with letrozole in patients with hormone receptor-positive and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer refractory to a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct 24.
Ayub A, Yip WK, Seow HF. Dual treatments targeting IGF-1R, PI3K, mTORC or MEK synergize to inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis, and arrest cell cycle at G1 phase in MDA-MB-231 cell line. Biomed Pharmacother. 2015;75:40–50.
Park H, Kim Y, Sul JW, Jeong IG, Yi HJ, Ahn JB, et al. Synergistic anticancer efficacy of MEK inhibition and dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Prostate. 2015;75(15):1747–59.
Karthik GM, Ma R, Lövrot J, Kis LL, Lindh C, Blomquist L, et al. mTOR inhibitors counteract tamoxifen-induced activation of breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2015;367(1):76–87.
Sweetlove M, Wrightson E, Kolekar S, Rewcastle GW, Baguley BC, Shepherd PR, et al. Inhibitors of pan-PI3K signaling synergize with BRAF or MEK inhibitors to prevent BRAF-mutant melanoma cell growth. Front Oncol. 2015;5:135.
Gedaly R, Angulo P, Hundley J, Daily MF, Chen C, Evers BM. PKI-587 and sorafenib targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MAPK pathways synergistically inhibit HCC cell proliferation. J Surg Res. 2012;176(2):542–8.
Di Cosimo S, Baselga J. Management of breast cancer with targeted agents: importance of heterogeneity. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7(3):139–47.
Deng L, Chen J, Zhong XR, Luo T, Wang YP, Huang HF, et al. Correlation between activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and prognosis of breast cancer in Chinese women. PLoS One. 2015;10(3), e0120511.
de la Rochefordiere A, Kamal M, Floquet A, Thomas L, Petrow P, Petit T, et al. PIK3CA pathway mutations predictive of poor response following standard radiochemotherapy ± cetuximab in cervical cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(11):2530–7.
Toi M, Iwata H, Fujiwara Y, Ito Y, Nakamura S, Tokuda Y, et al. Lapatinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed, advanced, or metastatic breast cancer: efficacy, safety, and biomarker results from Japanese patients phase II studies. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(10):1676–82.
Black JD, Lopez S, Cocco E, Bellone S, Altwerger G, Schwab CL, et al. PIK3CA oncogenic mutations represent a major mechanism of resistance to trastuzumab in HER2/neu overexpressing uterine serous carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2015;113(7):1020–6.
Bosch A, Li Z, Bergamaschi A, Ellis H, Toska E, Prat A, et al. PI3K inhibition results in enhanced estrogen receptor function and dependence in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(283):283ra51.
Glaysher S, Bolton LM, Johnson P, Atkey N, Dyson M, Torrance C, et al. Targeting EGFR and PI3K pathways in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(7):1786–94.
Crowder RJ, Phommaly C, Tao Y, Hoog J, Luo J, Perou CM, et al. PIK3CA and PIK3CB inhibition produce synthetic lethality when combined with estrogen deprivation in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3955e62.
Sabine VS, Crozier C, Brookes CL, Drake C, Piper T, van de Velde CJ, et al. Mutational analysis of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in tamoxifen exemestane adjuvant multinational pathology study. J Clin Oncol. 2014a;32(27):2951–8.
Jiang YZ, Yu KD, Bao J, Peng WT, Shao ZM. Favorable prognostic impact in loss of TP53 and PIK3CA mutations after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3399e407.
Yuan K, Wu H, Wang Y, Chen H, Jiao M, Fu R. Phospho-PRAS40Thr246 predicts trastuzumab response in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2015;9(2):785–9.
Majewski IJ, Nuciforo P, Mittempergher L, et al. PIK3CA mutations are associated with decreased benefit to neoadjuvant human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-targeted therapies in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(12):1334–9.
Liu S, Wang H, Zhang L, Tang C, Jones L, Ye H, et al. Rapid detection of genetic mutations in individual breast cancer patients by next-generation DNA sequencing. Hum Genomics. 2015;9(1):2.
Costa C, Ebi H, Martini M, Beausoleil SA, Faber AC, Jakubik CT, et al. Measurement of PIP3 levels reveals an unexpected role for p110β in early adaptive responses to p110α-specific inhibitors in luminal breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2015;27(1):97–108.
Tolaney S, Burris H, Gartner E, Mayer IA, Saura C, Maurer M, et al. Phase I/II study of pilaralisib (SAR245408) in combination with trastuzumab or trastuzumab plus paclitaxel in trastuzumab-refractory HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;149(1):151–61.
Berns K, Horlings HM, Hennessy BT, Madiredjo M, Hijmans EM, Beelen K, et al. A functional genetic approach identifies the PI3K pathway as a major determinant of trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:395–402.
Junttila TT, Akita RW, Parsons K, Fields C, Lewis Phillips GD, Friedman LS, et al. Ligand-independent HER2/HER3/PI3K complex is disrupted by trastuzumab and is effectively inhibited by the PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:429–40.
Liu P, Cheng H, Santiago S, Raeder M, Zhang F, Isabella A, et al. Oncogenic PIK3CA-driven mammary tumors frequently recur via PI3K pathway-dependent and PI3K pathway-independent mechanisms. Nat Med. 2011;17:1116–20.
Sabine V, Crozier C, Drake C, Piper T, van de Velde CJ, Hasenburg A, et al. PIK3CA mutations are linked to PgR expression: a tamoxifen exemestane adjuvant multinational (TEAM) pathology study. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1–5.
Liao X, Lochhead P, Nishihara R, Morikawa T, Kuchiba A, Yamauchi M, et al. Aspirin use, tumor PIK3CA mutation, and colorectal-cancer survival. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(17):1596–606.
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB, Engelman JA. The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(6):1075–83.
German S, Aslam HM, Saleem S, Raees A, Anum T, Alvi AA, et al. Carcinogenesis of PIK3CA. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2013;11(1):5.
Souglakos J, Philips J, Wang R, Marwah S, Silver M, Tzardi M, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of common mutations for treatment response and survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:465–72.
Mao C, Yang ZY, Hu XF, Chen Q, Tang JL. PIK3CA exon 20 mutations as a potential biomarker for resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(6):1518–25.
Oshiro C, Kagara N, Naoi Y, Shimoda M, Shimomura A, Maruyama N, et al. PIK3CA mutations in serum DNA are predictive of recurrence in primary breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;150(2):299–307.
Sudhakar N, George Priya Doss C, Thirumal Kumar D, Chakraborty C, Anand K, Suresh M. Deciphering the impact of somatic mutations in exon 20 and exon 9 of PIK3CA gene in breast tumors among Indian women through molecular dynamics approach. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015;34(1):1–13.
Yamaguchi T, Mukai H, Yamashita S, Fujii S, Ushijima T. Comprehensive DNA methylation and extensive mutation analyses of HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncology. 2015;88(6):377–84.
Papaxoinis G, Kotoula V, Alexopoulou Z, Kalogeras KT, Zagouri F, Timotheadou E, et al. Significance of PIK3CA mutations in patients with early breast cancer treated with adjuvant chemotherapy: a hellenic cooperative oncology group (HeCOG) study. PLoS One. 2015;10(10), e0140293.
Lips EH, Michaut M, Hoogstraat M, Mulder L, Besselink NJ, Koudijs MJ, et al. Next generation sequencing of triple negative breast cancer to find predictors for chemotherapy response. Breast Cancer Res. 2015;17(1):134.
Adamczyk A, Niemiec J, Janecka A, Harazin-Lechowska A, Ambicka A, Grela-Wojewoda A, et al. Prognostic value of PIK3CA mutation status, PTEN and androgen receptor expression for metastasis-free survival in HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab in adjuvant setting. Pol J Pathol. 2015;66(2):133–41.
Guarneri V, Dieci MV, Frassoldati A, Maiorana A, Ficarra G, Bettelli S, et al. Prospective biomarker analysis of the randomized CHER-LOB study evaluating the dual anti-HER2 treatment with trastuzumab and lapatinib plus chemotherapy as neoadjuvant therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncologist. 2015;20(9):1001–10.
Toro PV, Erlanger B, Beaver JA, Cochran RL, VanDenBerg DA, Yakim E, et al. Comparison of cell stabilizing blood collection tubes for circulating plasma tumor DNA. Clin Biochem. 2015;48(15):993–8.
Millis SZ, Gatalica Z, Winkler J, Vranic S, Kimbrough J, Reddy S, et al. Predictive biomarker profiling of >6000 breast cancer patients shows heterogeneity in TNBC, with treatment implications. Clin Breast Cancer. 2015;15(6):473–81.
Sueta A, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto-Ibusuki M, Hayashi M, Takeshita T, Yamamoto S, et al. An integrative analysis of PIK3CA mutation, PTEN, and INPP4B expression in terms of trastuzumab efficacy in HER2-positive breast cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9(12), e116054.
Pestrin M, Salvianti F, Galardi F, De Luca F, Turner N, Malorni L, et al. Heterogeneity of PIK3CA mutational status at the single cell level in circulating tumor cells from metastatic breast cancer patients. Mol Oncol. 2015;9(4):749–57.
Deb S, Wong SQ, Li J, Do H, Weiss J, Byrne D, et al. Mutational profiling of familial male breast cancer reveals similarities with luminal A female breast cancer with rare TP53 mutations. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(12):2351–60.
Mendelová A, Jezková E, Zubor P, Holubeková V, Lasabová Z, Plank L, et al. Correlation between the incidence of PIK3CA mutations in breast cancer and histopathological characteristics of the tumor. Ceska Gynekol. 2014 Summer;79(4):283–8.
Loibl S, von Minckwitz G, Schneeweiss A, Paepke S, Lehmann A, Rezai M, et al. PIK3CA mutations are associated with lower rates of pathologic complete response to anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (her2) therapy in primary HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(29):3212–20.
Arthur LM, Turnbull AK, Renshaw L, Keys J, Thomas JS, Wilson TR, et al. Changes in PIK3CA mutation status are not associated with recurrence, metastatic disease or progression in endocrine-treated breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;147(1):211–9.
Sabine VS, Crozier C, Brookes CL, Drake C, Piper T, van de Velde CJ, et al. Mutational analysis of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in tamoxifen exemestane adjuvant multinational pathology study. J Clin Oncol. 2014b;32(27):2951–8.
Zhang Y, Liu M, Yang H, Wang J, Liu H, Li X, et al. PIK3CA mutations are a predictor of docetaxel plus epirubicin neoadjuvant chemotherapy clinical efficacy in breast cancer. Neoplasma. 2014;61(4):461–7.
López-Knowles E, Segal CV, Gao Q, Garcia-Murillas I, Turner NC, Smith I, et al. Relationship of PIK3CA mutation and pathway activity with antiproliferative response to aromatase inhibition. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(3):R68.
Bai X, Zhang E, Ye H, Nandakumar V, Wang Z, Chen L, et al. PIK3CA and TP53 gene mutations in human breast cancer tumors frequently detected by ion torrent DNA sequencing. PLoS One. 2014;9(6), e99306.
Castaneda CA, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Pinto JA, Chirinos-Arias M, Doimi F, Neciosup SP, et al. PIK3CA mutations in Peruvian patients with HER2-amplified and triple negative non-metastaticbreast cancer. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2014;7(4):142–8.
Hashimoto K, Tsuda H, Koizumi F, Shimizu C, Yonemori K, Ando M, et al. Activated PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways are potential good prognostic markers in node-positive, triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(10):1973–9.
Wolters KL, Ang D, Warrick A, Beadling C, Corless CL, Troxell ML. Frequent PIK3CA mutations in radial scars. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2013;22(4):210–4.
Song J, Zhang J, Lv F, Cheng Y, Wang B, Feng L, et al. Multiplex detection of DNA mutations by the fluorescence fingerprint spectrum technique. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52(49):13020–3.
Welt A, Tewes M, Aktas B, Hoffmann O, Wiesweg M, Ting S, et al. Preemptive tumor profiling for biomarker-stratified early clinical drug development in metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;142(1):81–8.
Palimaru I, Brügmann A, Wium-Andersen MK, Nexo E, Sorensen BS. Expression of PIK3CA, PTEN mRNA and PIK3CA mutations in primary breast cancer: association with lymph node metastases. Springerplus. 2013;2:464.
Hohensee I, Lamszus K, Riethdorf S, Meyer-Staeckling S, Glatzel M, Matschke J, et al. Frequent genetic alterations in EGFR- and HER2-driven pathways in breast cancer brain metastases. Am J Pathol. 2013;183(1):83–95.
Kandula M, Chennaboina KK, Ys AR, Raju S. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3KCA) oncogene mutation analysis and gene expression profiling in primary breast cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(9):5067–72.
Karakas B, Colak D, Kaya N, Ghebeh H, Qasem A, Hendrayani F, et al. Prevalence of PIK3CA mutations and the SNP rs17849079 in Arab breast cancer patients. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14(10):888–96.
Deb S, Do H, Byrne D, Jene N, kConFab Investigators, Dobrovic A, et al. PIK3CA mutations are frequently observed in BRCAX but not BRCA2-associated male breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R69.
Schneck H, Blassl C, Meier-Stiegen F, Neves RP, Janni W, Fehm T, et al. Analysing the mutational status of PIK3CA in circulating tumor cells from metastatic breast cancer patients. Mol Oncol. 2013;7(5):976–86.
Loi S, Michiels S, Lambrechts D, Fumagalli D, Claes B, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, et al. Somatic mutation profiling and associations with prognosis and trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(13):960–7.
Cizkova M, Dujaric ME, Lehmann-Che J, Scott V, Tembo O, Asselain B, et al. Outcome impact of PIK3CA mutations in HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(9):1807–9.
Ramirez-Ardila DE, Helmijr JC, Look MP, Lurkin I, Ruigrok-Ritstier K, van Laere S, et al. Hotspot mutations in PIK3CA associate with first-line treatment outcome for aromatase inhibitors but not for tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;139(1):39–49.
Ang D, O'Gara R, Schilling A, Beadling C, Warrick A, Troxell ML, et al. Novel method for PIK3CA mutation analysis: locked nucleic acid--PCR sequencing. J Mol Diagn. 2013;15(3):312–8.
Flatley E, Ang D, Warrick A, Beadling C, Corless CL, Troxell ML. PIK3CA-AKT pathway mutations in micropapillary breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(7):1320–7.
Harlé A, Lion M, Lozano N, Husson M, Harter V, Genin P, et al. Analysis of PIK3CA exon 9 and 20 mutations in breast cancer using PCR-HRM and PCRARMS: correlation with clinicopathological criteria. Oncol Rep. 2013;29(3):1043–52.
Nishimura R, Arima N, Toyoshima S, Ohi Y, Anan K, Sagara Y, et al. Evaluation of PTEN loss and PIK3CA mutations and their correlation with efficacy of trastuzumab treatment in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: a retrospective study (KBCSG 1001). Mol Clin Oncol. 2013;1(1):47–52.
Beltran H, Yelensky R, Frampton GM, Park K, Downing SR, MacDonald TY, et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing of advanced prostate cancer identifies potential therapeutic targets and disease heterogeneity. Eur Urol. 2013;63(5):920–6.
Mangone FR, Bobrovnitchaia IG, Salaorni S, Manuli E, Nagai MA. PIK3CA exon 20 mutations are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012;67(11):1285–90.
Chandarlapaty S, Sakr RA, Giri D, Patil S, Heguy A, Morrow M, et al. Frequent mutational activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(24):6784–91.
Santarpia L, Qi Y, Stemke-Hale K, Wang B, Young EJ, Booser DJ, et al. Mutation profiling identifies numerous rare drug targets and distinct mutation patterns in different clinical subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;134(1):333–43.
Higgins MJ, Jelovac D, Barnathan E, Blair B, Slater S, Powers P, et al. Detection of tumor PIK3CA status in metastatic breast cancer using peripheral blood. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(12):3462–9.
Cizkova M, Susini A, Vacher S, Cizeron-Clairac G, Andrieu C, Driouch K, et al. PIK3CA mutation impact on survival in breast cancer patients and in ERα, PR and ERBB2-based subgroups. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14(1):R28.
Janku F, Wheler JJ, Westin SN, Moulder SL, Naing A, Tsimberidou AM, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in patients with breast and gynecologic malignancies harboring PIK3CA mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(8):777–82.
Jensen JD, Knoop A, Laenkholm AV, Grauslund M, Jensen MB, Santoni-Rugiu E, et al. PIK3CA mutations, PTEN, and pHER2 expression and impact on outcome in HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and trastuzumab. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(8):2034–42.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Dr. Pınar Uysal Onganer and Nihan Verimli for their critical revision of the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant (SBAG-111S161 to MA) from the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dirican, E., Akkiprik, M. & Özer, A. Mutation distributions and clinical correlations of PIK3CA gene mutations in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 7033–7045 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4924-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4924-2