Abstract
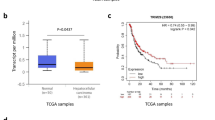
The aim of our work is to clarify the clinical implication and functional role of tripartite motif 21 (TRIM21) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We validated that TRIM21 was downregulated in liver cancer samples by immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. We also demonstrated that its downregulation was associated with several clinicopathologic features such as tumor numbers, T stage, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage, and Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) stage of HCC patients. Importantly, the expression of TRIM21 in tumor samples is significantly correlated with the prognosis of the patients. We further silenced TRIM21 in HCC cell HepG2 and LM3 and confirmed that TRIM21 silencing will promote cancer cell proliferation (CCK-8 assay), colony forming (plate colony-forming assay), migration (transwell assay), and the ability of antiapoptosis (annexin V-FITC/PI staining) in vitro. Then, we predicted gene sets influenced by TRIM21 by using bioinformatic tools. For the first time, we prove that TRIM21 is a potential tumor suppressor in HCC and its low expression indicates poor prognosis. Our findings provide useful insight into the mechanism of HCC origin and progression and offer clues to novel HCC therapies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E. Forman D. Global Cancer Stat. 2011;61:69–90.
Kishi Y, Shimada K, Nara S, Esaki M, Kosuge T. Role of hepatectomy for recurrent or initially unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2014;6:836–43.
Ikeda K, Inoue S. TRIM proteins as RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:27–37.
Schwamborn JC, Berezikov E, Knoblich JA. The TRIM-NHL protein TRIM32 activates microRNAs and prevents self-renewal in mouse neural progenitors. Cell. 2009;136:913–25.
Uchil PD, Pawliczek T, Reynolds TD, Ding S, Hinz A, Munro JB, et al. TRIM15 is a focal adhesion protein that regulates focal adhesion disassembly. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:3928–42.
Cambiaghi V, Giuliani V, Lombardi S, Marinelli C, Toffalorio F, Pelicci PG. TRIM proteins in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:77–91.
Kawai T, Akira S. Regulation of innate immune signalling pathways by the tripartite motif (TRIM) family proteins. EMBO Mol Med. 2011;3:513–27.
Petrera F, Meroni G. TRIM proteins in development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:131–41.
Kanno Y, Watanabe M, Kimura T, Nonomura K, Tanaka S, Hatakeyama S. TRIM29 as a novel prostate basal cell marker for diagnosis of prostate cancer. Acta Histochem. 2014;116:708–12.
Bell JL, Malyukova A, Kavallaris M, Marshall GM, Cheung BB. TRIM16 inhibits neuroblastoma cell proliferation through cell cycle regulation and dynamic nuclear localization. Cell Cycle. 2013;12:889–98.
Liu Y, Raheja R, Yeh N, Ciznadija D, Pedraza AM, Ozawa T, et al. TRIM3, a tumor suppressor linked to regulation of p21 (Waf1/Cip1). Oncogene. 2014;33:308–15.
Reddy BA, van der Knaap JA, Bot AG, Mohd-Sarip A, Dekkers DH, Timmermans MA, et al. Nucleotide biosynthetic enzyme GMP synthase is a TRIM21-controlled relay of p53 stabilization. Mol Cell. 2014;53:458–70.
McEwan WA, James LC. TRIM21-dependent intracellular antibody neutralization of virus infection. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;129:167–87.
Kyriakidis NC, Kapsogeorgou EK, Gourzi VC, Konsta OD, Baltatzis GE, Tzioufas AG. Toll-like receptor 3 stimulation promotes Ro52/TRIM21 synthesis and nuclear redistribution in salivary gland epithelial cells, partially via type I interferon pathway. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014;178:548–60.
Young JA, Sermwittayawong D, Kim HJ, Nandu S, An N, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21 interact to negatively regulate virus-induced interferon production. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:6521–31.
Espinosa A, Zhou W, Ek M, Hedlund M, Brauner S, Popovic K, et al. The Sjogren’s syndrome-associated autoantigen Ro52 is an E3 ligase that regulates proliferation and cell death. J Immunol. 2006;176:6277–85.
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Lee JS, et al. A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10202–12.
Marisa L, de Reyniès A, Duval A, Selves J, Gaub MP, Vescovo L, et al. Gene expression classification of colon cancer into molecular subtypes: characterization, validation, and prognostic value. PLoS Med. 2013;10:e1001453.
Rousseaux S, Debernardi A, Jacquiau B, Vitte AL, Vesin A, Nagy-Mignotte H, et al. Ectopic activation of germline and placental genes identifies aggressive metastasis-prone lung cancers. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:186ra66.
Menéndez A, Gómez J, Escanlar E, Caminal-Montero L, Mozo L. Clinical associations of anti-SSA/Ro60 and anti-Ro52/TRIM21 antibodies: Diagnostic utility of their separate detection. Autoimmunity. 2013;46:32–9.
Oke V, Wahren-Herlenius M. The immunobiology of Ro52 (TRIM21) in autoimmunity: a critical review. J Autoimmun. 2012;39:77–82.
Vaysburd M, Watkinson RE, Cooper H, Reed M, O’Connell K, Smith J, et al. Intracellular antibody receptor TRIM21 prevents fatal viral infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:12397–401.
Higgs R, Ní Gabhann J, Ben Larbi N, Breen EP, Fitzgerald KA, Jefferies CA. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Ro52 negatively regulates IFN-beta production post-pathogen recognition by polyubiquitin-mediated degradation of IRF3. J Immunol. 2008;181:1780–6.
McEwan WA, Tam JC, Watkinson RE, Bidgood SR, Mallery DL, James LC. Intracellular antibody-bound pathogens stimulate immune signaling via the Fc receptor TRIM21. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:327–36.
Lee OH, Lee J, Lee KH, Woo YM, Kang JH, Yoon HG, et al. Role of the focal adhesion protein TRIM15 in colon cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853;2015:409–21.
Chen N, Balasenthil S, Reuther J, Killary AM. DEAR1, a novel tumor suppressor that regulates cell polarity and epithelial plasticity. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5683–9.
Quintás-Cardama A, Post SM, Solis LM, Xiong S, Yang P, Chen N, et al. Loss of the novel tumour suppressor and polarity gene Trim62 (Dear1) synergizes with oncogenic Ras in invasive lung cancer. J Pathol. 2014;234:108–19.
Jia D, Wei L, Guo W, Zha R, Bao M, Chen Z, et al. Genome-wide copy number analyses identified novel cancer genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2011;54:1227–36.
Herquel B, Ouararhni K, Khetchoumian K, Ignat M, Teletin M, Mark M, et al. Transcription cofactors TRIM24, TRIM28, and TRIM33 associate to form regulatory complexes that suppress murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:8212–7.
Jauharoh SN, Saegusa J, Sugimoto T, Ardianto B, Kasagi S, Sugiyama D, et al. SS-A/Ro52 promotes apoptosis by regulating Bcl-2 production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417:582–7.
Zhang J, Fang L, Zhu X, Qiao Y, Yu M, Wang L, et al. Ro52/SSA sensitizes cells to death receptor-induced apoptosis by down-regulating c-FLIP (L). Cell Biol Int. 2012;36:463–8.
He P, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu BB, Liu YK. The targeted expression of interleukin-2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2000;19:183–7.
Palmieri G, Montella L, Milo M, Fiore R, Biondi E, Bianco AR, et al. Ultra-low dose interleukin-2 in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002;25:224–6.
Ikeguchi M, Hirooka Y. Interleukin-2 gene expression is a new biological prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinomas. Onkologie. 2005;28:255–9.
Ishii T, Ohnuma K, Murakami A, Takasawa N, Yamochi T, Iwata S, et al. SS-A/Ro52, an autoantigen involved in CD28-mediated IL-2 production. J Immunol. 2003;170:3653–61.
Wada K, Niida M, Tanaka M, Kamitani T. Ro52-mediated monoubiquitination of IKKβ down-regulates NF-kB signalling. J Biochem. 2009;146:821–32.
Erstad DJ, Cusack Jr JC. Targeting the NF-κB pathway in cancer therapy. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2013;22:705–46.
Zheng T, Hong X, Wang J, Pei T, Liang Y, Yin D, et al. Gankyrin promotes tumor growth and metastasis through activation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling in human cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;59:935–46.
Kim YC, Cao Y, Pitterle DM, O’Briant KC, Bepler G. SSA/RO52gene and expressed sequence tags in an 85 kb region of chromosome segment 11p15.5. Int J Cancer. 2000;87:61–7.
Acknowledgments
The first author would thank Liu Can from College of Chinese Language and Literature, Wuhan University for her kind encouragement. The authors also would like to thank Dr. Wang Bicheng and Dr. Zeng Zhi for the technical help on pathology. The study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272963 and No. 81172350).
Authors’ contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: QD, HY.
Performed the experiments: QD, DH, HL, XW.
Contributed funds/reagents/materials: KH, GX, HY.
Wrote the paper: QD, QZ, MT, JD.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ding Qianshan and He Du contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Q., He, D., He, K. et al. Downregulation of TRIM21 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma carcinogenesis and indicates poor prognosis of cancers. Tumor Biol. 36, 8761–8772 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3572-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3572-2