Abstract
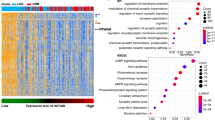
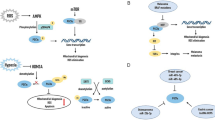
Fenofibrate, a fibric acid derivative, is known to possess lipid-lowering effects. Although fenofibrate-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) transcriptional activity has been reported to exhibit anticancer effects, the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms behind the antiproliferative effects of fenofibrate in U87MG cells (human glioma cell line) using the WST-8 Cell Proliferation Assay Kit. Furthermore, we examined genome-wide gene expression profiles and molecular networks using the DAVID online software. Fenofibrate reduced the expression of 405 genes and increased the expression of 2280 genes. DAVID analysis suggested that fenofibrate significantly affected cell cycle progression and pathways involved in cancer, including the mTOR signaling pathway and insulin signaling pathway. Results of flow cytometry analysis indicated that fenofibrate induced cell cycle G0/G1 arrest in U87MG cells. Furthermore, we identified the FoxO1–p27kip signaling axis to be involved in fenofibrate-induced cell cycle arrest. Our findings suggest that in addition to its known lipid-lowering effects, fenofibrate may be used as an antitumor agent in glioma therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. New Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96.
Drappatz J, Norden AD. Wen PY Therapeutic strategies for inhibiting invasion in glioblastoma. Expert Rev Neurother. 2009;9:519–34.
Blane GF. Review of European clinical experience with fenofibrate. Cardiology. 1989;76 Suppl 1:1–10. discussion 10–13.
Jiao H. Cytotoxic effect of peroxisome proliferator fenofibrate on human HepG2 hepatoma cell line and relevant mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;185:172–9.
Saidi SA, Holland CM, Charnock-Jones DS, et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of the PPAR-alpha agonists fenofibrate and retinoic acid in endometrial cancer. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:13.
Panigrahy D, Kaipainen A, Huang S, et al. PPARα agonist fenofibrate suppresses tumor growth through direct and indirect angiogenesis inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:985–90.
Drukala J, Urbanska K, Wilk A, et al. ROS accumulation and IGF-IR inhibition contribute to fenofibrate/PPARα -mediated inhibition of glioma cell motility in vitro. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:159.
Grabacka M, Placha W, Plonka PM, et al. Inhibition of melanoma metastases by fenofibrate. Arch Dermatol Res. 2004;296:54–8.
Grabacka M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activation decreases metastatic potential of melanoma cells in vitro via down-regulation of Akt. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3028–36.
Urbanska K, Pannizzo P, Grabacka M, et al. Activation of PPARα inhibits IGF-I‐mediated growth and survival responses in medulloblastoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:1015–24.
Guttilla IK. White BA Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:23204–16.
Goto T, Takano M, Albergaria A, et al. Mechanism and functional consequences of loss of FOXO1 expression in endometrioid endometrial cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27:9–19.
Dong XY, Chen CS, Sun XD, et al. FOXO1A is a candidate for the 13q14 tumor suppressor gene inhibiting androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6998–7006.
Kojima T, Shimazui T, Horie R, et al. FOXO1 and TCF7L2 genes involved in metastasis and poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Gene Chromosome Canc. 2010;49:379–89.
Machida S, Spangenburg EE. Booth FW Forkhead transcription factor FOXO1 transduces insulin-like growth factor’s signal to p27Kip1 in primary skeletal muscle satellite cells. J Cell Physiol. 2003;196:523–31.
Aoki M, Jiang H. Vogt PK Proteasomal degradation of the FoXO1 transcriptional regulator in cells transformed by the P3k and Akt oncoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:13613–7.
Lau CJ, Koty Z. Nalbantoglu J Differential response of glioma cells to FOXO1-directed therapy. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5433–40.
Lupi M, Cappella P, Matera G, et al. Interpreting cell cycle effects of drugs: the case of melphalan. Cancer Chemoth Pharm. 2006;57:443–57.
Gorczyca W, Gong J, Ardelt B, et al. The cell cycle related differences in susceptibility of HL-60 cells to apoptosis induced by various antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3186–92.
von Daniken A, Lutz WK. Schlatter C Lack of covalent binding to rat liver DNA of the hypolipidemic drugs clofibrate and fenofibrate. Toxicol Lett. 1981;7:305–10.
Zeng R, Xiong Y, Zhu FM, et al. Fenofibrate attenuated glucose-induced mesangial cells proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis via PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2. Plos One. 2013;8:e76836.
Li T, Zhang Q, Zhang J, et al. Fenofibrate induces apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells via activation of NF-kappaB pathway. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:96.
Wilk A, Wyczechowska D, Zapata A, et al. Molecular mechanisms of fenofibrate-induced metabolic catastrophe and glioblastoma cell death. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;57:744.
Yamasaki F, Hama S, Yoshioka H, et al. Staurosporine-induced apoptosis is independent of p16 and p21 and achieved via arrest at G2/m and at G1 in U251MG human glioma cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:271–83.
Engelman JA. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:550–62.
Huang HJ. Tindall DJ Dynamic FoXO transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:2479–87.
Chen W-L, Chen Y-L, Chiang Y-M, et al. Fenofibrate lowers lipid accumulation in myotubes by modulating the PPARα/AMPK/FoXO1/ATGL pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84:522–31.
Liang J, Zubovitz J, Petrocelli T, et al. PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat Med. 2002;8:1153–60.
Ciarallo S, Subramaniam V, Hung W, et al. Altered p27(Kip1) phosphorylation, localization, and function in human epithelial cells resistant to transforming growth factor beta-mediated G(1) arrest. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:2993–3002.
Schiappacassi M, Lovat F, Canzonieri V, et al. p27Kip1 expression inhibits glioblastoma growth, invasion, and tumor-induced neoangiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:1164–75.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863) (2012AA02A508), Research Special Fund For Public Welfare Industry of Health (201402008), National Natural Science Foundation of China (91229121, 81272792, 81472362,81172389, 81372709, 81302185), Jiangsu Province’s Natural Science Foundation (20131019), Jiangsu Province’s Key Provincial Talents Program (RC2011051), Jiangsu Province’s Key Discipline of Medicine (XK201117), Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science (BL2012028), Program for Development of Innovative Research Team in the First Affiliated Hospital of NJMU, and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dong-feng Han, Jun-xia Zhang, and Wen-jin Wei contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
SFigure 1
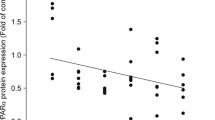
Positive correlation between FoxO1 and PPARα in GBM samples. (A) FoxO1 showed positive correlation with PPARα in 89 GBM patients downloaded from CGGA. (B) FoxO1 showed positive correlation with PPARα in 169 GBM patients downloaded from TCGA. (TIFF 149 kb)
ESM 2
(XLSX 183 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Df., Zhang, Jx., Wei, Wj. et al. Fenofibrate induces G0/G1 phase arrest by modulating the PPARα/FoxO1/p27kip pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Tumor Biol. 36, 3823–3829 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3024-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3024-4