Abstract
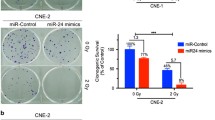
Radioresistance severely impedes the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Recent evidence has shown that the abnormal expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) contributes to radiosensitivity. The aim of this study, therefore, was to investigate whether expression of the miRNAs correlated with radiosensitivity in the context of NPC. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to quantify miR-451 expression in two representative NPC cell lines. The role of miR-451 in NPC radiosensitivity was analyzed using a colony formation assay and an immunofluorescence assay with overexpression of miR-451 in NPC cells. Luciferase reporter assays, RT-PCR, and Western blot were performed to confirm the target of miR-451. High levels of miR-451 expression enhanced radiosensitivity in NPC cells by inhibiting the repair of irradiation-induced double-strand breaks (DSBs) and increasing apoptosis. The results also demonstrated that miR-451 directly targeted ras-related protein 14 (RAB14). Downregulation of RAB14 partially replicated the miR-451-mediated DSBs induced by ionizing radiation (IR). MiR-451 could be a potential target for enhancing radiosensitivity of NPC cells by targeting RAB14.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fahraeus R, Fu HL, Ernberg I, Finke J, Rowe M, Klein G, et al. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988;42:329–38.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30.
Zongaro S, Hukema R, D’Antoni S, Davidovic L, Barbry P, Catania MV, et al. The 3′ UTR of FMR1 mRNA is a target of miR-101, miR-129-5p and miR-221: implications for the molecular pathology of FXTAS at the synapse. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22:1971–82.
Minguzzi S, Selcuklu SD, Spillane C, Parle-McDermott A. An NTD-associated polymorphism in the 3′ UTR of MTHFD1L can affect disease risk by altering miRNA binding. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:96–104.
Duan W, Xu Y, Dong Y, Cao L, Tong J, Zhou X. Ectopic expression of miR-34a enhances radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells, partly by suppressing the LyGDI signaling pathway. J Radiat Res. 2013;54:611–9.
Lin J, Liu C, Gao F, Mitchel RE, Zhao L, Yang Y, et al. MiR-200c enhances radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114:606–15.
Zhang X, Sun K, Lei S, Zhong Y, Deng H, Ou W, Wu C. [Anti-microRNA-221 enhances radiosensitivity of colorectal carcinoma cells by up-regulating PTEN]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2013;33:728–732.
Cheng L, Yang T, Kuang Y, Kong B, Yu S, Shu H, et al. MicroRNA-23a promotes neuroblastoma cell metastasis by targeting CDH1. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:839–45.
Sakai H, Sato A, Aihara Y, Ikarashi Y, Midorikawa Y, Kracht M, Nakagama H, Okamoto K. MKK7 mediates miR-493-dependent suppression of liver metastasis of colon cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(4):425–30. doi:10.1111/cas.12380.
Zhang J, Cheng C, Yuan X, He JT, Pan QH, Sun FY. MicroRNA-155 acts as an oncogene by targeting the tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:602–10.
Qu C, Liang Z, Huang J, Zhao R, Su C, Wang S, et al. MiR-205 determines the radioresistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting PTEN. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:785–96.
Li G, Liu Y, Su Z, Ren S, Zhu G, Tian Y, Qiu Y. MicroRNA-324-3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by directly targeting WNT2B. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(11):2596–607. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2013.03.001.
Fan F, Lei C, Dong-Liang L, Peng S. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor mimicking malignant meningioma in the middle cranial fossa: a case report. Chin Med Sci J. 2012;27:185–187.
Liu N, Jiang N, Guo R, Jiang W, He QM, Xu YF, et al. MiR-451 inhibits cell growth and invasion by targeting MIF and is associated with survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:123.
Zhai X, Yang Y, Wan J, Zhu R, Wu Y. Inhibition of LDH-A by oxamate induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis and increases radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:2983–91.
Zafar F, Seidler SB, Kronenberg A, Schild D, Wiese C. Homologous recombination contributes to the repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by high-energy iron ions. Radiat Res. 2010;173:27–39.
Moncharmont C, Levy A, Gilormini M, Bertrand G, Chargari C, Alphonse G, et al. Targeting a cornerstone of radiation resistance: cancer stem cell. Cancer Lett. 2012;322:139–47.
Shi L, Zhang S, Wu H, Zhang L, Dai X, Hu J, et al. MiR-200c increases the radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cell line A549 by targeting VEGF-VEGFR2 pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8:e78344.
Magnon C, Opolon P, Ricard M, Connault E, Ardouin P, Galaup A, et al. Radiation and inhibition of angiogenesis by canstatin synergize to induce HIF-1alpha-mediated tumor apoptotic switch. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1844–55.
Wang Y, Yin W, Zhu X. Blocked autophagy enhances radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE-2 in vitro. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014;134:105–10.
Zhao YX, Cheng C, Zhu F, Wu HG, Ren JH, Chen WH, et al. Suppression of low-dose hyper-radiosensitivity in human lung cancer cell line A549 by radiation-induced autophagy. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 2013;33:770–4.
Guo P, Lan J, Ge J, Nie Q, Guo L, Qiu Y, et al. MiR-26a enhances the radiosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme cells through targeting of ataxia-telangiectasia mutated. Exp Cell Res. 2014;320:200–8.
Tian Y, Nan Y, Han L, Zhang A, Wang G, Jia Z, et al. MicroRNA miR-451 downregulates the PI3K/AKT pathway through CAB39 in human glioma. Int J Oncol. 2012;40:1105–12.
Bandres E, Bitarte N, Arias F, Agorreta J, Fortes P, Agirre X, et al. microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:2281–90.
Xie Z, Chen G, Zhang X, Li D, Huang J, Yang C, et al. Salivary microRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e57502.
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J, Ilnytskyy Y, Tryndyak VP, Chekhun VF, et al. Involvement of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:2152–9.
Godlewski J, Bronisz A, Nowicki MO, Chiocca EA, Lawler S. MicroRNA-451: a conditional switch controlling glioma cell proliferation and migration. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:2742–8.
Nan Y, Han L, Zhang A, Wang G, Jia Z, Yang Y, et al. MiRNA-451 plays a role as tumor suppressor in human glioma cells. Brain Res. 2010;1359:14–21.
Chen MB, Wei MX, Han JY, Wu XY, Li C, Wang J, et al. MicroRNA-451 regulates AMPK/mtTORC1 signaling and fascin1 expression in HT-29 colorectal cancer. Cell Signal. 2014;26:102–9.
Wang R, Wang ZX, Yang JS, Pan X, De W, Chen LB. MicroRNA-451 functions as a tumor suppressor in human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ras-related protein 14 (RAB14). Oncogene. 2011;30:2644–58.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the excellent technical support and sincere help of the Functional Genomics and Bioinformatics Cores of Southern Medical University. We also appreciate the language support by Samitha Fernando (Imperial College London, UK). This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272508), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20114433110015), and the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project Fund (11C22120714).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tian Zhang and Quanquan Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Sun, Q., Liu, T. et al. MiR-451 increases radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by targeting ras-related protein 14 (RAB14). Tumor Biol. 35, 12593–12599 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2581-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2581-x