Abstract
Background
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are newly identified therapeutic targets for sepsis. CircRNA mmu_circ_0001679 dysregulation is underlying the pathogenesis and treatment of sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI). Here, the expression and role of its human homologoue circRNA-Kelch-like family member 2 (circKLHL2; hsa_circ_0071374) were explored in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced human ALI.
Objective
Expression levels of circKLHL2, microRNA (miR)-338-3p and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) were detected by quantitative PCR and western blotting, and dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed target relationships among them. Cell injury was measured using cell-counting kit-8, reactive oxygen species (ROS)/malondialdehyde (MDA)/superoxide dismutase (SOD) assays, Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate apoptosis assay, western blotting and cysteine-requiring aspartate proteases (caspases) activity assays.
Result
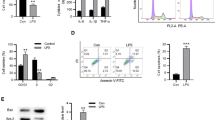
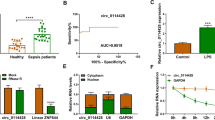
The expression of circKLHL2 and ATF6 was upregulated in sepsis-damaged human lung tissues and LPS-stressed human bronchial epithelial cells (16HBE), with a concomitant decrease of miR-338-3p. RNA interfering of circKLHL2 improved cell viability of LPS-challenged 16HBE cells, and suppressed apoptosis, oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, as evidenced by the increased bcl-2 level and SOD activity, and the decreased apoptosis rate, caspase3/9 activity and levels of bcl-2-associated X protein, ROS, MDA, ATF6 and C/EBP-homologous protein. Moreover, circKLHL2 knockdown exerted similar results to ER stress inhibitor 4-phenyl butyric acid in LPS injury. In addition, circKLHL2 knockdown reversed LPS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. ATF6 and circKLHL2 were competing endogenous RNAs of miR-338-3p, and either exhausting miR-338-3p or restoring ATF6 could counteract circKLHL2 knockdown-mediated roles in LPS injuries.
Conclusion
Depleting circKLHL2 suppressed LPS-induced ALI through suppressing mitochondrial dysfunction and cytotoxicity and oxidative and ER stresses-induced apoptosis via circKLHL2-miR-338-3p/ATF6 axis.
Highlights
-
1.
CircKLHL2 was upregulated in sepsis-damaged lung tissues and LPS-induced bronchial epithelial cells.
-
2.
Interfering circKLHL2 attenuated LPS-elicited cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and oxidative and ER stresses, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
-
3.
ATF6 upregulation and miR-338-3p downregulation counteracted the role of circKLHL2 depletion.
-
4.
CircKLHL2 and ATF6 were ceRNAs for miR-338-3p.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao X, Zhang Q, Liu N, Zhuang S, Li Z, Meng Q, Sun H, Bai J, Zhou X, Tang L (2019) Characteristics of circular RNA expression of pulmonary macrophages in mice with sepsis-induced acute lung injury. J Cell Mol Med 23(10):7111–7115
Brealey D, Brand M, Hargreaves I, Heales S, Land J, Smolenski R, Davies NA, Cooper CE, Singer M (2002) Association between mitochondrial dysfunction and severity and outcome of septic shock. Lancet (london, England) 360(9328):219–223
Brooks D, Barr LC, Wiscombe S, McAuley DF, Simpson AJ, Rostron AJ (2020) Human lipopolysaccharide models provide mechanistic and therapeutic insights into systemic and pulmonary inflammation. Europ Res J 56(1):1901298
Carré JE, Orban JC, Re L, Felsmann K, Iffert W, Bauer M, Suliman HB, Piantadosi CA, Mayhew TM, Breen P et al (2010) Survival in critical illness is associated with early activation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182(6):745–751
Endo M, Mori M, Akira S, Gotoh T (2006) C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) is crucial for the induction of caspase-11 and the pathogenesis of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. J Immunol 176(10):6245–6253
Force ADT, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, Fan E, Camporota L, Slutsky AS (2012) Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the berlin definition. JAMA 307(23):2526–2533
Gewandter JS, Staversky RJ, O’Reilly MA (2009) Hyperoxia augments ER-stress-induced cell death independent of BiP loss. Free Radical Biol Med 47(12):1742–1752
Guo W, Wang Z, Wang S, Liao X, Qin T (2021) Transcriptome sequencing reveals differential expression of circRNAs in sepsis induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Life Sci 278:119566
Ho J, Chan H, Wong SH, Wang MH, Yu J, Xiao Z, Liu X, Choi G, Leung CC, Wong WT et al (2016) The involvement of regulatory non-coding RNAs in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care 20(1):383
Huang CY, Deng JS, Huang WC, Jiang WP, Huang GJ (2020) Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by Hispolon in Mice, through regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways, and suppressing oxidative stress-mediated er stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy. Nutrients 12(6):1742
Kim SR, Kim HJ, Kim DI, Lee KB, Park HJ, Jeong JS, Cho SH, Lee YC (2015) Blockade of interplay between IL-17A and endoplasmic reticulum stress attenuates LPS-Induced Lung Injury. Theranostics 5(12):1343–1362
Li B, Dong C, Wang G, Zheng H, Wang X, Bai C (2011) Pulmonary epithelial CCR3 promotes LPS-induced lung inflammation by mediating release of IL-8. J Cell Physiol 226(9):2398–2405
Li S, Guo L, Qian P, Zhao Y, Liu A, Ji F, Chen L, Wu X, Qian G (2015) Lipopolysaccharide Induces Autophagic cell death through the PERK-dependent branch of the unfolded protein response in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physio Biochem Pharmacol 36(6):2403–2417
Li Y, Chen P, Zu L, Liu B, Wang M, Zhou Q (2016) MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses metastasis of lung cancer cells by targeting the EMT regulator Sox4. Am J Cancer Res 6(2):127–140
Lin X, Barravecchia M, Kothari P, Young JL, Dean DA (2016) beta1-Na(+), K(+)-ATPase gene therapy upregulates tight junctions to rescue lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Gene Ther 23(6):489–499
Liu G, Wan Q, Li J, Hu X, Gu X, Xu S (2020) Circ_0038467 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury in human bronchial epithelial cells through sponging miR-338-3p. Thoracic Cancer 11(5):1297–1308
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW, Martin TR (2008) Animal models of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295(3):L379-399
Nakada EM, Sun R, Fujii U, Martin JG (2021) The impact of endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein modifications, folding and degradation on lung structure and function. Front Physiol 12:665622
Namba T, Ishihara T, Tanaka K, Hoshino T, Mizushima T (2007) Transcriptional activation of ATF6 by endoplasmic reticulum stressors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355(2):543–548
Perrin-Cocon L, Aublin-Gex A, Sestito SE, Shirey KA, Patel MC, Andre P, Blanco JC, Vogel SN, Peri F, Lotteau V (2017) TLR4 antagonist FP7 inhibits LPS-induced cytokine production and glycolytic reprogramming in dendritic cells, and protects mice from lethal influenza infection. Sci Rep 7:40791
Rial MJ, Canas JA, Rodrigo-Munoz JM, Valverde-Monge M, Sastre B, Sastre J, Del Pozo V (2021) Changes in serum MicroRNAs after anti-IL-5 biological treatment of severe asthma. Int J Molecular Sci 22(7):3558
Shah D, Romero F, Guo Z, Sun J, Li J, Kallen CB, Naik UP, Summer R (2017) Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes lung endothelial dysfunction and promotes acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 57(2):204–215
Shi L, Xin Q, Chai R, Liu L, Ma Z (2015) Ectopic expressed miR-203 contributes to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via targeting TAK1 and PIK3CA. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(9):10662–10670
Shi L, Dong N, Ji D, Huang X, Ying Z, Wang X, Chen C (2018) Lipopolysaccharide-induced CCN1 production enhances interleukin-6 secretion in bronchial epithelial cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 34(1):39–49
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM et al (2016) The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 315(8):801–810
Sohn EJ (2018) MicroRNA 200c–3p regulates autophagy via upregulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in PC-3 cells. Cancer Cell Int 18:2
Takashima K, Matsushima M, Hashimoto K, Nose H, Sato M, Hashimoto N, Hasegawa Y, Kawabe T (2014) Protective effects of intratracheally administered quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Respir Res 15:150
Tauseef M, Knezevic N, Chava KR, Smith M, Sukriti S, Gianaris N, Obukhov AG, Vogel SM, Schraufnagel DE, Dietrich A et al (2012) TLR4 activation of TRPC6-dependent calcium signaling mediates endotoxin-induced lung vascular permeability and inflammation. J Exp Med 209(11):1953–1968
Wang X, Adler KB, Erjefalt J, Bai C (2007) Airway epithelial dysfunction in the development of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Expert Rev Respir Med 1(1):149–155
Wang M, Yang C, Liu X, Zheng J, Xue Y, Ruan X, Shen S, Wang D, Li Z, Cai H et al (2020) An upstream open reading frame regulates vasculogenic mimicry of glioma via ZNRD1-AS1/miR-499a-5p/ELF1/EMI1 pathway. J Cell Mol Med 24(11):6120–6136
Wang W, Yang N, Wen R, Liu CF, Zhang TN (2021) Long noncoding RNA: regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential in sepsis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:563126
Wu H, Yang Y, Guo S, Yang J, Jiang K, Zhao G, Qiu C, Deng G (2017) Nuciferine ameliorates inflammatory responses by inhibiting the TLR4-mediated pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Front Pharmacol 8:939
Xie MY, Hou LJ, Sun JJ, Zeng B, Xi QY, Luo JY, Chen T, Zhang YL (2019) Porcine milk exosome MiRNAs attenuate LPS-induced apoptosis through inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB and p53 pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. J Agric Food Chem 67(34):9477–9491
Yang H, Song Z, Hong D, (2020) CRBN knockdown mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppression of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress associated NF-kappaB signaling. Biomedicine pharmacotherapy = Biomed pharmacotherapie, 123:109761.
Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K, Yanagi H, Yura T, Negishi M, Mori K (2000) ATF6 activated by proteolysis binds in the presence of NF-Y (CBF) directly to the cis-acting element responsible for the mammalian unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 20(18):6755–6767
Yuan C, Gu J, Wu J, Yin J, Zhang M, Miao H, Li J (2020a) Circular RNA expression in the lungs of a mouse model of sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture. Heliyon 6(7):e04532
Yuan Q, Xu T, Chen Y, Qu W, Sun D, Liu X, Sun L (2020b) MiR-185–5p ameliorates endoplasmic reticulum stress and renal fibrosis by downregulation of ATF6. Lab Investigation J Tech Method Pathol 100(11):1436–1446
Zhang TN, Li D, Xia J, Wu QJ, Wen R, Yang N, Liu CF (2017a) Non-coding RNA: a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for sepsis. Oncotarget 8(53):91765–91778
Zhang G, Zheng H, Zhang G, Cheng R, Lu C, Guo Y, Zhao G (2017b) MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting sphingosine kinase 2. Cancer Cell Int 17:46
Zhang Z, Wu S, Muhammad S, Ren Q, Sun C (2018) miR-103/107 promote ER stress-mediated apoptosis via targeting the Wnt3a/beta-catenin/ATF6 pathway in preadipocytes. J Lipid Res 59(5):843–853
Zou Z, Wang Q, Zhou M, Li W, Zheng Y, Li F, Zheng S, He Z (2020) Protective effects of P2X7R antagonist in sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice via regulation of circ_0001679 and circ_0001212 and downstream Pln, Cdh2, and Nprl3 expression. J Gene Med 22(12):e3261
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been involved in the management of the patient and in the conception of the manuscript. ZCM and ZZY have been involved in the drafting of the manuscript or its critical revision for important intellectual content. WRR and ZZY have been involved in data collection. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Chunmei Zhang declares that he/she has no conflict of interest, author Ruoran Wu declares that he/she has no conflict of interest, and the author Zhongyan Zhao declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study protocol was reviewed and approved by China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University and written informed consents were obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13273_2023_349_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 Role of ER stress inhibitor in LPS-stimulated 16HBE cells. (A-H) 10 μg/mL of LPS-administrated 16HBE cells were pre-treated with 5 mM 4-PBA for 2 h. (A) CCK8 assay measured the percentage of cell viability. (B) Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and FCM determined the percentage of apoptotic cells. (C) Caspase3 and caspase9 activity assays tested the indicated activity. (D, H) Western blotting detected protein expression of bcl-2, bax, ATF6, CHOP, and GAPDH (as loading control). (E-G) ROS, MDA and SOD assay kits tested ROS level, MDA level and SOD activity, respectively. *P<0.05. (TIF 1537 KB)
13273_2023_349_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 Role of circKLHL2 exhaustion in cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and oxidative and ER stresses. (A-I) 16HBE cells were expressed with sh-NC and sh-circKLHL2 via 24 h-transfection, and then insulted by 10 μg/mL of LPS for 24 h. (A) QPCR examined circKLHL2 expression. (B) CCK8 assay measured the percentage of cell viability. (C) Annexin V-FITC/PI staining and FCM determined the percentage of apoptotic cells. (D) Caspase3 and caspase9 activity assays tested the indicated activity. (E, I) Western blotting detected protein expression of bcl-2, bax, ATF6, CHOP, and GAPDH (as loading control). (F-H) ROS, MDA and SOD assay kits tested ROS level, MDA level and SOD activity, respectively. *P<0.05. (TIF 1183 KB)
13273_2023_349_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 Role of circKLHL2/miR-338-3p/ATF6 axis in mitochondrial dysfunction. (A) Evaluation of ΔΨm in 16HBE cells by FCM. (B) Detection of ATP levels in 16HBE cells. (C) Relative mtDNA copy numbers in 16HBE cells. *P<0.05. (TIF 338 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Wu, R. & Zhao, Z. CircKLHL2 mitigates septic lung injury via circKLHL2-miR-338-3p-ATF6 ceRNA pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 20, 353–365 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-023-00349-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-023-00349-y